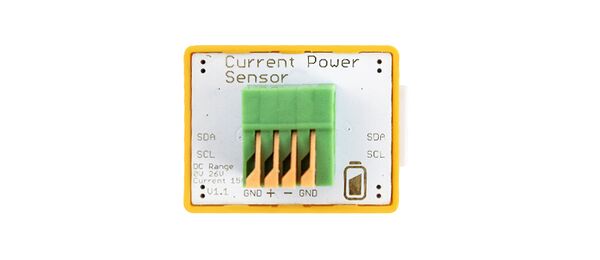
Crowbits-CurrentPower Sensor
Description¶
The module can detect the size of the current in the circuit. By detecting the size of the current, you can learn about the power consumption of the circuit, the power of other meta-electronic devices and so on.
Features¶
- Easy to use
Specification¶
- Interface Type: I2C
- Operating Voltage: 3.3V DC
- Measuring voltage range: DC 0-26V
- Dimensions: 31.5(L)*24.5(W)*13(H)mm
Usage¶
The following sketch demonstrates a simple application of the module.
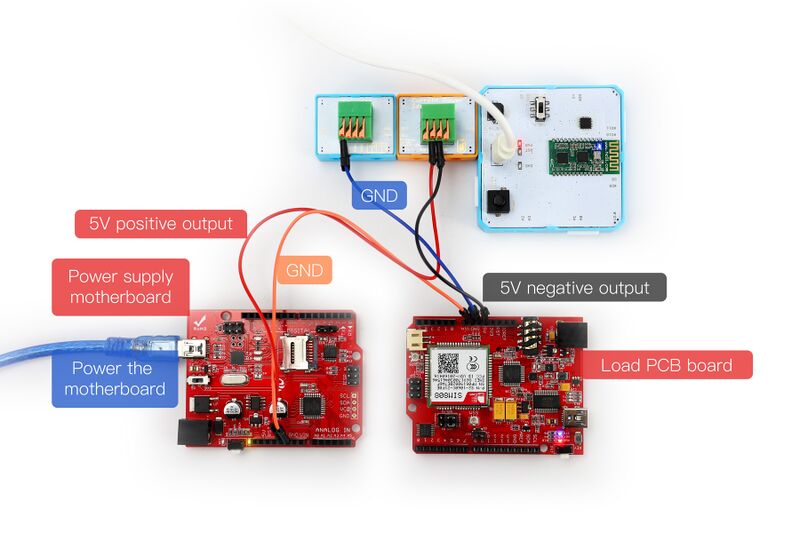
1. You need to prepare a Crowbits motherboard, such as Crowbits-UNO board. An expansion module, such as Crowbits-Terminal board. There is also a power supply motherboard and a load motherboard.
2. Connect the module to the I2C interface on the Crowbits-UNO board, Crowbits-Terminal is connected behind it. The connection requirements are as follows.
2.1. Connect the ground of the power supply main board and the ground of the load PCB board with a DuPont line.
2.2. Connect the 5V output of the power supply motherboard to the positive terminal of the Crowbits-Current Power terminal with a DuPont cable.
2.3. Connect the negative pole of the Crowbits-Current Power terminal to the 5V input end of the load PCB board with Dupont wire.
2.4. Use a MINI USB cable to connect the external 5V power supply to the power supply PCB.
2.5.Connect the GND on the Crowbits-Terminal board to the GND of the load motherboard with a DuPont cable.
3. Download the library “INA219”. Unzip and put it in the libraries file of the Arduino IDE, for example: C:\Program Files (x86)\Arduino\libraries.
4. Upload the following code to the Crowbits-UNO board.
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_INA219.h>
Adafruit_INA219 ina219;
void setup(void)
{
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial) {
// will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
delay(1);
}
uint32_t currentFrequency;
Serial.println("Hello!");
// Initialize the INA219.
// By default the initialization will use the largest range (32V, 2A). However
// you can call a setCalibration function to change this range (see comments).
ina219.begin();
// To use a slightly lower 32V, 1A range (higher precision on amps):
//ina219.setCalibration_32V_1A();
// Or to use a lower 16V, 400mA range (higher precision on volts and amps):
//ina219.setCalibration_16V_400mA();
Serial.println("Measuring voltage and current with INA219 ...");
}
void loop(void)
{
float shuntvoltage = 0;
float busvoltage = 0;
float current_mA = 0;
float loadvoltage = 0;
shuntvoltage = ina219.getShuntVoltage_mV();
busvoltage = ina219.getBusVoltage_V();
current_mA = ina219.getCurrent_mA();
loadvoltage = busvoltage + (shuntvoltage / 1000);
Serial.print("Bus Voltage: "); Serial.print(busvoltage); Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Shunt Voltage: "); Serial.print(shuntvoltage); Serial.println(" mV");
Serial.print("Load Voltage: "); Serial.print(loadvoltage); Serial.println(" V");
Serial.print("Current: "); Serial.print(current_mA); Serial.println(" mA");
Serial.println("");
delay(2000);
}
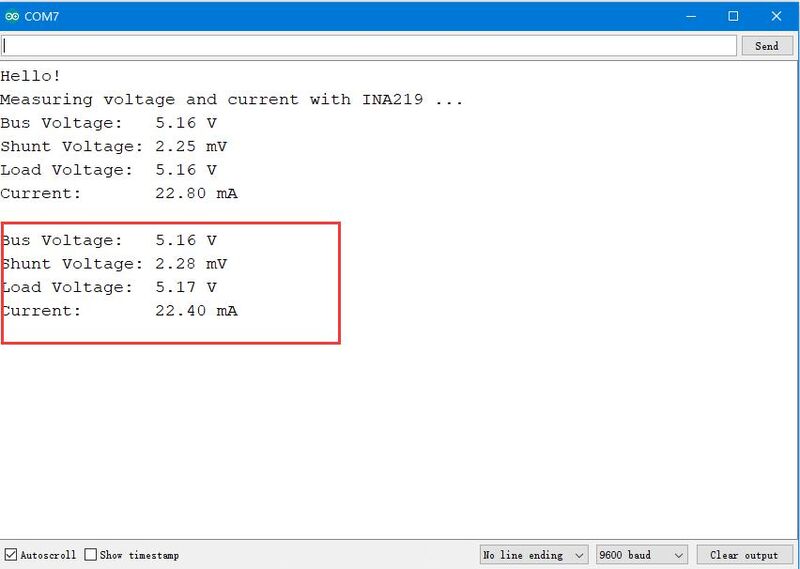
5. After the upload is successful, open the serial port monitor, the baud rate is set to 9600. The serial port will print out the voltage, current, and power values, as shown in the figure: