Crowbits-Pulse Sensor
Description¶
The Pulse Sensor is used to measure the heart rate of the human. Heart rate data can be really useful whether you’re designing an exercise routine, studying your activity or anxiety levels or just want your shirt to blink with your heart beat. The problem is that heart rate can be difficult to measure. Luckily, the Pulse Sensor Amped can solve that problem! The Pulse Sensor Amped is a plug-and-play heart-rate sensor for Arduino.
Features¶
- Easy to use
Specification¶
- Interface Type: Analog input
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V DC
- Dimensions: 31.5(L)*24.5(W)*13(H)mm
Usage¶
The following sketch demonstrates a simple application of the module.
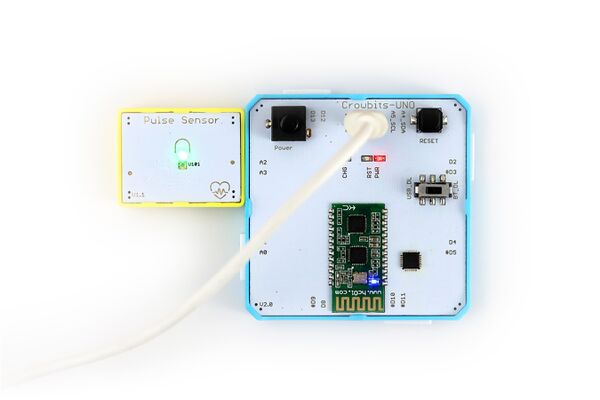
1. You need to prepare a Crowbits motherboard, such as Crowbits-UNO board.
2. Connect the module to the A2 interface o the Crowbits-UNO board, as shown in the figure:
3. Upload the following code to the Crowbits-UNO board.
/*
>> Pulse Sensor Amped 1.2 <<
This code is for Pulse Sensor Amped by Joel Murphy and Yury Gitman
www.pulsesensor.com
>>> Pulse Sensor purple wire goes to Analog Pin 0 <<<
Pulse Sensor sample aquisition and processing happens in the background via Timer 2 interrupt. 2mS sample rate.
PWM on pins 3 and 11 will not work when using this code, because we are using Timer 2!
The following variables are automatically updated:
Signal : int that holds the analog signal data straight from the sensor. updated every 2mS.
IBI : int that holds the time interval between beats. 2mS resolution.
BPM : int that holds the heart rate value, derived every beat, from averaging previous 10 IBI values.
QS : boolean that is made true whenever Pulse is found and BPM is updated. User must reset.
Pulse : boolean that is true when a heartbeat is sensed then false in time with pin13 LED going out.
This code is designed with output serial data to Processing sketch "PulseSensorAmped_Processing-xx"
The Processing sketch is a simple data visualizer.
All the work to find the heartbeat and determine the heartrate happens in the code below.
Pin 13 LED will blink with heartbeat.
If you want to use pin 13 for something else, adjust the interrupt handler
It will also fade an LED on pin fadePin with every beat. Put an LED and series resistor from fadePin to GND.
Check here for detailed code walkthrough:
http://pulsesensor.myshopify.com/pages/pulse-sensor-amped-arduino-v1dot1
Code Version 1.2 by Joel Murphy & Yury Gitman Spring 2013
This update fixes the firstBeat and secondBeat flag usage so that realistic BPM is reported.
*/
// VARIABLES
int pulsePin = 2; // Pulse Sensor purple wire connected to analog pin 0
int blinkPin = 13; // pin to blink led at each beat
int fadePin = 5; // pin to do fancy classy fading blink at each beat
int fadeRate = 0; // used to fade LED on with PWM on fadePin
// these variables are volatile because they are used during the interrupt service routine!
volatile int BPM; // used to hold the pulse rate
volatile int Signal; // holds the incoming raw data
volatile int IBI = 600; // holds the time between beats, must be seeded!
volatile boolean Pulse = false; // true when pulse wave is high, false when it's low
volatile boolean QS = false; // becomes true when Arduoino finds a beat.
void setup(){
pinMode(blinkPin,OUTPUT); // pin that will blink to your heartbeat!
pinMode(fadePin,OUTPUT); // pin that will fade to your heartbeat!
Serial.begin(115200); // we agree to talk fast!
interruptSetup(); // sets up to read Pulse Sensor signal every 2mS
// UN-COMMENT THE NEXT LINE IF YOU ARE POWERING The Pulse Sensor AT LOW VOLTAGE,
// AND APPLY THAT VOLTAGE TO THE A-REF PIN
//analogReference(EXTERNAL);
}
void loop(){
sendDataToProcessing('S', Signal); // send Processing the raw Pulse Sensor data
if (QS == true){ // Quantified Self flag is true when arduino finds a heartbeat
fadeRate = 255; // Set 'fadeRate' Variable to 255 to fade LED with pulse
sendDataToProcessing('B',BPM); // send heart rate with a 'B' prefix
sendDataToProcessing('Q',IBI); // send time between beats with a 'Q' prefix
QS = false; // reset the Quantified Self flag for next time
}
ledFadeToBeat();
delay(20); // take a break
}
void ledFadeToBeat(){
fadeRate -= 15; // set LED fade value
fadeRate = constrain(fadeRate,0,255); // keep LED fade value from going into negative numbers!
analogWrite(fadePin,fadeRate); // fade LED
}
void sendDataToProcessing(char symbol, int data ){
Serial.print(symbol); // symbol prefix tells Processing what type of data is coming
Serial.println(data); // the data to send culminating in a carriage return
}
4.Unzip the compressed processing file and run the processing software inside.
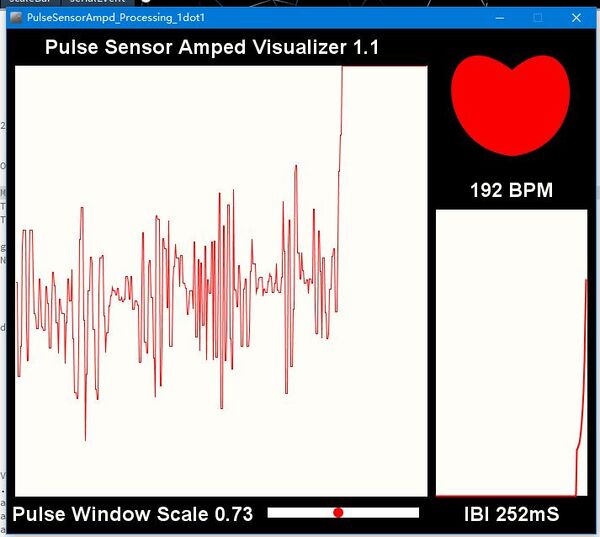
5.Open the sample code PulseSensorAmpd_Processing_1dot1 in the folder, and then run the program.
//**************
//IR receive demo v1.0
//Connect the IR sent pins to D2 for this demo
//******************************
#include <IRSendRev.h>
//#include <IRSendRevInt.h>
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
IR.Init(2);
Serial.println("init over");
}
unsigned char dta[20];
void loop()
{
if(IR.IsDta())
{
// IR.Recv(dta);
int length= IR.Recv(dta);
for (int i =0;i<length;i++)
{
Serial.print(dta[i]);
Serial.print("\t");
}
Serial.println();
// Very Important:
// the received data is comprised of the trsmission parameters , please refer to
// the sendTest.ino in the library ;
}
}
6. After downloading the two programs, open the serial port of the motherboard connected to the Crowbits of the Crowbits-IR Receiver module, the baud rate is set to 9600, and then you will receive the information sent by the transmitter module, as shown in the figure: