Story
Overview
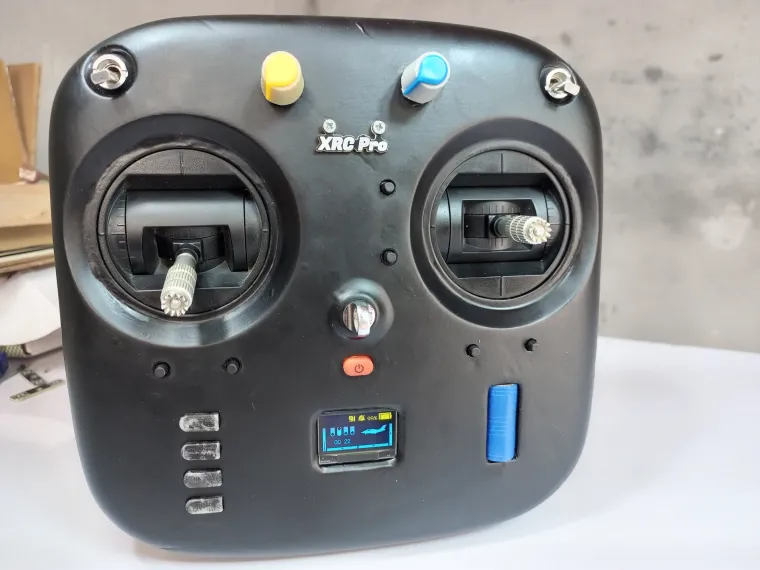
The XRC PRO is an advanced, open-source RC transmitter and receiver system designed to offer professional-level performance in a compact and customizable package. Built around the STM32F103C8T6 microcontroller and the NRF24L01 wireless transceiver module, the XRC PRO provides precise, real-time control for various RC applications like drones, cars, and boats. With a compact design, robust functionality, and user-friendly interface, the XRC PRO is an ideal tool for both hobbyists and professionals.
Key features
| Feature | Description |
| OLED Display | Displays real-time signal strength, settings, battery percentage, and control data. |
| Trim Buttons & Rotary Encoder | Fine-tune controls and navigate through menus effortlessly for enhanced usability. |
| Multi-Menus | Intuitive menu system for adjusting channel settings, polarity, and output modes. |
| PPM & SBUS Outputs | Offers versatile output options to support various RC receivers for expanded functionality. |
| NRF24L01 Power Control | Adjustable signal strength settings for short and long-range control. |
| Stick Calibration | Real-time calibration of sticks with visual feedback on the OLED display for precise adjustments. |
| Compact Receivers | Two efficient options for 8-channel PWM+PPM and PPM+SBUS outputs, designed for optimal performance. |
| Throttle Mode | Choose between left or right throttle hand mode for personalized control preferences. |
| PC Simulator Compatibility | Utilize the PPM output for playing simulators on a computer, with the option to toggle PPM output on/off. |
| Express ELRS Integration | Utilize PPM output with an ELRS adapter for compatibility with various ELRS modules. |
| Buzzer On/Off Mode | Easily toggle the buzzer on or off for audio feedback during operations. |
| Adjustable Setting Unit | Customize the unit of measurement for settings (e.g., degrees, percentages) according to user preference. |
| Battery Voltage Calibration | Calibrate battery voltage display to reflect accurate percentage readings for better monitoring. |
| Reset to Default Settings | Quickly restore all settings to default through a simple menu option for ease of use. |
Tech Specs
| Component | Specification |
| Microcontroller | STM32F103C8T6 ARM® Cortex®-M3: • ARM® Cortex®-M3 core up to 72 MHz • 20KB onboard SRAM • 64KB Flash |
| Wireless Module | NRF24L01 GT24 Mini: • 2.4 GHz ISM band • High data rate up to 2 Mbps • Supports multiple data pipes |
| Display | 0.96" OLED Display: • Displays signal strength, battery percentage, and control data |
| Power | AMS117 3.3V Regulator, Power input from 7.4V to 12V (2S to 3S LiPo battery) |
| Weight | 200g (without battery) |
| Dimensions | 160 mm x 120 mm x 40 mm (without antenna) |
| Enclosure | DJI Phantom 2 Remote (or customizable based on user preference, can use Arduino joysticks as an alternative) |
Components
The XRC PRO is designed with readily available, off-the-shelf components, making it easy for others to replicate or modify. Below are the key components:
Transmitter
| No. | Component | Description/Note | Quantity | Buy Link |
| 1 | STM32F103C8T6 | Desolder components from the STM32F103C8T6 development board, then solder to the transmitter PCB | 1 | Click to Buy |
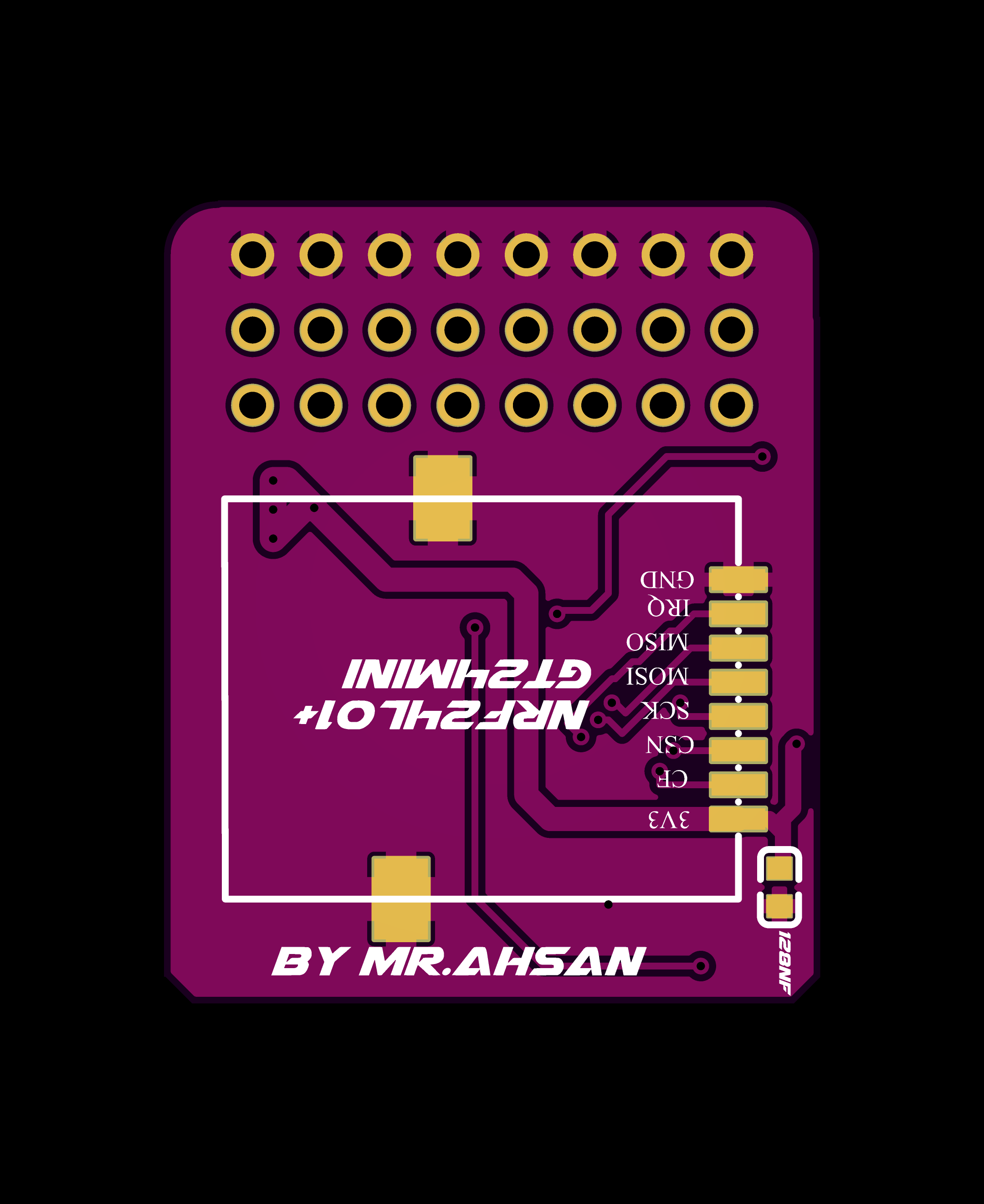
| 2 | NRF24L01 GT24 Mini | Wireless Transceiver Module | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 3 | E11 Rotary Encoder (ENC) | Rotary Encoder for menu navigation | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 4 | SMD 8MHz Crystal (3225) | Crystal Oscillator for STM32 | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 5 | FC-135 32.768kHz Crystal | Real-Time Clock (RTC) Crystal | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 6 | CH340C SMD | USB to Serial Converter | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 7 | Y1 (8050) | NPN Transistor | 2 | Click to Buy |
