Crowtail- Serial Wifi
Description¶
The serial wifi module based on ESP-12.which is an ultra-low power UART-WiFi module. It has excellent dimensions and ULP technology compared to other similar modules. The module is special design for mobile devices and Internet of Things . Once firmware is upgraded to the appropriate version, a compatible Android device can run the IOT.APK to do the following:control the PWM, I/O pin, or Serial communication. For example,you can use this module transmit date with it serial port.It is easy to communication with other device.
Model: CT0019SW
Features¶
- Connection Mode:U(UART)
- One high speed serial port
- Working voltage:5v
- 802.11 b/g/n protocol
- Wi-Fi Direct (P2P), soft-AP
- Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack
- Integrated TR switch, balun, LNA, power amplifier and matching network
- Integrated PLL, regulators, and power management units
- +19.5dBm output power in 802.11b mode
- Dimensions(mm):45.0(L)x20.0(W)x6.8(H)
Electronic Characteristics¶
1.Current Consumption
The following current consumption is based on 3.3V supply, and 25℃ ambient, using internal regulators. Measurements are done at antenna port without SAW filter. All the transmitter’s measurements are based on 90% duty cycle, continuous transmit mode.
| Mode | Min | Typ | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transmit 802.11b, CCK 1Mbps, POUT=+19.5dBm | 215 | mA | ||
| Transmit 802.11b, CCK 11Mbps, POUT=+18.5dBm | 197 | mA | ||
| Transmit 802.11g, OFDM 54Mbps, POUT =+16dBm | 145 | mA | ||
| Transmit 802.11n, MCS7, POUT=+14dBm | 135 | mA | ||
| Receive 802.11b, packet length=1024 byte, -80dBm | 100 | mA | ||
| Receive 802.11g, packet length=1024 byte, -70dBm | 100 | mA | ||
| Receive 802.11n, packet length=1024 byte, -65dBm | 102 | mA | ||
| Total shutdown | 0.5 | uA |
2.RF Performance
The following are measured under room temperature conditions with 3.3V and 1.1V power supplies.
| Description | Min | Typical | Max | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input frequency | 2412 | 2484 | MHz | |
| Input impedance | 50 | Ω | ||
| Input reflection | -10 | dB | ||
| Output power of PA for 72.2Mbps | 14 | 15 | 16 | dBm |
| Output power of PA for 11b mode | 17.5 | 18.5 | 19.5 | dBm |
| Sensitivity | ||||
| CCK, 1Mbps | -98 | dBm | ||
| CCK, 11Mbps | -91 | dBm | ||
| 6Mbps (½ BPSK) | -93 | dBm | ||
| 54Mbps (¾ 64-QAM) | -75 | dBm | ||
| HT20, MCS7 (65Mbps, 72.2Mbps) | -71 | dBm |
Hardware¶
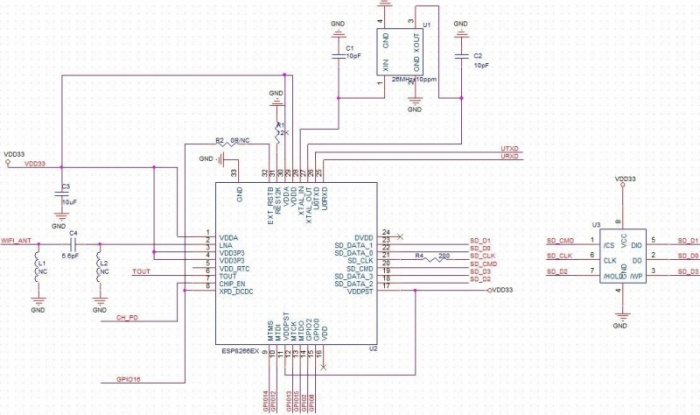
Schematic¶
Application Notes¶
- Smart power plugs
- Home automation
- Mesh network
- Industrial wireless control
- Baby monitors
- IP Cameras
- Sensor networks
- Wearable electronics
- Wi-Fi location-aware devices
- Security ID tags
- Wi-Fi position system beacons
AT Commands¶
Format
- Baud rate at 115200
- x is the commands
(Click the picture to zoom in)
| Set | Inquiry | Test | Execute |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT+<x>=<…> | AT+<x>? | AT+<x>=? | AT+<x> |
| AT+CWMODE=<mode> | AT+CWMODE? | AT+CWMODE=? | - |
| Set the network mode | Check current mode | Return which modes supported | - |
Commands
- carefully there are must be no any spaces between the " and IP address or port
| Commands | Description | Type | Set/Execute | Inquiry | test | Parameters and Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | general test | basic | - | - | - | - |
| AT+RST | restart the module | basic | - | - | - | - |
| AT+GMR | check firmware version | basic | - | - | - | - |
| AT+CWMODE | wifi mode | wifi | AT+CWMODE=<mode> | AT+CWMODE? | AT+CWMODE=? | 1= Sta, 2= AP, 3=both, Sta is the default mode of router, AP is a normal mode for devices |
| AT+CWJAP | join the AP | wifi | AT+ CWJAP =<ssid>,< pwd > | AT+ CWJAP? | - | ssid = ssid, pwd = wifi password |
| AT+CWLAP | list the AP | wifi | AT+CWLAP | |||
| AT+CWQAP | quit the AP | wifi | AT+CWQAP | - | AT+CWQAP=? | |
| AT+ CWSAP | set the parameters of AP | wifi | AT+ CWSAP= <ssid>,<pwd>,<chl>, <ecn> | AT+ CWSAP? | ssid, pwd, chl = channel, ecn = encryption; eg. Connect to your router: AT+CWJAP="www.electrodragon.com","helloworld"; and check if connected: AT+CWJAP? | |
| AT+CWLIF | check join devices' IP | wifi | AT+CWLIF | - | - | |
| AT+ CIPSTATUS | get the connection status | TCP/IP | AT+ CIPSTATUS | <id>,<type>,<addr>,<port>,<tetype>= client or server mode | ||
| AT+CIPSTART | set up TCP or UDP connection | TCP/IP | 1)single connection (+CIPMUX=0) AT+CIPSTART= <type>,<addr>,<port>; 2) multiple connection (+CIPMUX=1) AT+CIPSTART= <id><type>,<addr>, <port> | - | AT+CIPSTART=? | id = 0-4, type = TCP/UDP, addr = IP address, port= port; eg. Connect to another TCP server, set multiple connection first: AT+CIPMUX=1; connect: AT+CIPSTART=4,"TCP","X1.X2.X3.X4",9999 |
| AT+CIPMODE | set data transmission mode | TCP/IP | AT+CIPMODE=<mode> | AT+CIPSEND? | 0 not data mode, 1 data mode; return "Link is builded" | |
| AT+CIPSEND | send data | TCP/IP | 1)single connection(+CIPMUX=0) AT+CIPSEND=<length>; 2) multiple connection (+CIPMUX=1) AT+CIPSEND= <id>,<length> | AT+CIPSEND=? | eg. send data: AT+CIPSEND=4,15 and then enter the data. | |
| AT+CIPCLOSE | close TCP or UDP connection | TCP/IP | AT+CIPCLOSE=<id> or AT+CIPCLOSE | AT+CIPCLOSE=? | ||
| AT+CIFSR | Get IP address | TCP/IP | AT+CIFSR | AT+ CIFSR=? | ||
| AT+ CIPMUX | set mutiple connection | TCP/IP | AT+ CIPMUX=<mode> | AT+ CIPMUX? | 0 for single connection 1 for multiple connection | |
| AT+ CIPSERVER | set as server | TCP/IP | AT+ CIPSERVER= <mode>[,<port> ] | mode 0 to close server mode, mode 1 to open; port = port; eg. turn on as a TCP server: AT+CIPSERVER=1,8888, check the self server IP address: AT+CIFSR=? | ||
| AT+ CIPSTO | Set the server timeout | AT+CIPSTO=<time> | AT+CIPSTO? | <time>0~28800 in second | ||
| +IPD | received data | For Single Connection mode(CIPMUX=0): + IPD, <len>: For Multi Connection mode(CIPMUX=1): + IPD, <id>, <len>: <data> |
Usage¶
Use the ESP8266-12 and Arduino as a Webserver¶
1.Hardware Connection. Connected the Serial Wifi to U2 of the Crowtail- base shiled( D2 and D3) are used as software UART. Baud Rate:9600. 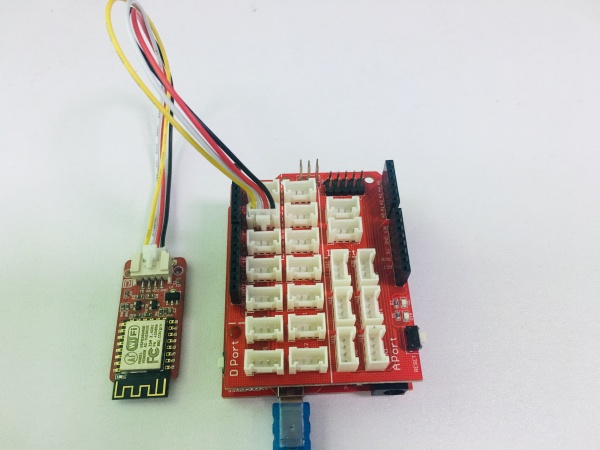
2.Connect the board to PC using USB cable.
3:Download the code: WWebserver for ESPduino or copy it to you new skecth.
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
#define DEBUG true
SoftwareSerial esp8266(2,3); // make RX Arduino line is pin 2, make TX Arduino line is pin 3.