| 8 | 1AM (3904) | NPN Transistor | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 9 | 0.96" OLED Display | For displaying transmitter data (status, menus, etc.) | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 10 | 10k Ohm Resistor (SMD) | SMD Resistor for various circuits | 4 | Click to Buy |
| 11 | 1k Ohm Resistor (SMD) | SMD Resistor for various circuits | 4 | Click to Buy |
| 12 | 100nF Capacitor (SMD) | Capacitor for signal filtering | 20 | Click to Buy |
| 13 | Buzzer | Audio feedback for transmitter alerts | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 14 | AMS117 (3.3V Voltage Regulator) | Provides 3.3V to various components on the board | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 15 | 10uF Capacitor | For power stabilization and filtering | 2 | Click to Buy |
| 16 | Male Headers | Used for connecting modules or components to the PCB | 30 | Click to Buy |
| 17 | DJI Phantom 2 Remote | Used as the enclosure for the transmitter, or use any suitable remote/joystick | 1 |
Find yourself any suiteable broken transmitter for enclosure and sticks. |
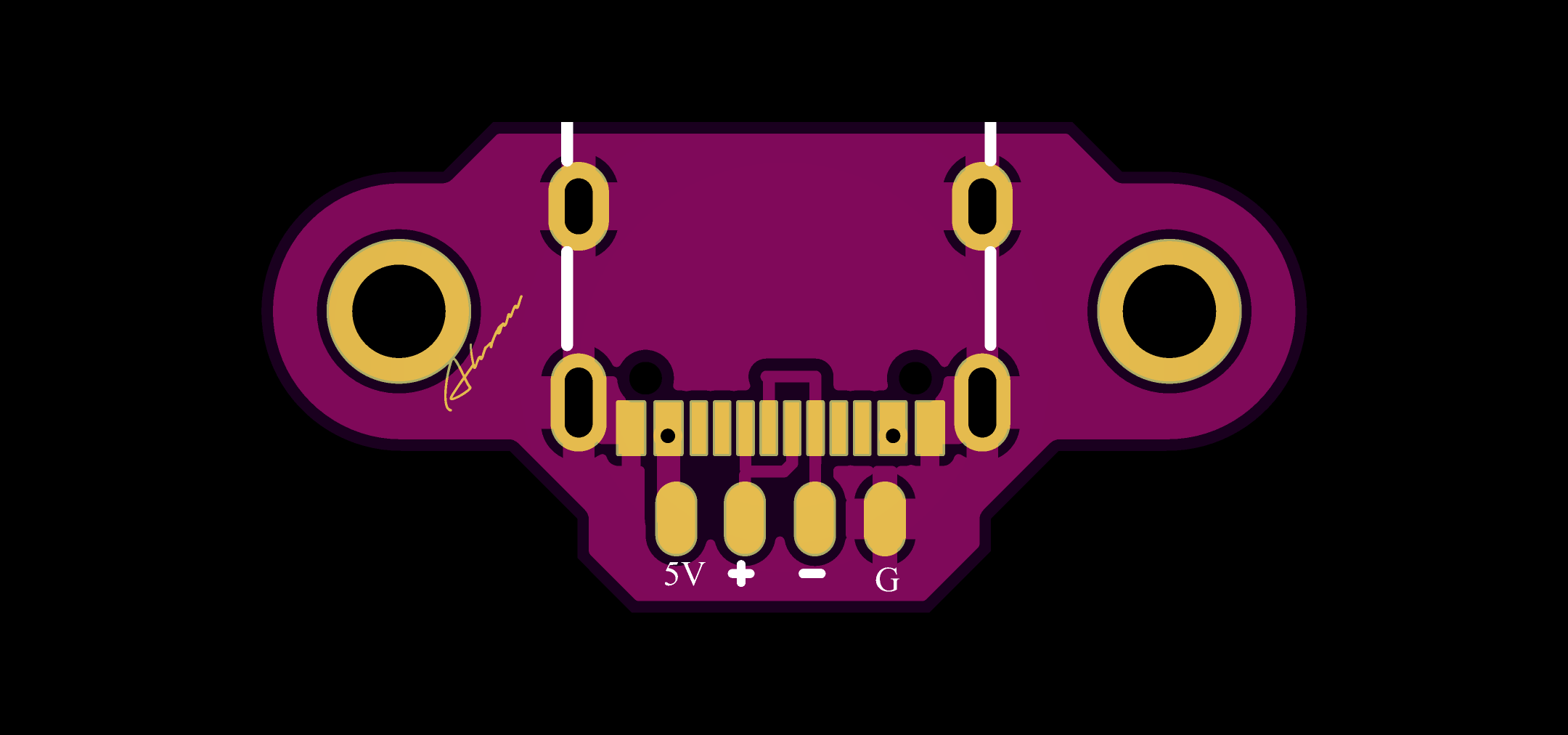
Receivers(PWM+PPM)
| No. | Component | Description/Note | Quantity | Buy Link |
| 1 | STM32F103C8T6 | Desolder components from the STM32F103C8T6 development board, then solder to the receiver PCB | 1 | Click to buy |
| 2 | NRF24L01 GT24 Mini | Wireless Transceiver Module | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 3 | SMD 8MHz Crystal (3225) | Crystal Oscillator for STM32 | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 4 | 1AM (3904) | NPN Transistor | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 5 | AMS117 (3.3V Voltage Regulator) | Provides 3.3V to various components on the board | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 6 | 10uF Capacitor | For power stabilization and filtering | 2 | Click to Buy |
| 7 | 100nF Capacitor (SMD) | Capacitor for signal filtering | 4 | Click to Buy |
| 8 | Male Headers | Used for connecting modules or components to the PCB | 30 | Click to Buy |
Receivers(PPM+SBUS)
| No. | Component | Description/Note | Quantity | Buy Link |
| 1 | STM32F103C8T6 | Desolder components from the STM32F103C8T6 development board, then solder to the receiver PCB | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 2 | NRF24L01 GT24 Mini | Wireless Transceiver Module | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 3 | SMD 8MHz Crystal (3225) | Crystal Oscillator for STM32 | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 4 | 1AM (3904) | NPN Transistor | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 5 | AMS117 (3.3V Voltage Regulator) | Provides 3.3V to various components on the board | 1 | Click to Buy |
| 6 | 10uF Capacitor | For power stabilization and filtering | 2 | Click to Buy |
| 7 | 100nF Capacitor (SMD) | Capacitor for signal filtering | 4 | Click to Buy |
| 8 | Male Headers | Used for connecting modules or components to the PCB | 30 | Click to Buy |
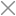
Schematic and PCB Layout
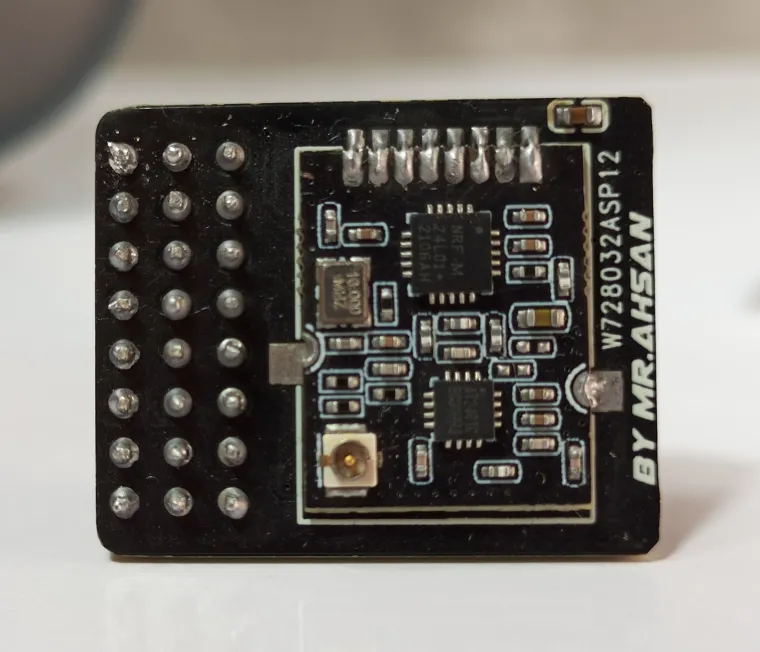
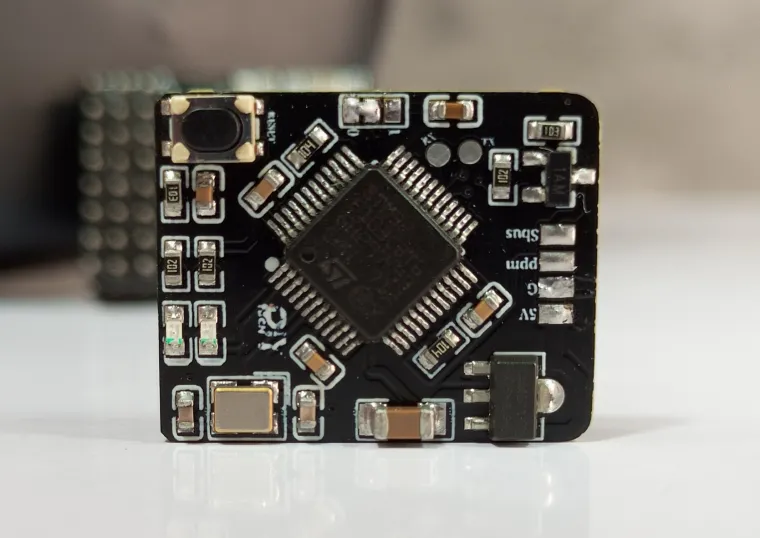
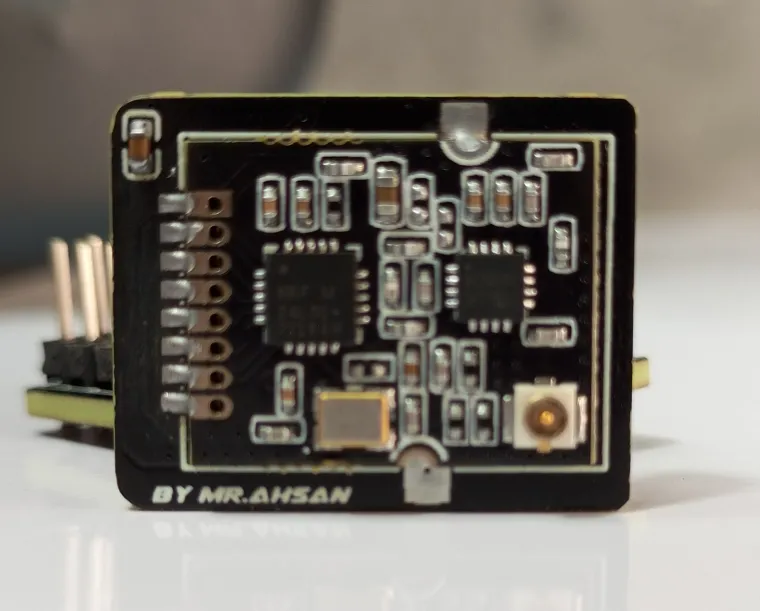
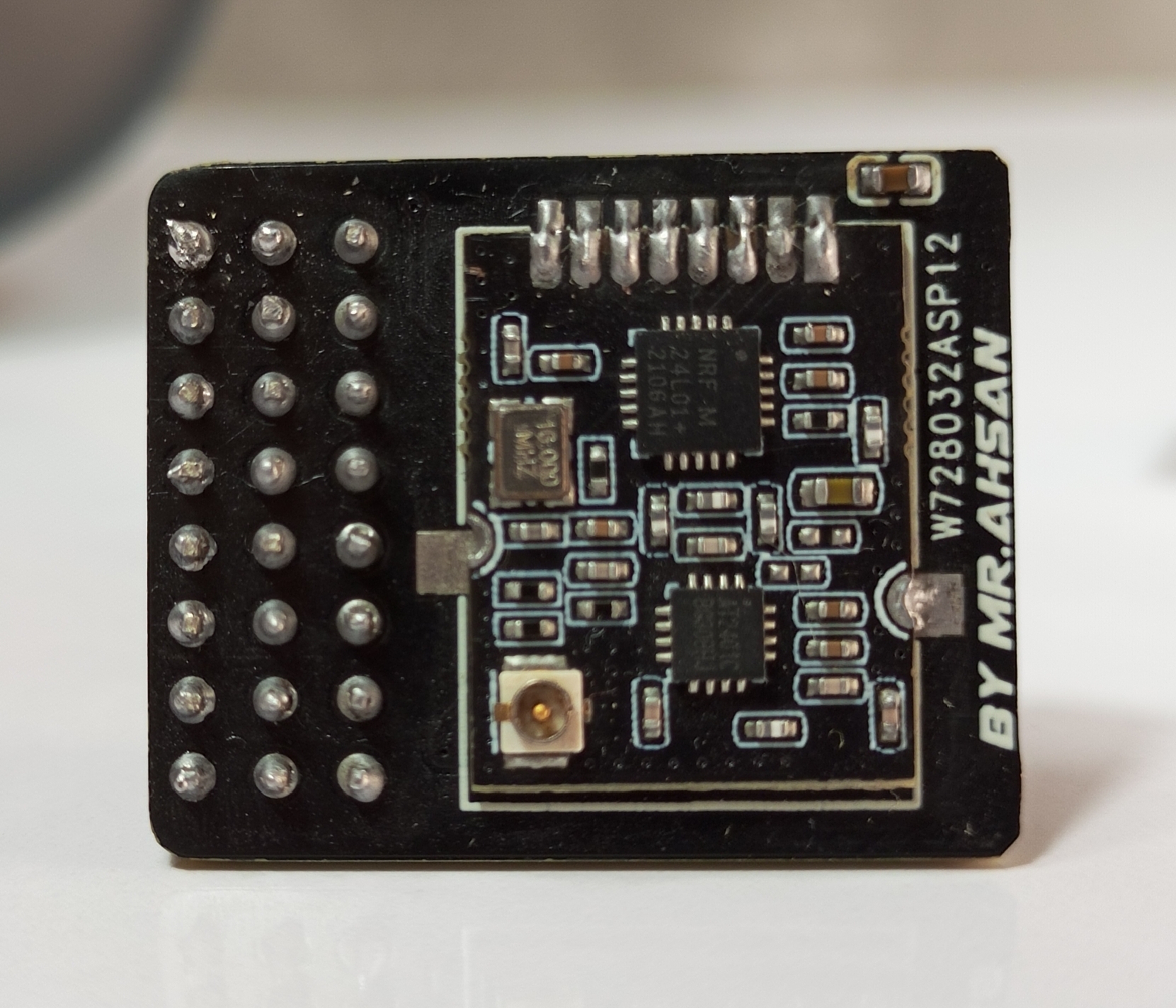
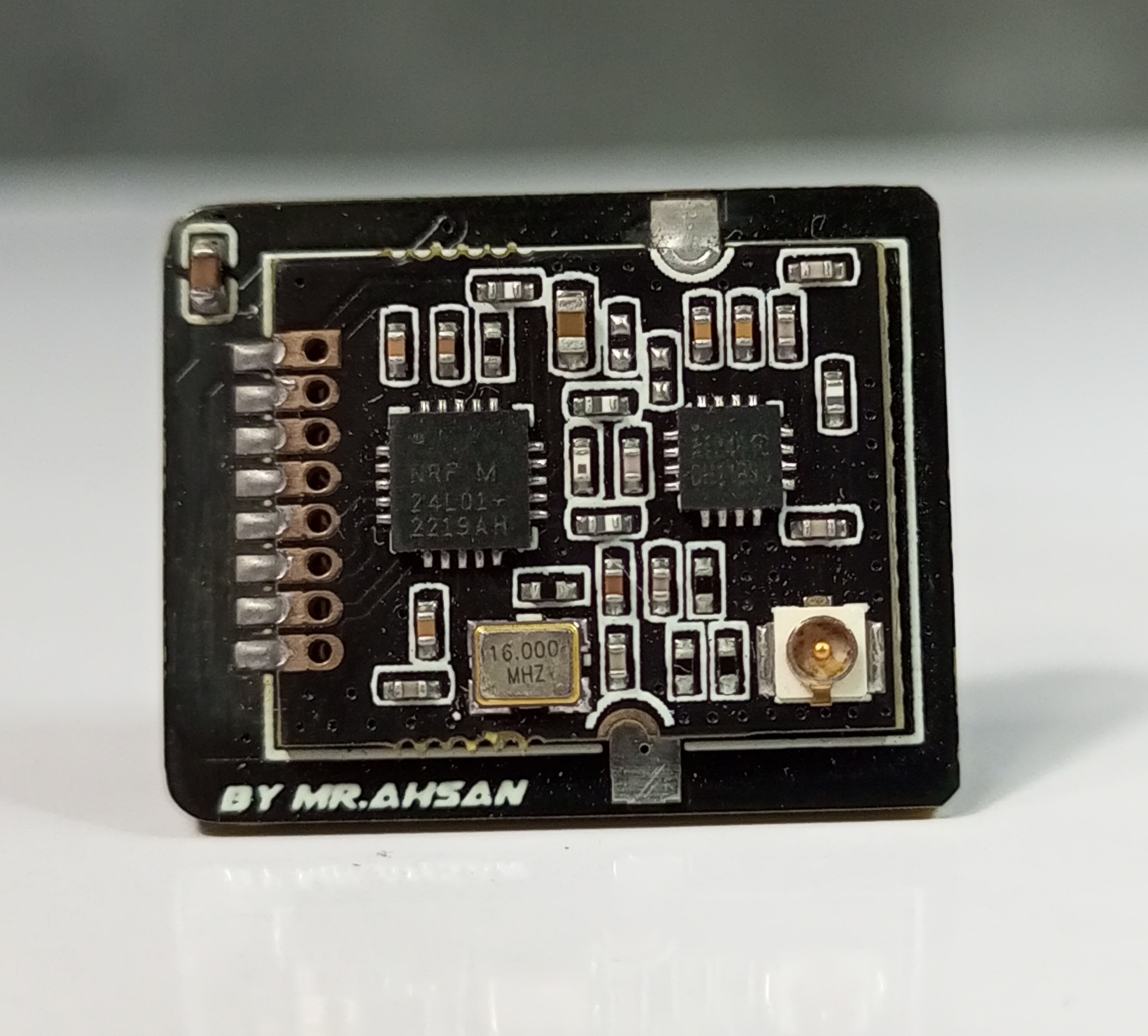
The XRC PRO has multiple PCBs and it consists of three main PCBs: the Transmitter PCB, the 8-channel PWM+PPM Receiver PCB, and the PPM+SBUS Receiver PCB. Each PCB was carefully designed for space efficiency and optimal performance.
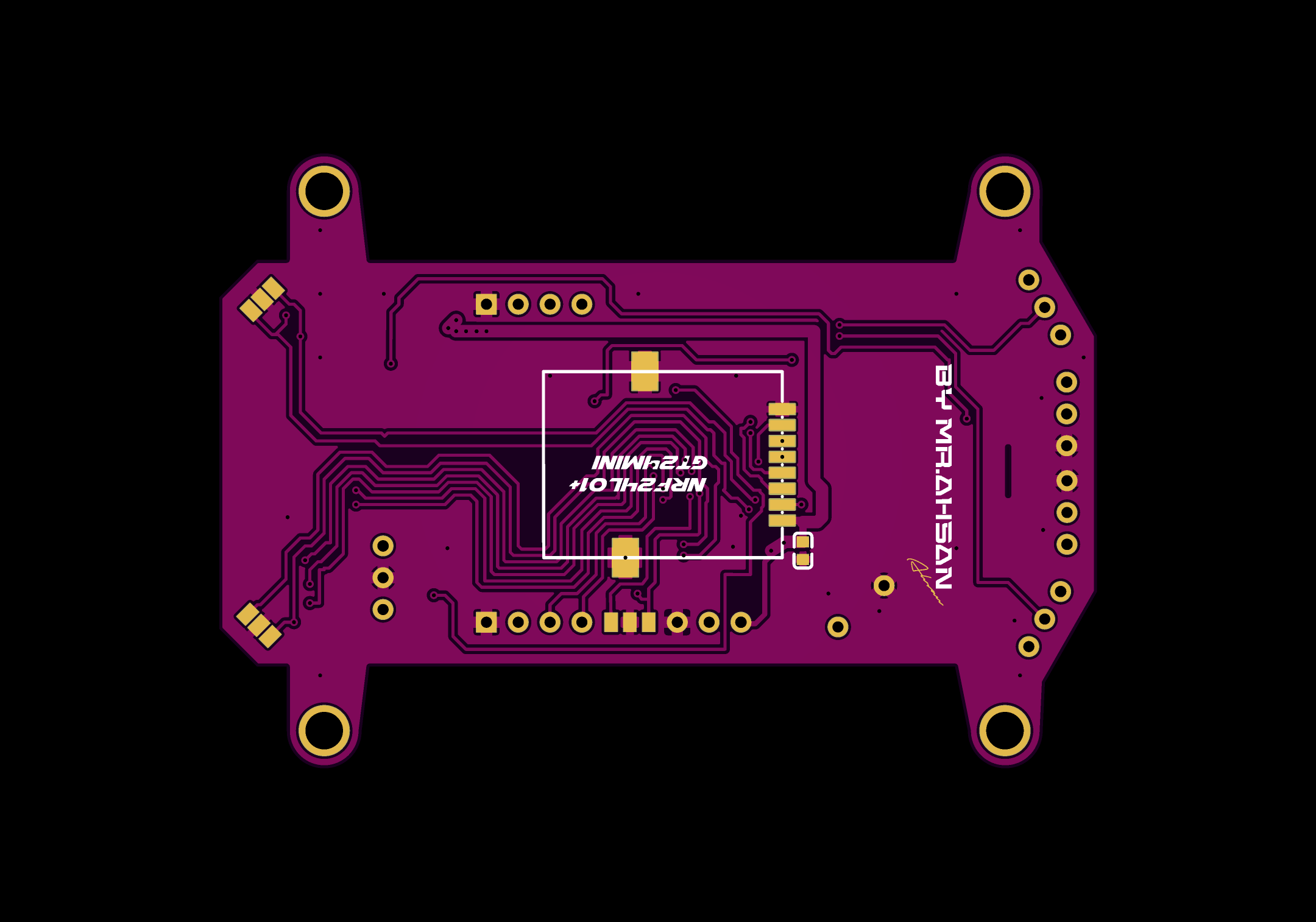
Transmitter PCBs
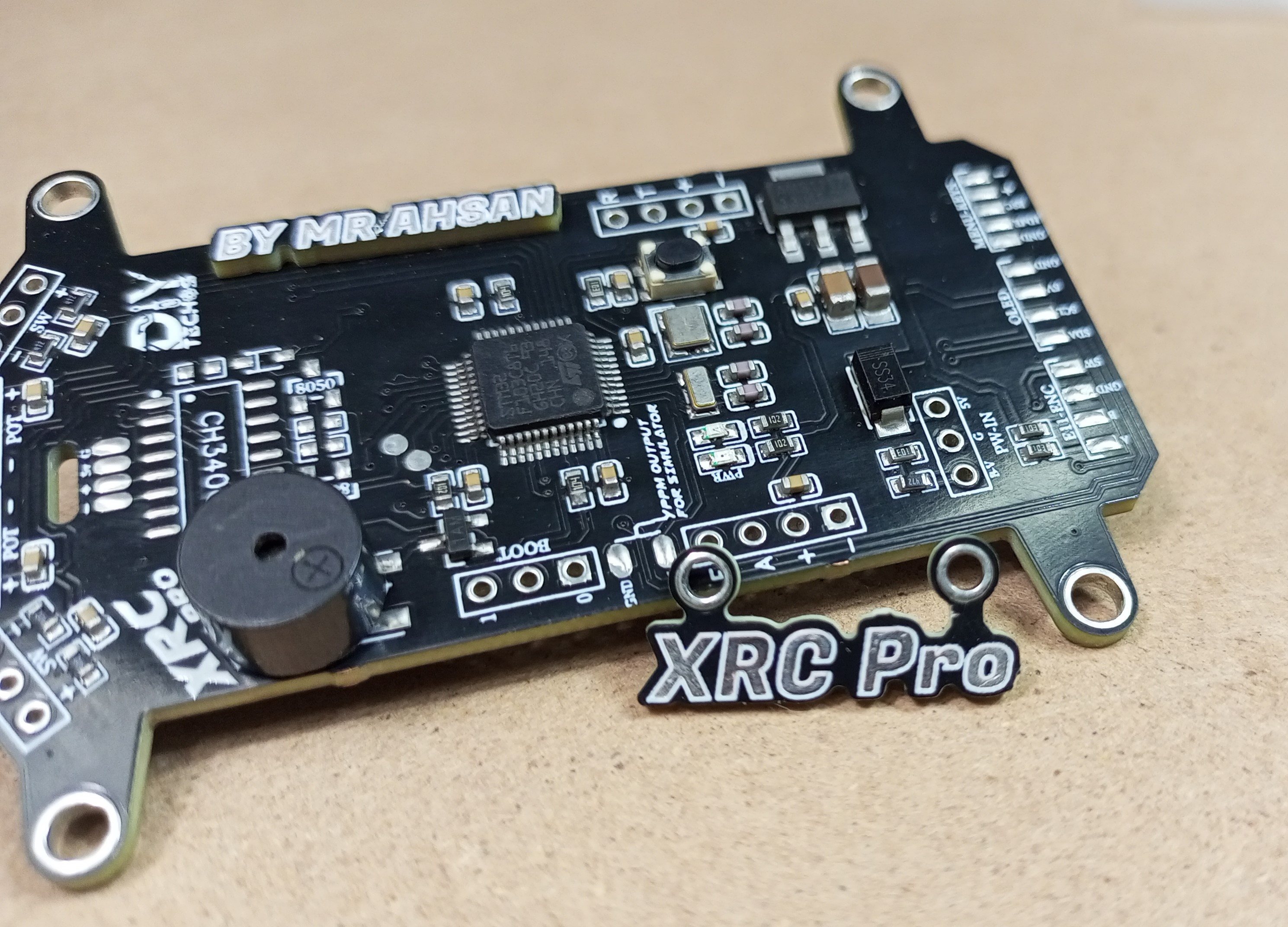
The Transmitter PCB is built around the STM32F103C8T6, NRF24L01 module, OLED display, and various input buttons (trim, menu, encoder). The schematic includes connections for power management (5v to 3.3v), data lines for the OLED, and button inputs for settings navigation etc.
Schematic
| Aspect | Description |
| STM32 Connections | STM32 is connected to NRF24L01 via SPI, OLED via I2C, and buttons for control inputs. |
| Power Supply Circuit | Features a stable power supply using a 5V to 3.3V step-down regulator, ensuring reliable operation. |