// This means that you need to connect the TX line from the esp to the Arduino's pin 2
// and the RX line from the esp to the Arduino's pin 3
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
esp8266.begin(9600); // your esp's baud rate might be different
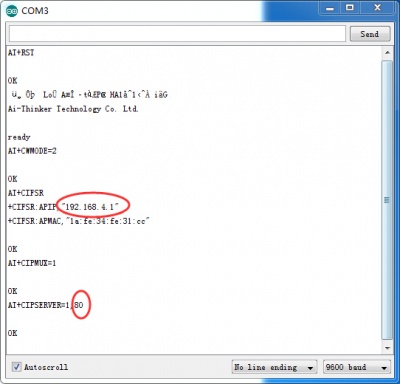
sendData("AT+RST\r\n",2000,DEBUG); // reset module
sendData("AT+CWMODE=2\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // configure as access point
sendData("AT+CIFSR\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // get ip address
sendData("AT+CIPMUX=1\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // configure for multiple connections
sendData("AT+CIPSERVER=1,80\r\n",1000,DEBUG); // turn on server on port 80
}
void loop()
{
if(esp8266.available()) // check if the esp is sending a message
{
/*
while(esp8266.available())
{
// The esp has data so display its output to the serial window
char c = esp8266.read(); // read the next character.
Serial.write(c);
} */
if(esp8266.find("+IPD,"))
{
delay(1000);
int connectionId = esp8266.read()-48; // subtract 48 because the read() function returns
// the ASCII decimal value and 0 (the first decimal number) starts at 48
String webpage = "<h1>Hello World!</h1>";
String cipSend = "AT+CIPSEND=";
cipSend += connectionId;
cipSend += ",";
cipSend +=webpage.length();
cipSend +="\r\n";
sendData(cipSend,1000,DEBUG);
sendData(webpage,1000,DEBUG);
String closeCommand = "AT+CIPCLOSE=";
closeCommand+=5; // append connection id
closeCommand+="\r\n";
sendData(closeCommand,3000,DEBUG);
}
}
}
String sendData(String command, const int timeout, boolean debug)
{
String response = "";
esp8266.print(command); // send the read character to the esp8266
long int time = millis();
while( (time+timeout) > millis())
{
while(esp8266.available())
{
// The esp has data so display its output to the serial window
char c = esp8266.read(); // read the next character.
response+=c;
}
}
if(debug)
{
Serial.print(response);
}
return response;
}
4.Upload the code and Open the serial monitor.You can see some configuration information.
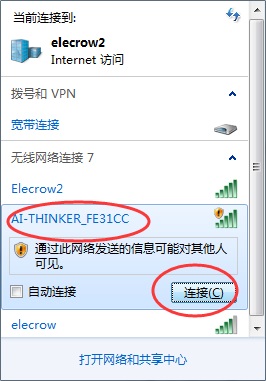
5.PC connect to the wifi of ESP8266.
6.Then you can visit the Webserver of the ESP8266.
Upgrading ESP8266 Firmware¶
How to upgrade ESP8266 firmware?
We use NodeMCU flasher here, the download links:
- English version: https://github.com/nodemcu/nodemcu-flasher
Note: use nodemcu flasher to flash Firmware to ESP8266, its default firmware is Lau language. If you want to flash AT Commands firmware, go to ESP8266 forum to get one.
- Chinese version: File:ESP8266Flasher-x86-v0.9.2.3.zip
1. Connect your ESP8266 module as follows:
- Vcc = 3.3V (needs around 300-400mA peak)
- Gnd = -ve ground
- CH_PD = Chip enable so always +ve
- RST = Leave floating or ground to reset
- GPIO0 = Normally floating but this needs to be grounded when you start the update.
- GPIO2 = high level
- UTXD = Tx data connect to RX on FTDI/Serial interface
- URXD = Rx data connect to TX of FTDI/Serial interface
English Version: Please refer to the NodeMCU flasher user guide.
Chinese Version: Please see the next step below
2. Open the software, choose the right COM and click the button that is circled in the following picture. When a tick appears in the bottom-left corner, it suggests that the firmware upgrade successfully.
3. This software contains an existing firmware, but if you want to upgrade other ESP8266 firmware, please click the button that is circled in the following picture, and only two file paths are available to choose.
Other ways of ESP8266 firmware upgrading
Useful Link¶
Reference:
Example
- Arduino Smart Home for Environment Tree
- The ESP8266 Becomes a Terrible Browser - http://hackaday.io/project/3072/instructions
- http://blog.iteadstudio.com/esp8266-use-android-phone-to-control-itead-rboard/
- SDK for ESP8266 - http://hackaday.com/2014/10/25/an-sdk-for-the-esp8266-wifi-chip/
- An ESP8266 Based Smartmeter - http://hackaday.com/2014/10/25/an-sdk-for-the-esp8266-wifi-chip/