| PPM Output Pin | PPM output pin is mapped for direct use with simulators or external RC receivers. |
PCB Layout
| Aspect | Description |
| Size Optimization | Minimized PCB size using almost all components in SMD package to achieve a professional and compact design. |
| Decoupling Capacitors | Added 100nF decoupling capacitors to each channel to reduce noise and smooth signal performance. |
| Compact Design | Designed to fit within the DJI Phantom 2 remote enclosure, ensuring a sleek and practical design. |
| Button & Display Placement | All buttons, display, and rotary encoder pads are neatly arranged for ease of use and functionality. |
| Signal Routing | Careful routing of SPI and I2C lines to avoid interference and ensure clean signal transmission. |
Schematic and PCB Layout
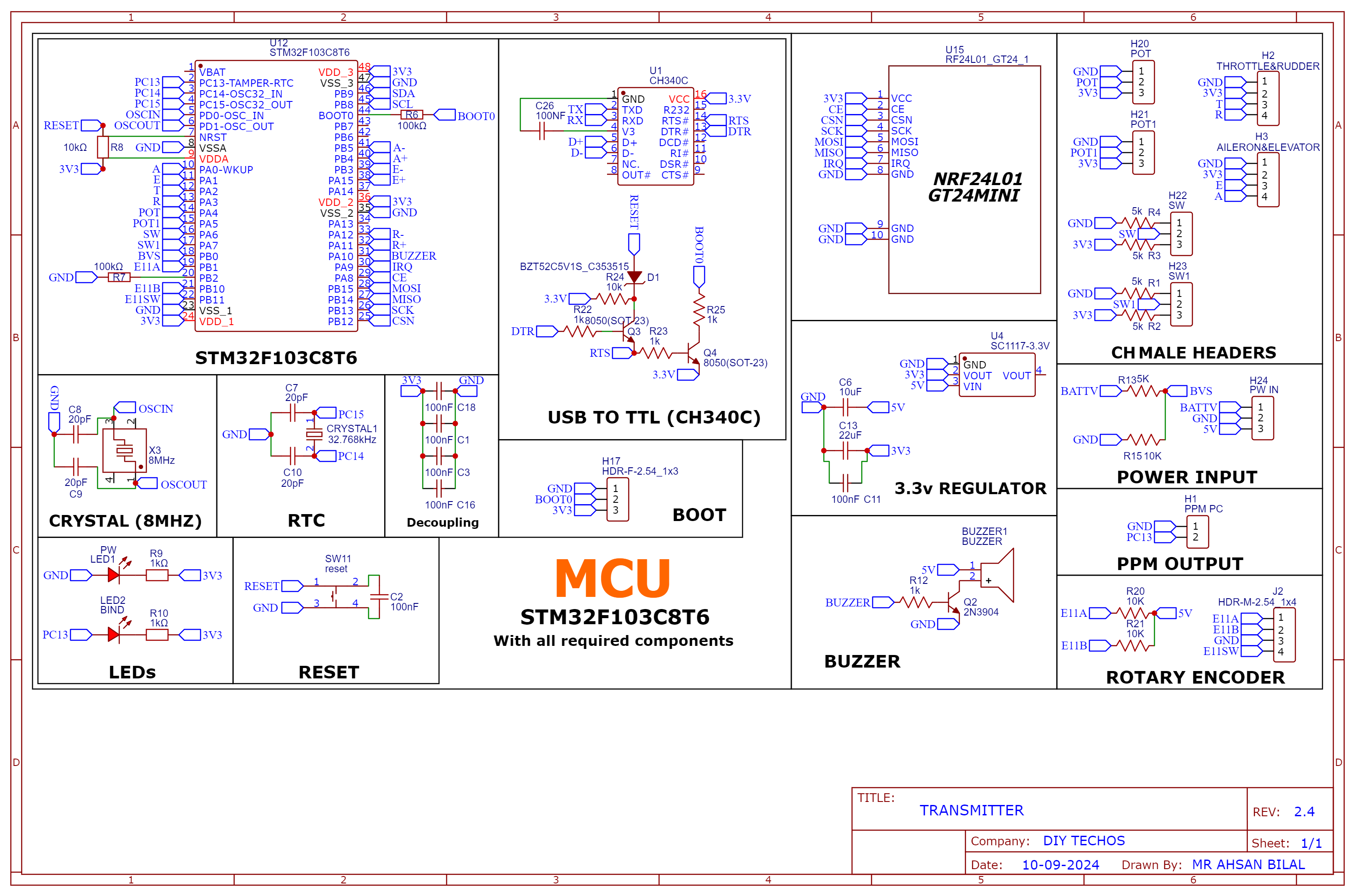
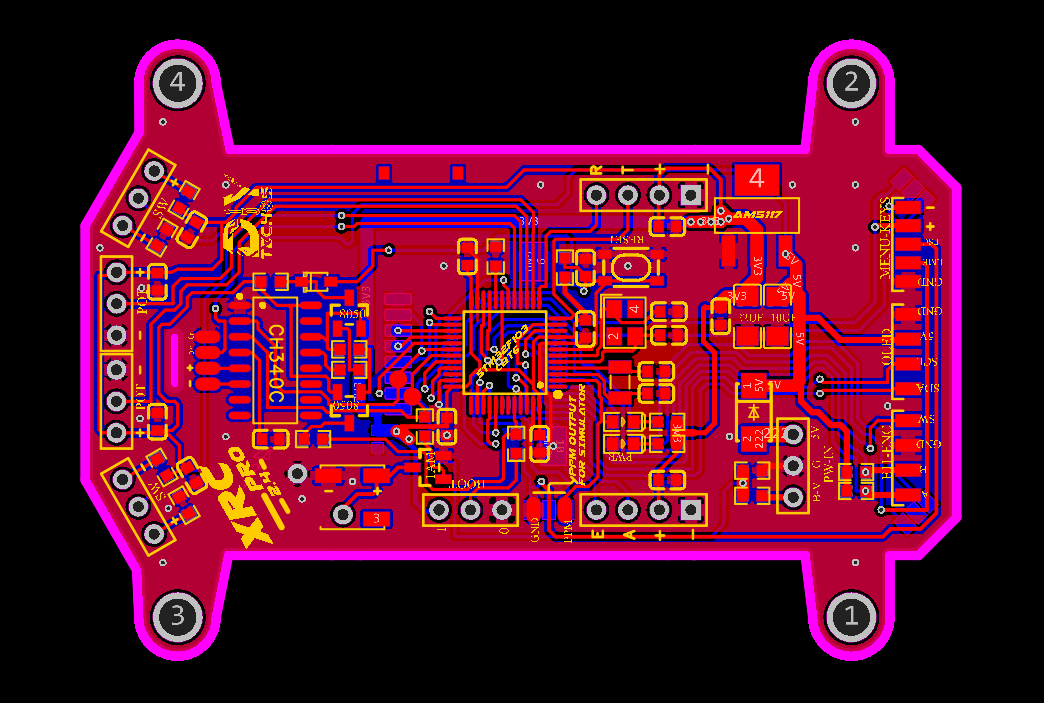
2D and 3D Preview


Final Result

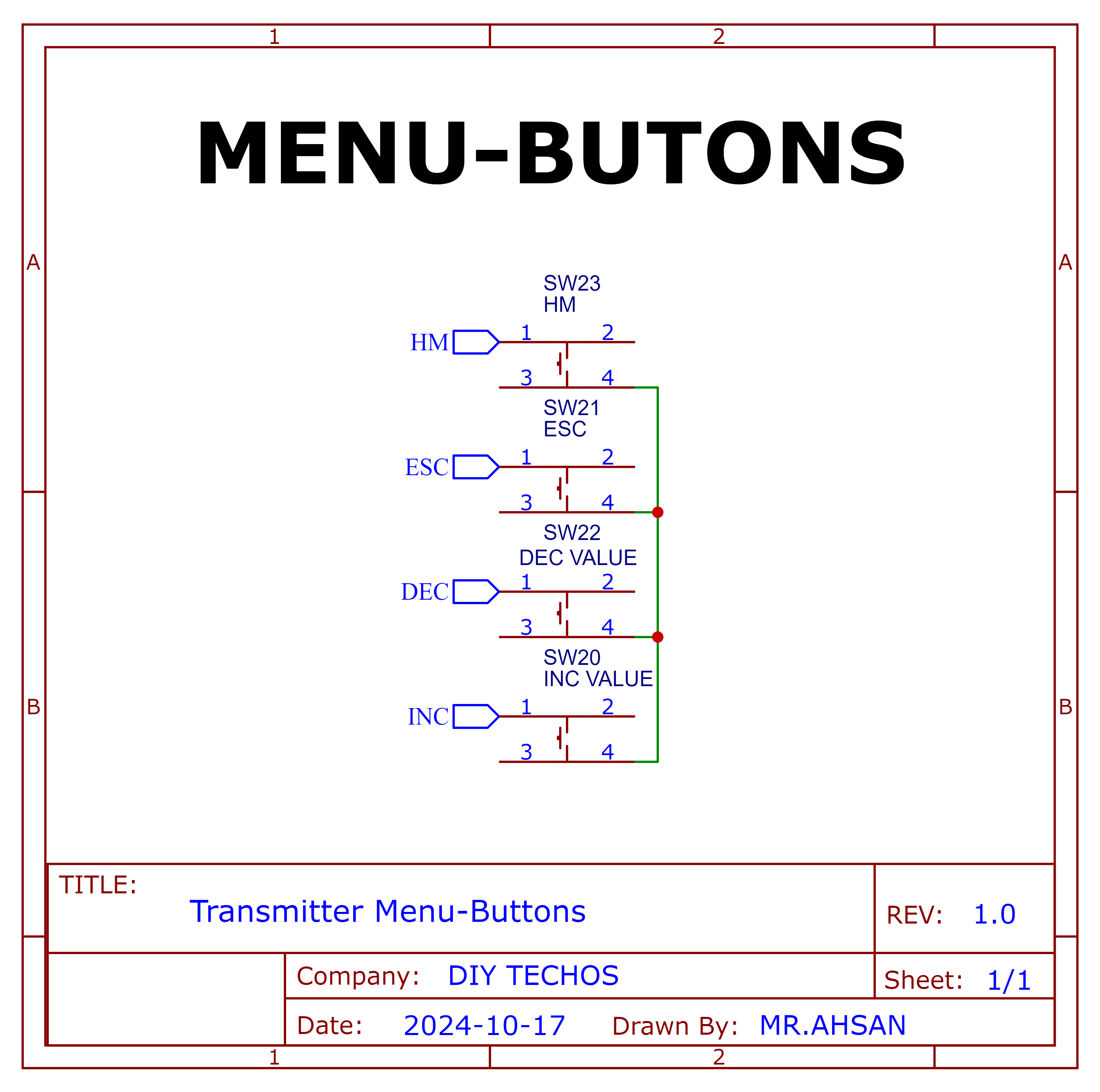
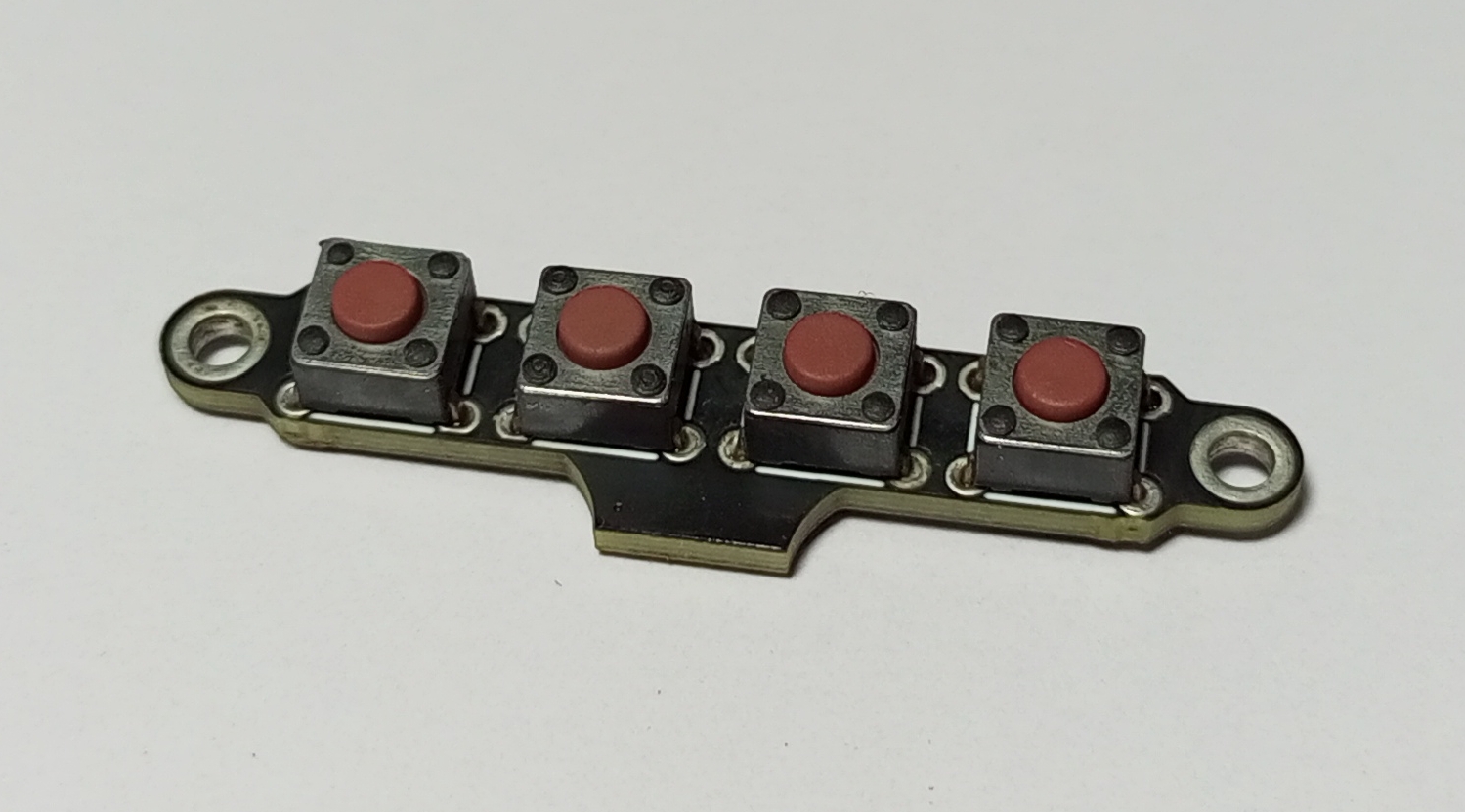
Menu-Keys
Schematic and PCB Layout
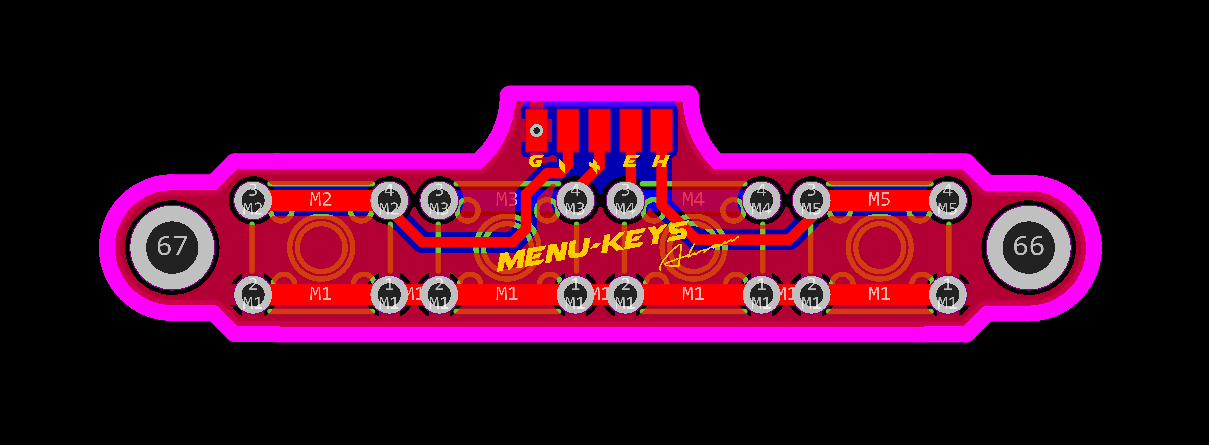
2D and 3D Preview



Final Result
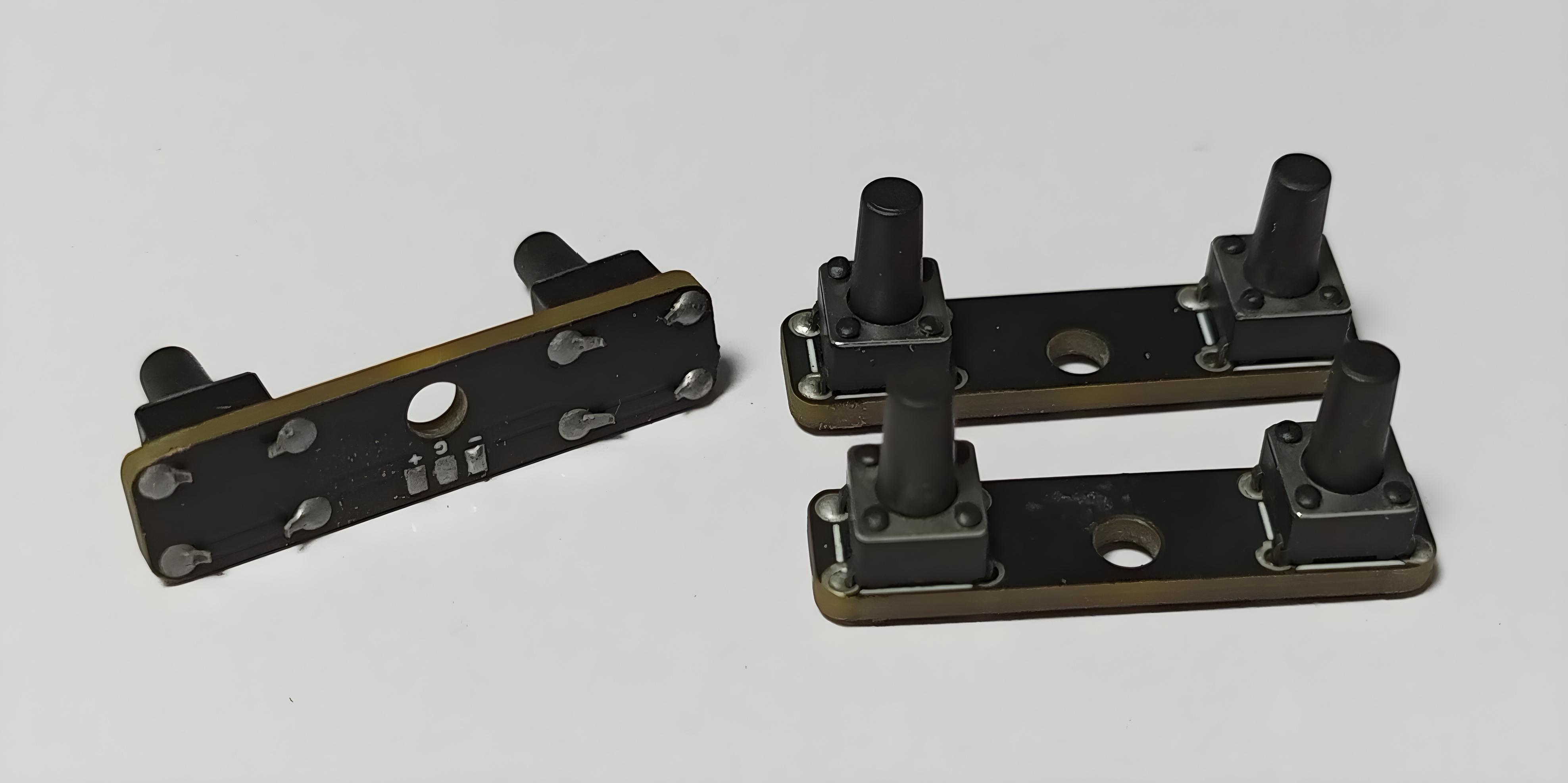
Rotary Encoder+Switch
Schematic and PCB Layout
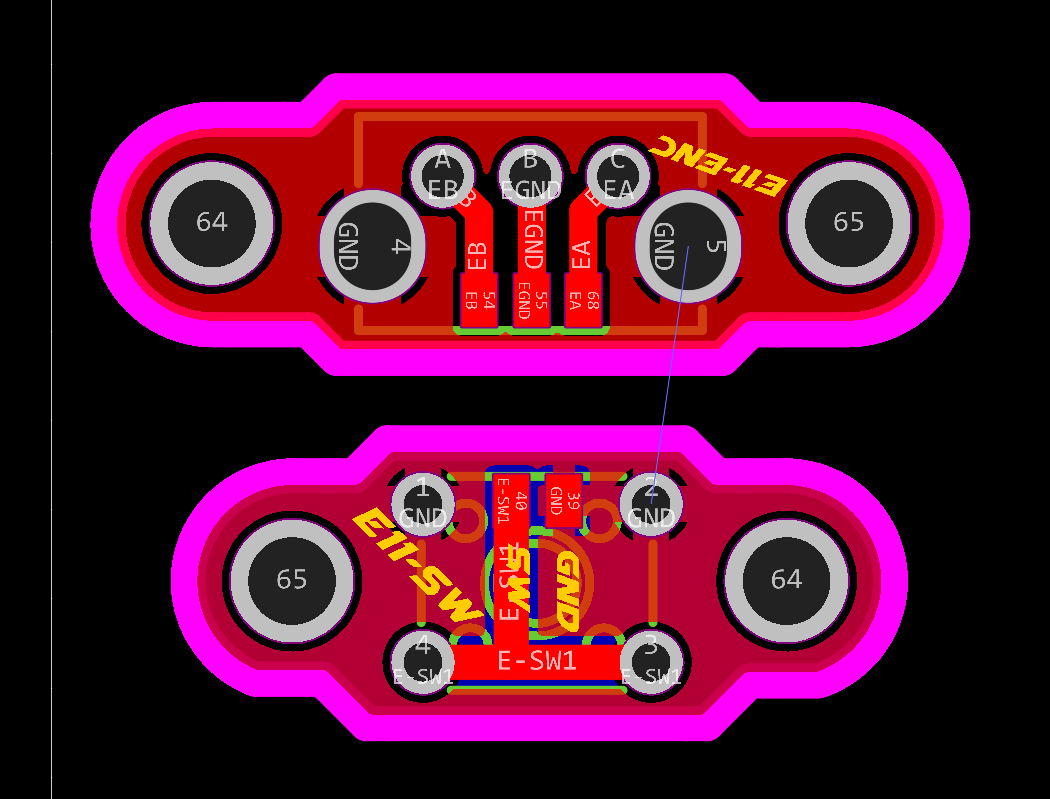
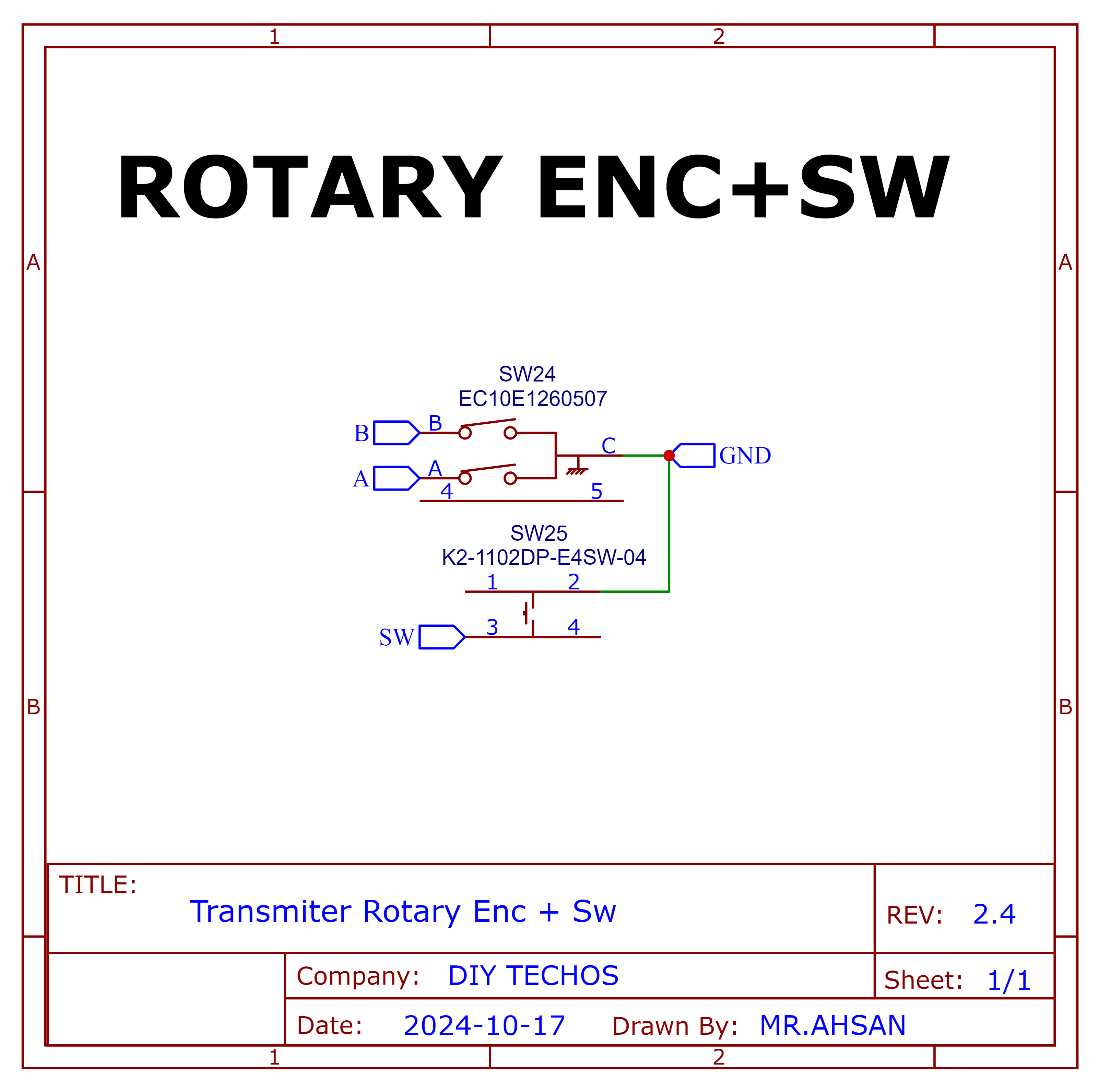

2D and 3D Preview
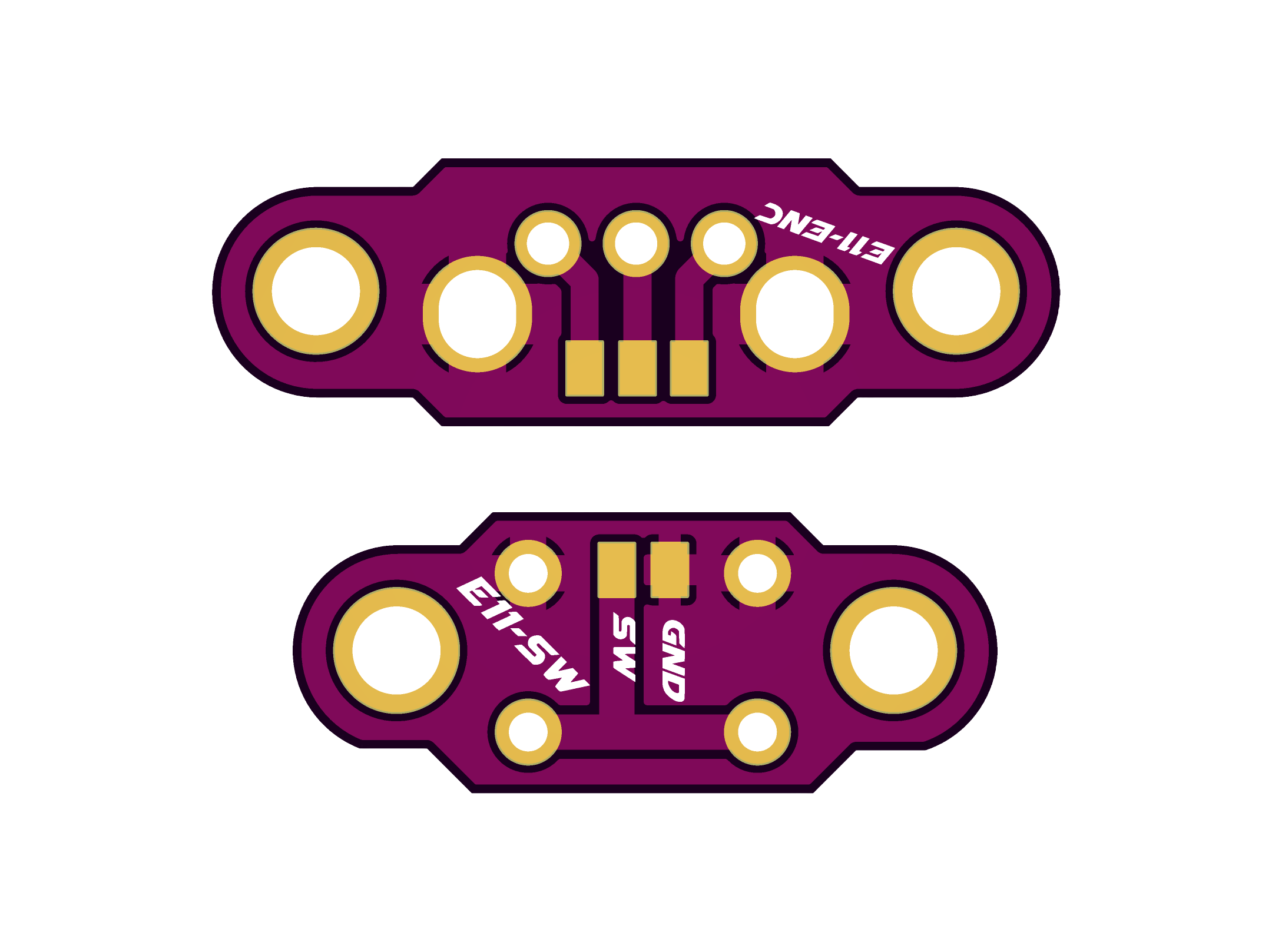


Final Result
Trim Buttons
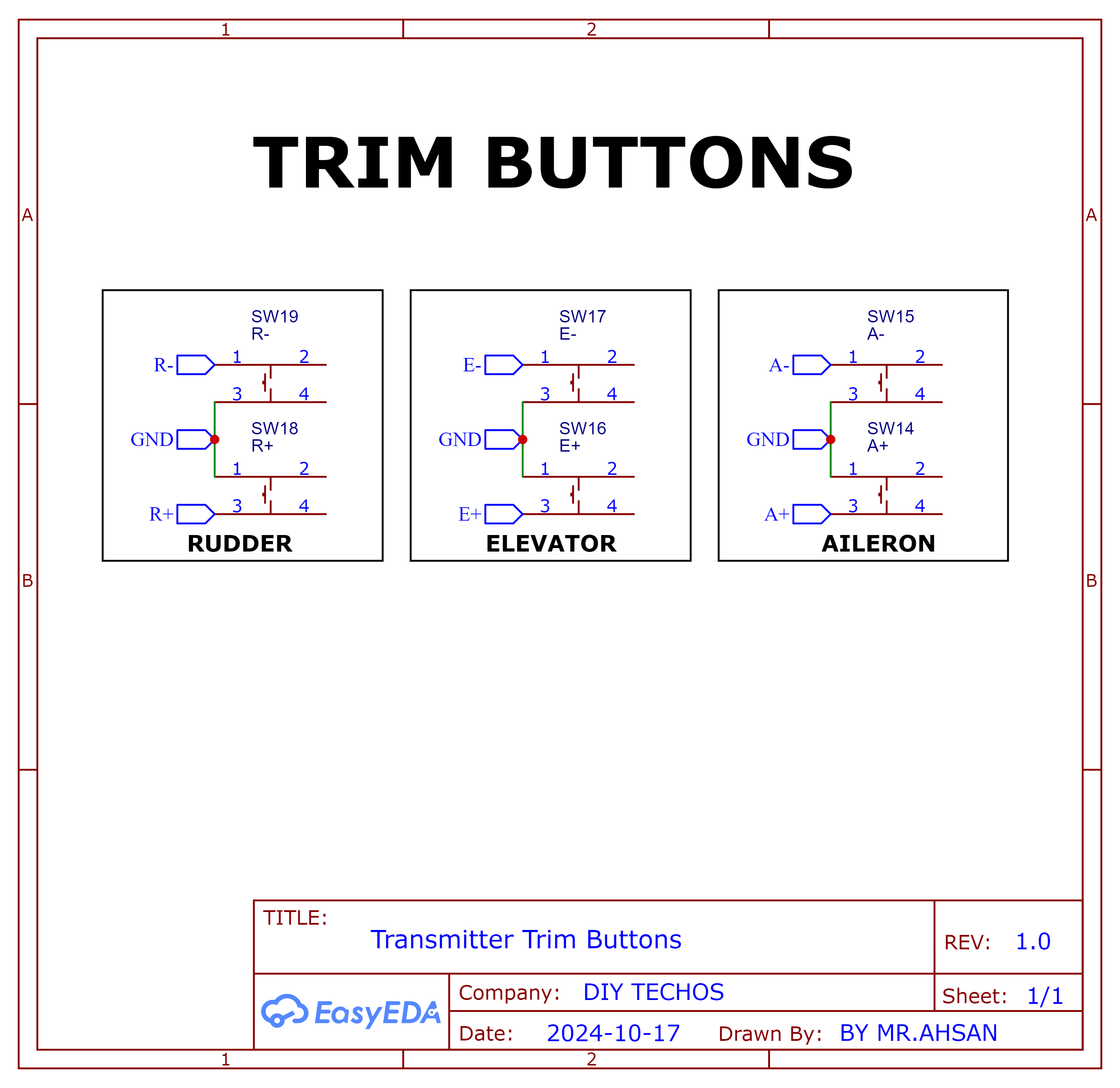
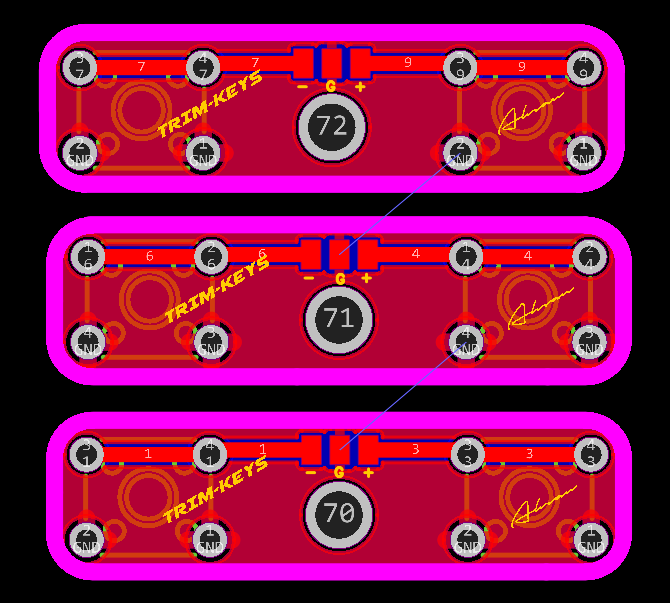
2D and 3D Preview
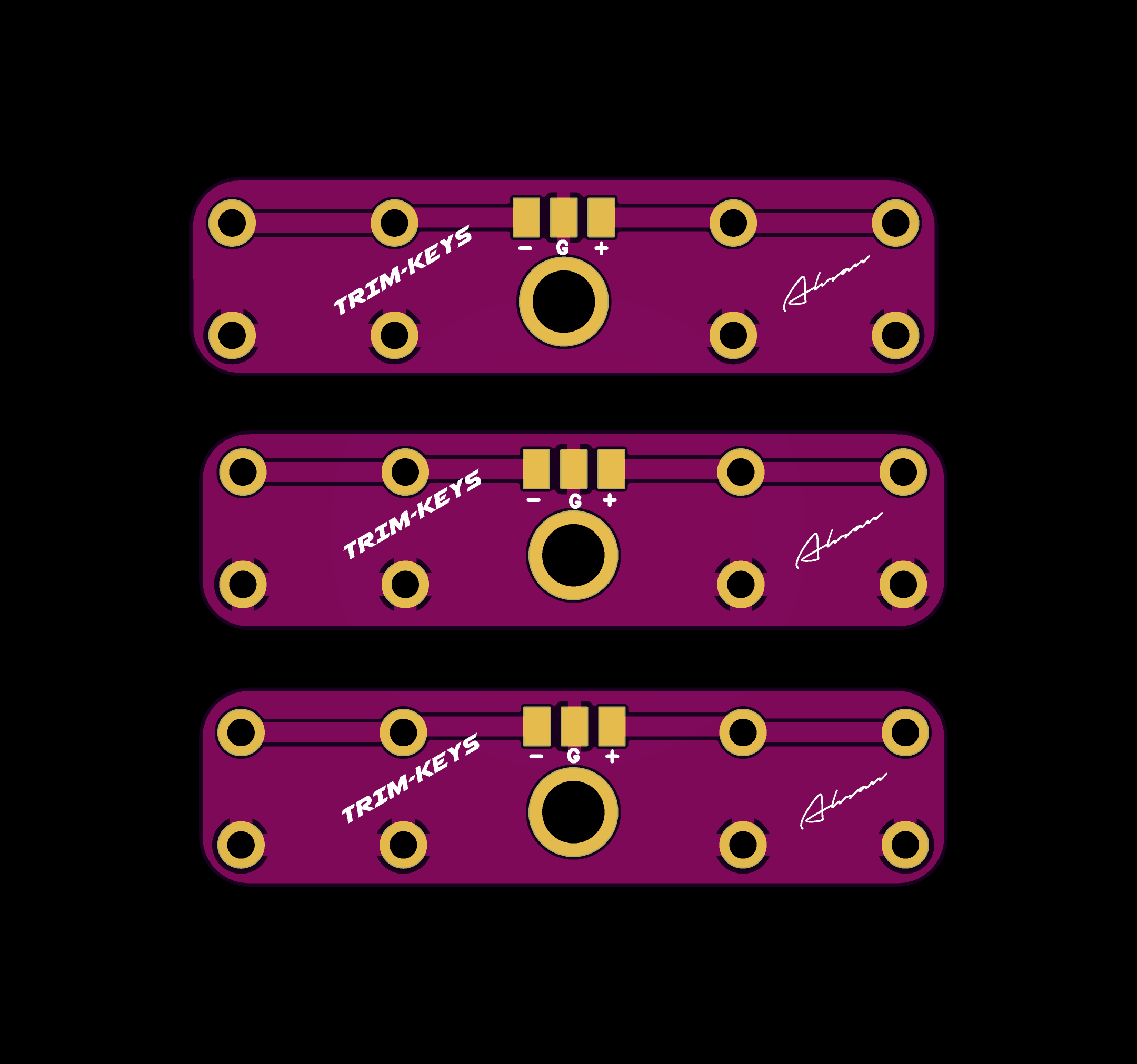


Final Result

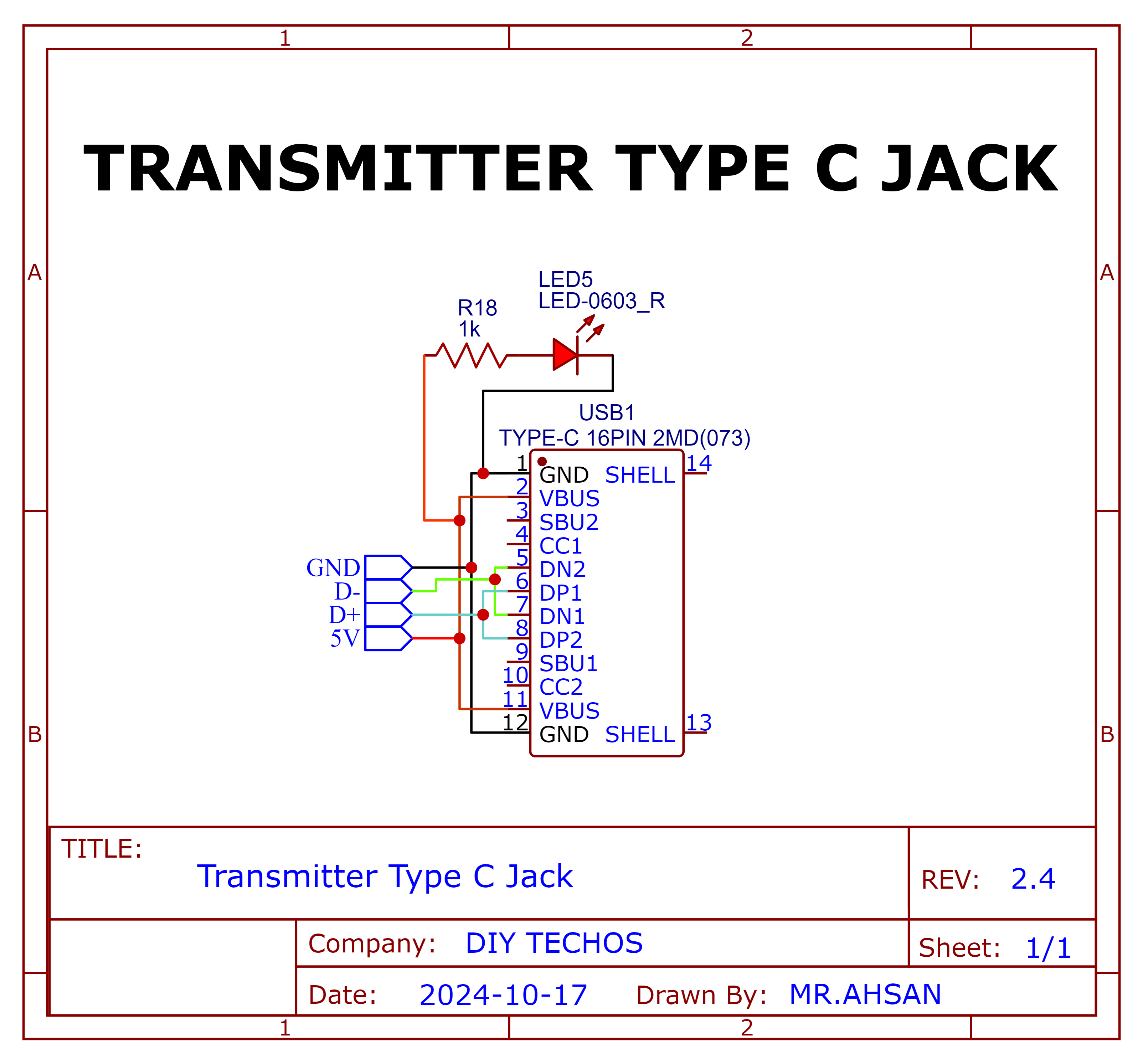
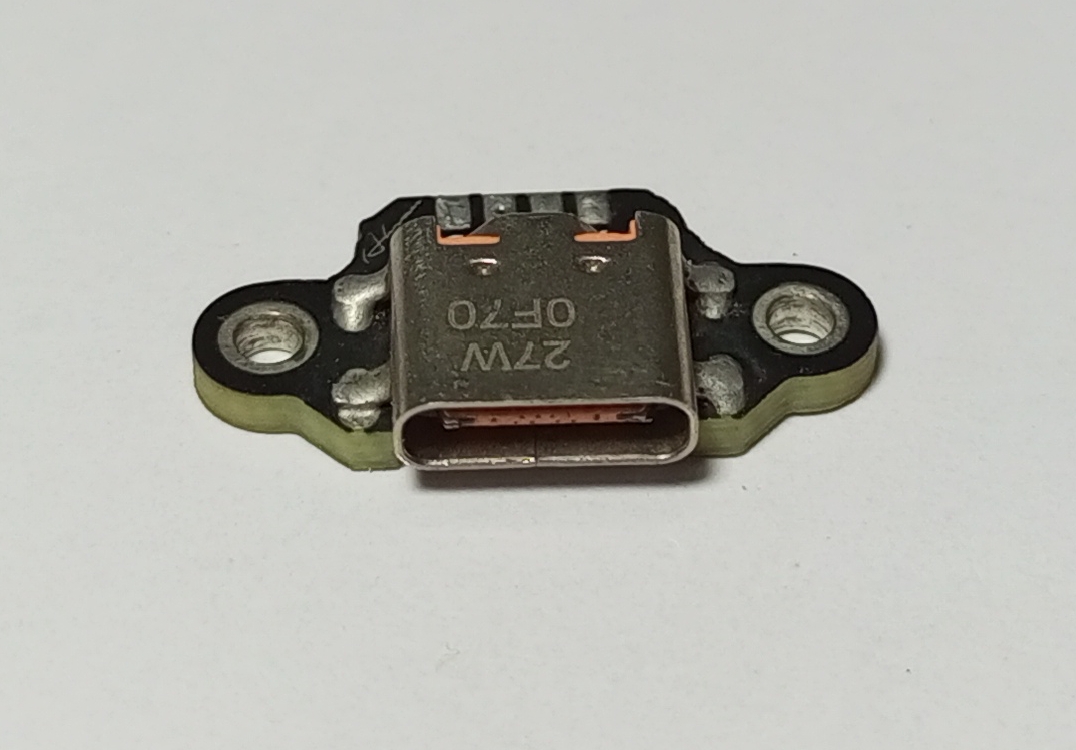
Type C Jack
Schematic and PCB Layout
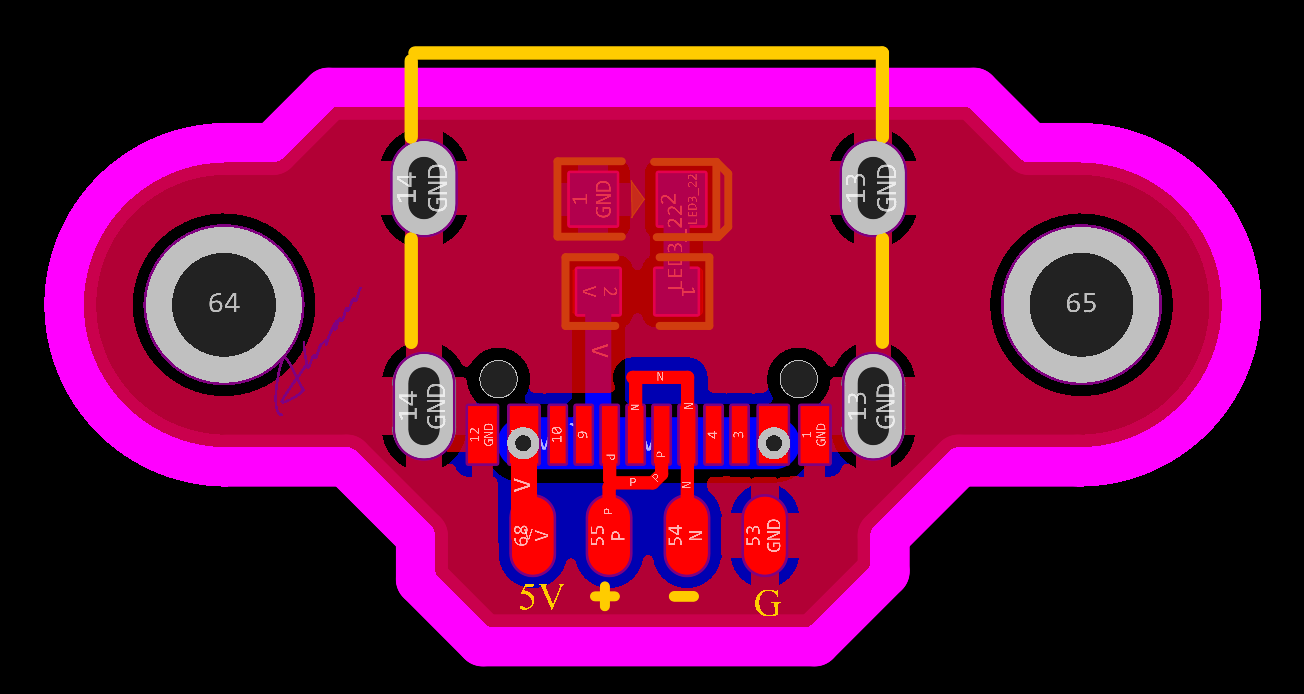
2D and 3D Preview


Final Result

Receciver PCBs
8-channel PWM+PPM Receiver PCB
The 8-channel receiver supports both PWM and PPM outputs. It is based on the NRF24L01 and STM32F103C8T6 for signal decoding and generation.
Schematic
| Aspect | Description |
| Signal Decoding | Decodes signals from the NRF24L01 transceiver using the SPI interface for reliable data communication. |
| 8 PWM Output Pins | Provides 8 PWM output pins for controlling multiple servos, enhancing RC model functionality. |
| PPM Output Pin | PPM output pin designed for connecting to flight controllers or other compatible devices. |
PCB Layout
| Aspect | Description |
| Compact Design | Compact PCB layout for seamless integration into various RC models, optimizing space usage. |
| Efficient Signal Routing | Efficient routing of signal and power lines to minimize noise and avoid signal interference. |
Schematic and PCB Layout
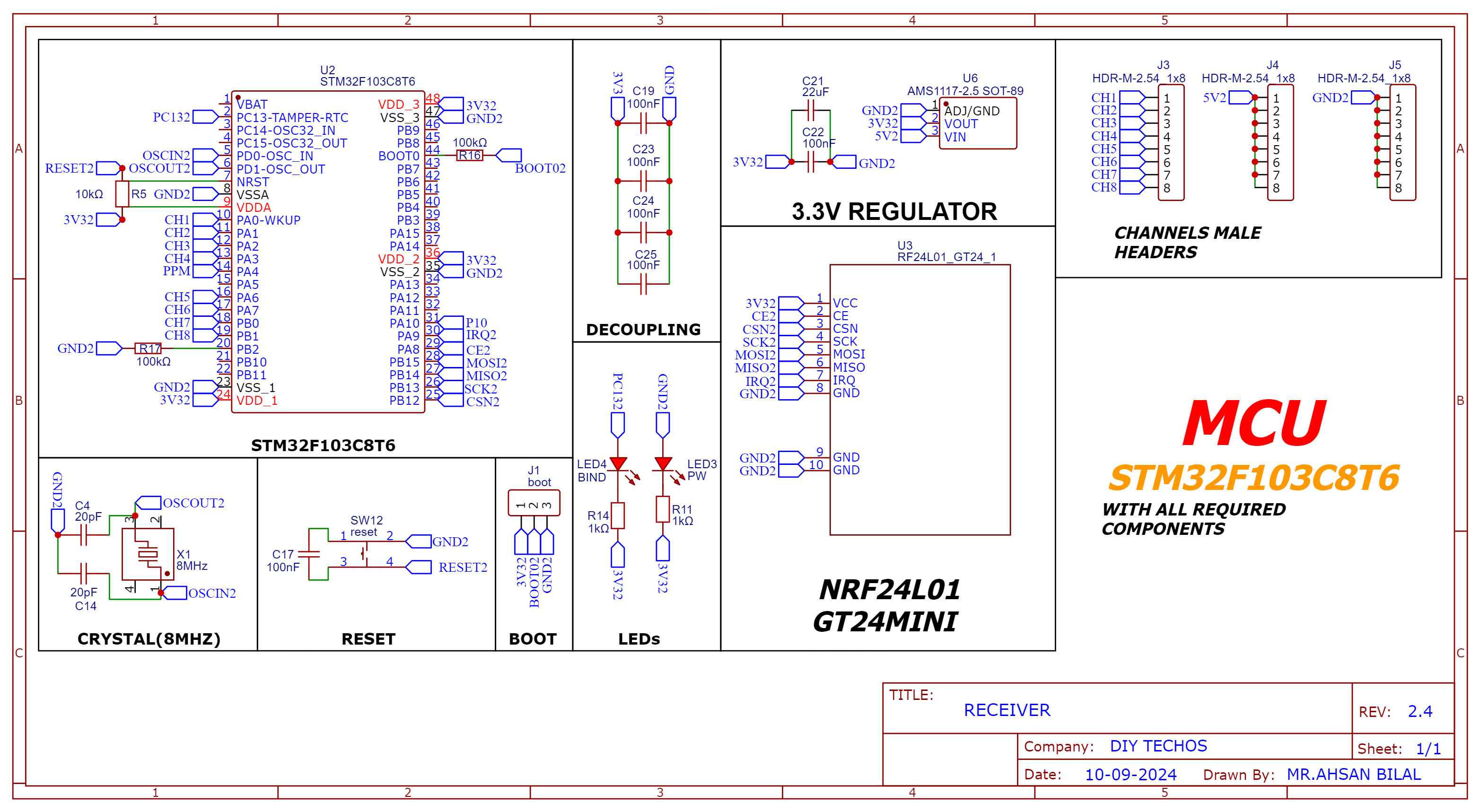
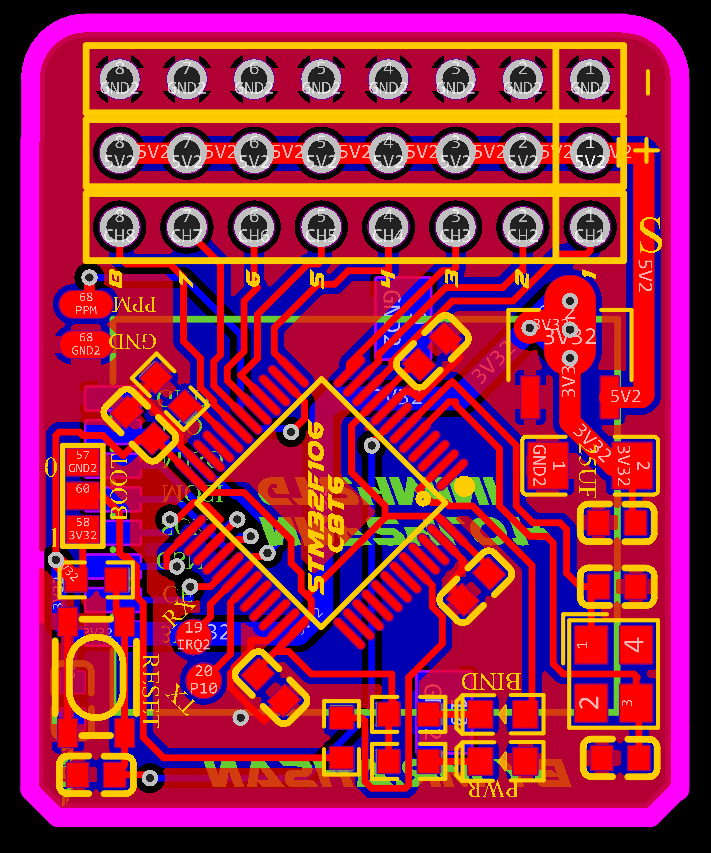
2D and 3D Preview



Final Result
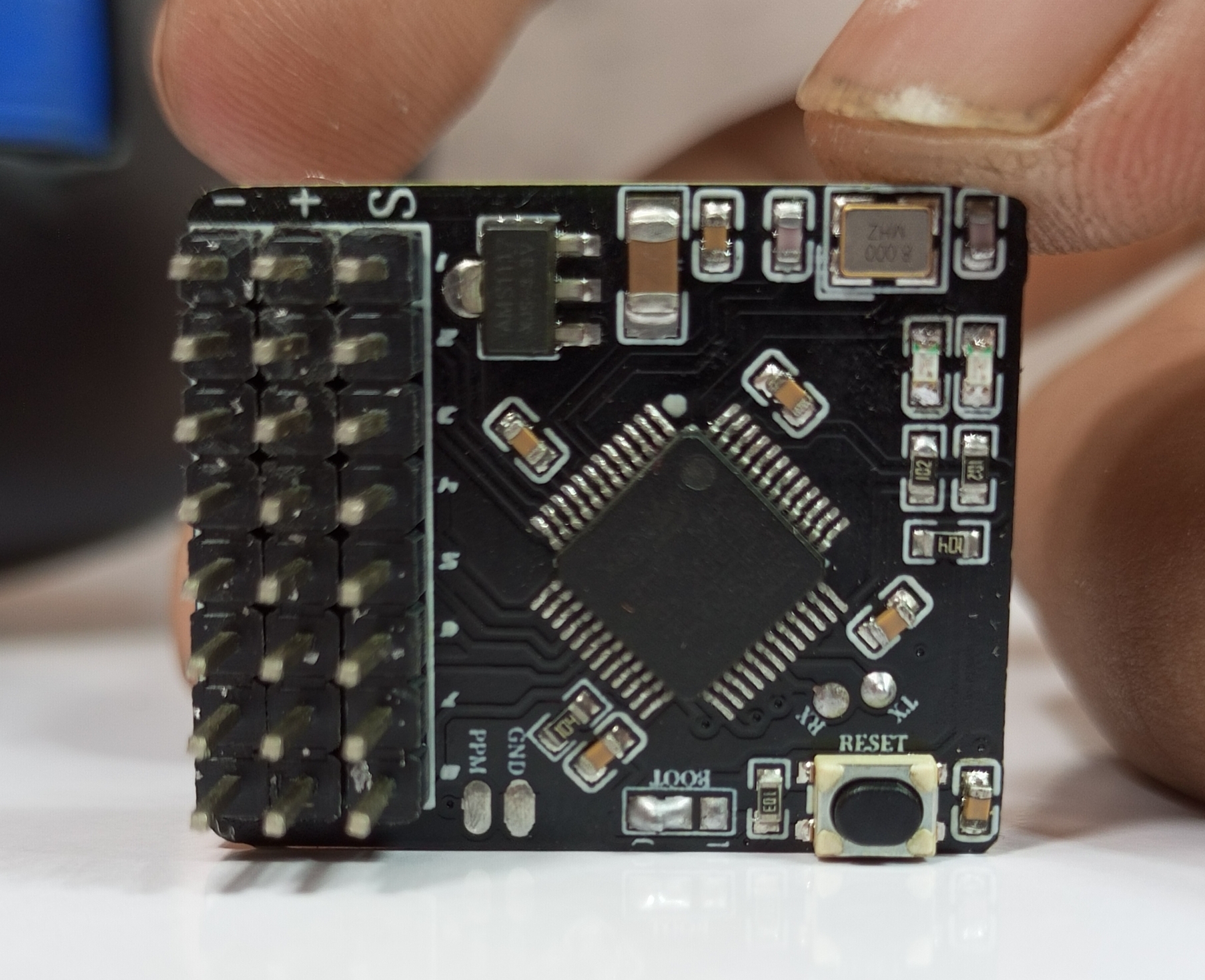
PPM+SBUS Receiver PCB
The PPM+SBUS receiver is another compact design focused on supporting more advanced control protocols. It also features the STM32F103C8T6 for signal processing and output.
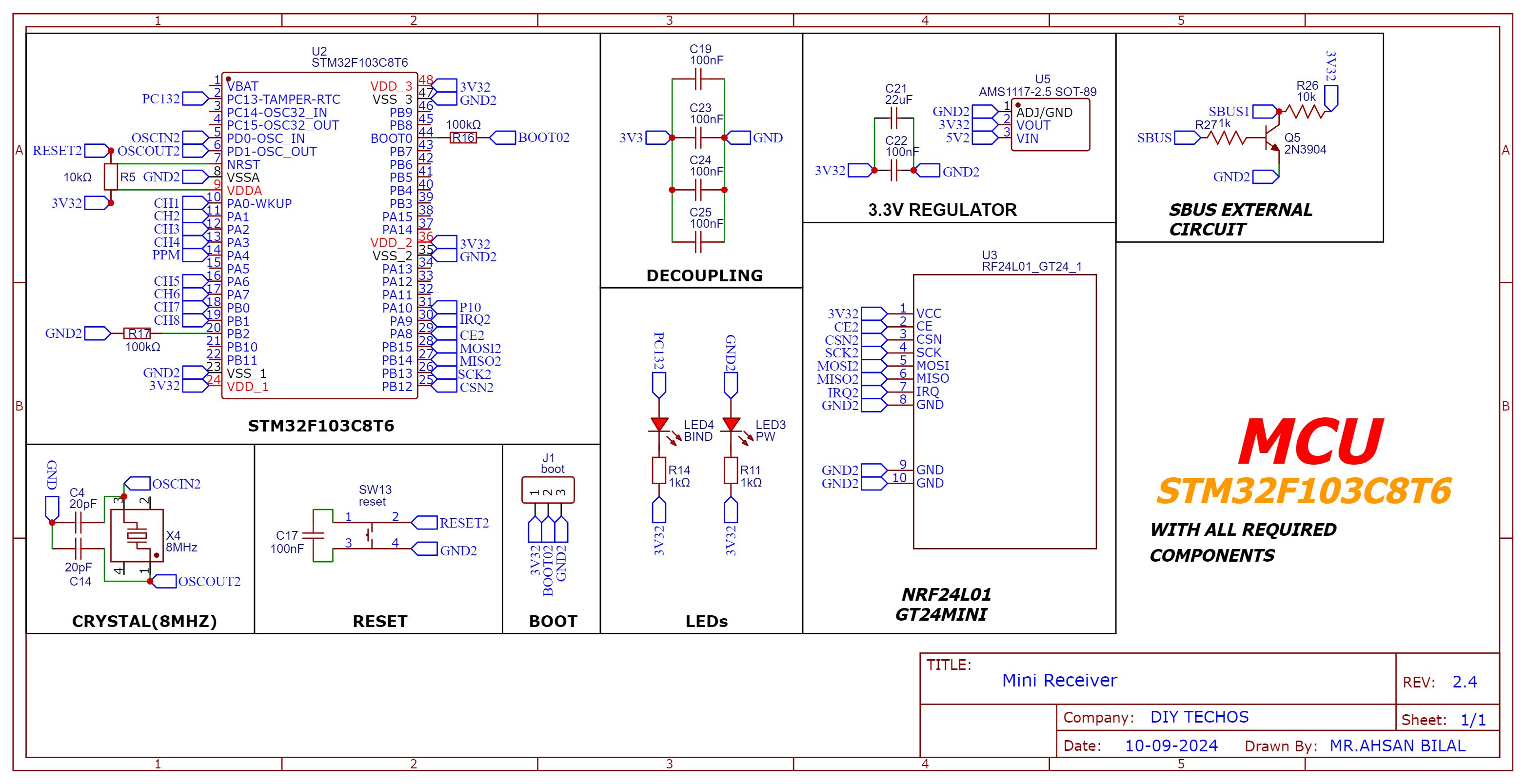
Schematic
| Aspect | Description |
| Signal Decoding | Decodes signals from the NRF24L01 transceiver using the SPI interface for reliable data communication. |
| SBUS Output Pins | SBUS output pin designed for connecting to flight controllers or other compatible devices. |
| PPM Output Pin | PPM output pin designed for connecting to flight controllers or other compatible devices. |
PCB Layout
| Aspect | Description |
| Compact Design | Compact PCB layout for seamless integration into various RC models, optimizing space usage. |
| Efficient Signal Routing | Efficient routing of signal and power lines to minimize noise and avoid signal interference. |
Schematic and PCB Layout
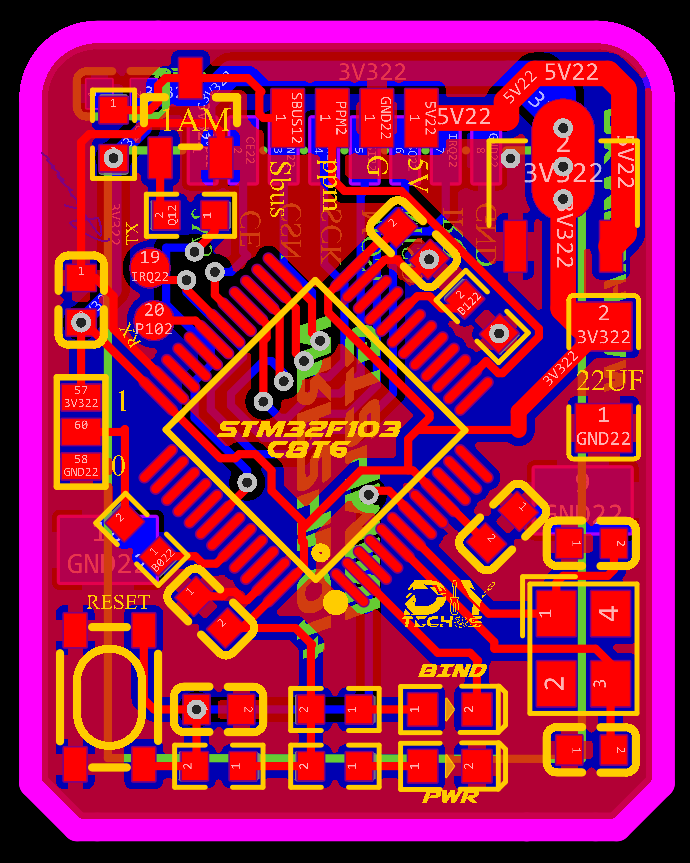
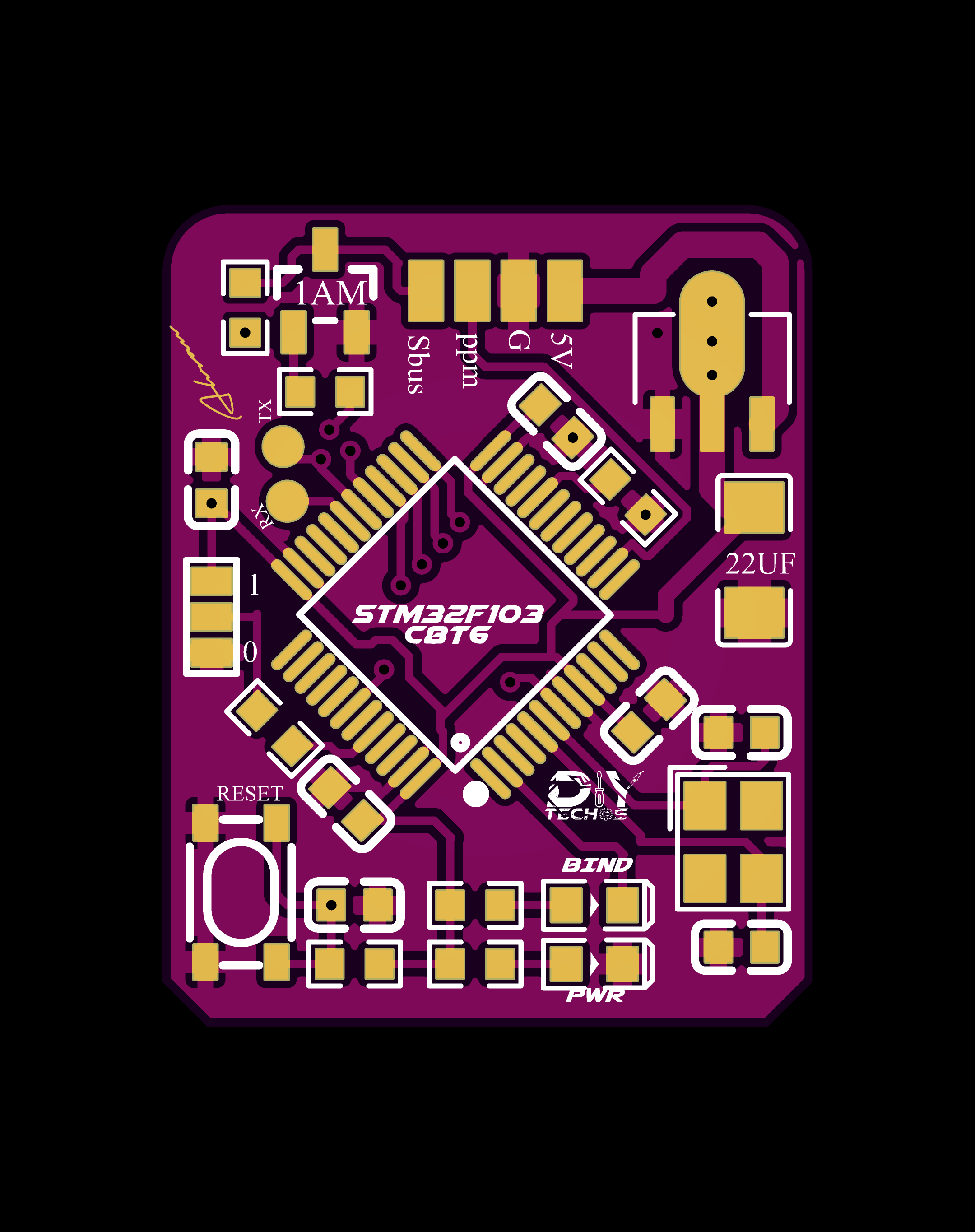
2D and 3D Preview
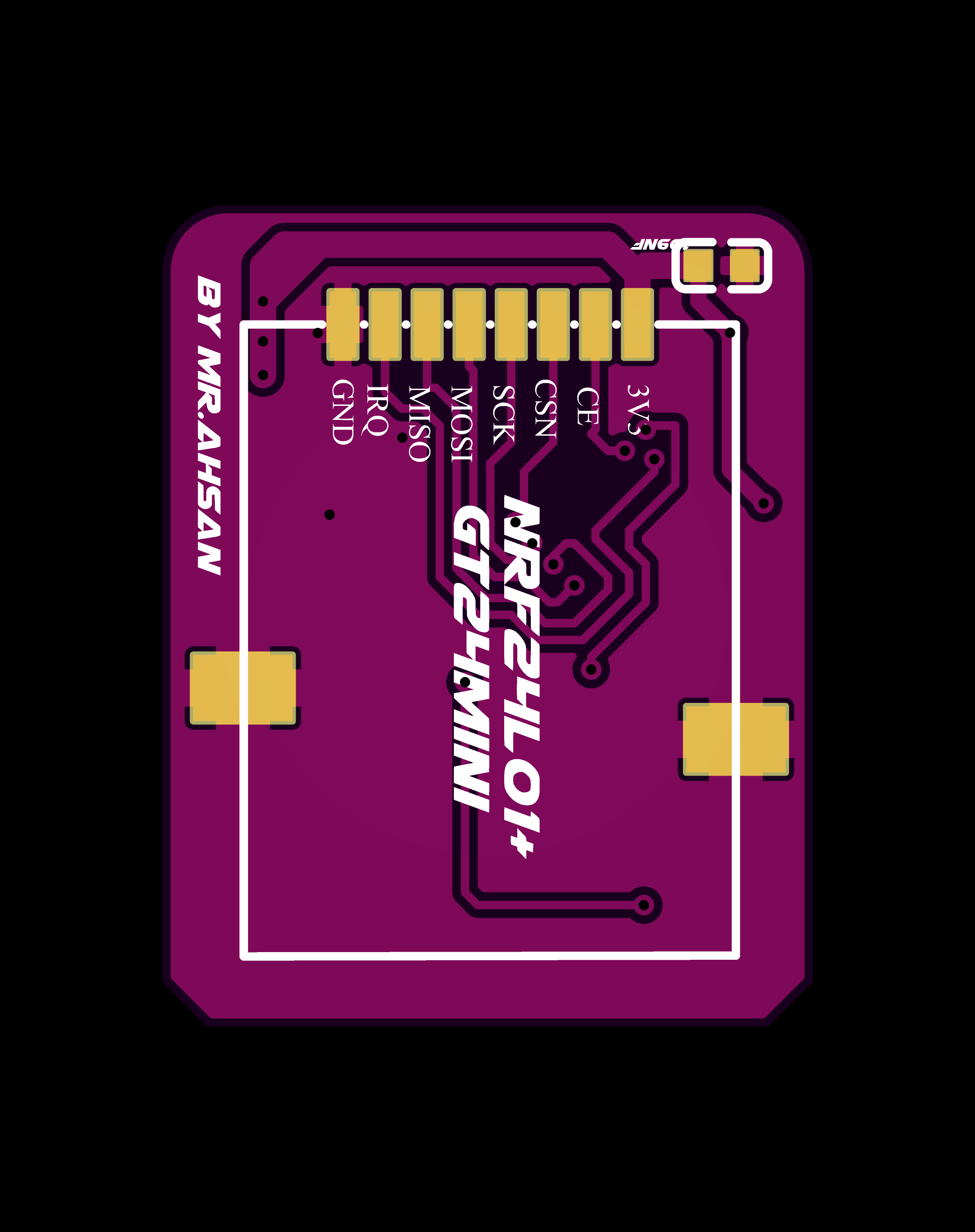


Final Result
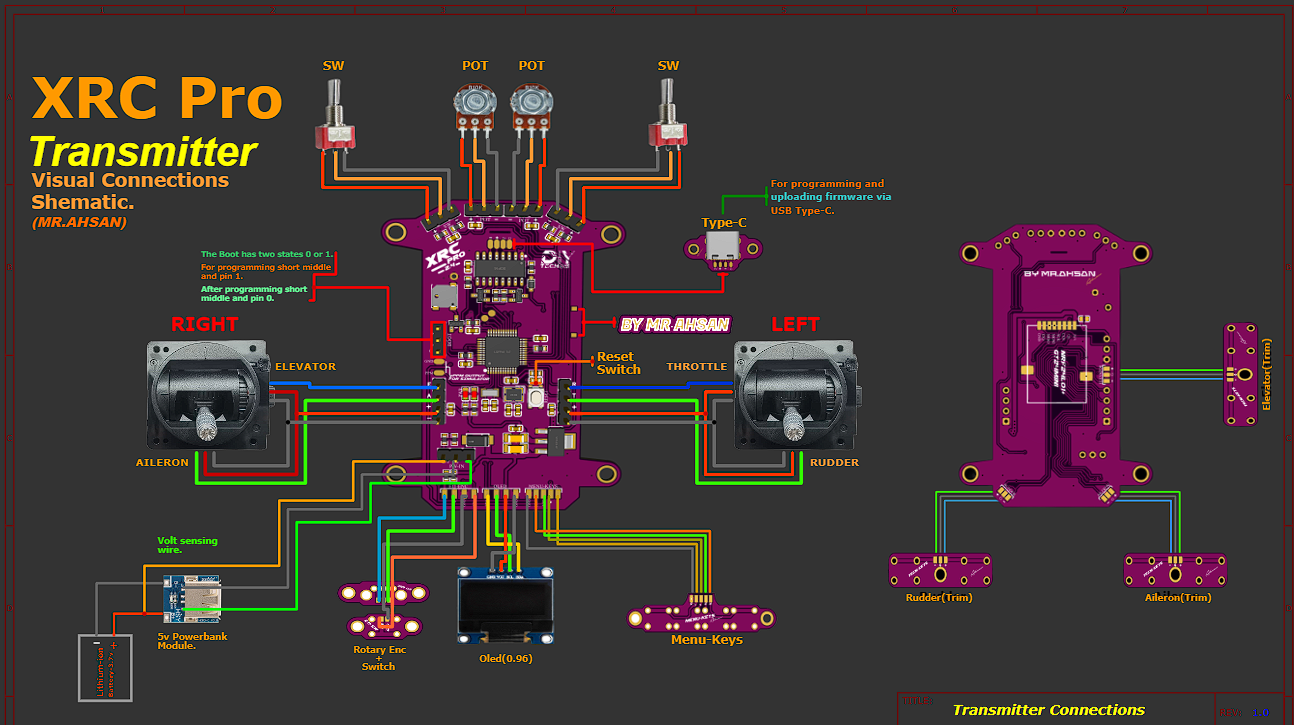
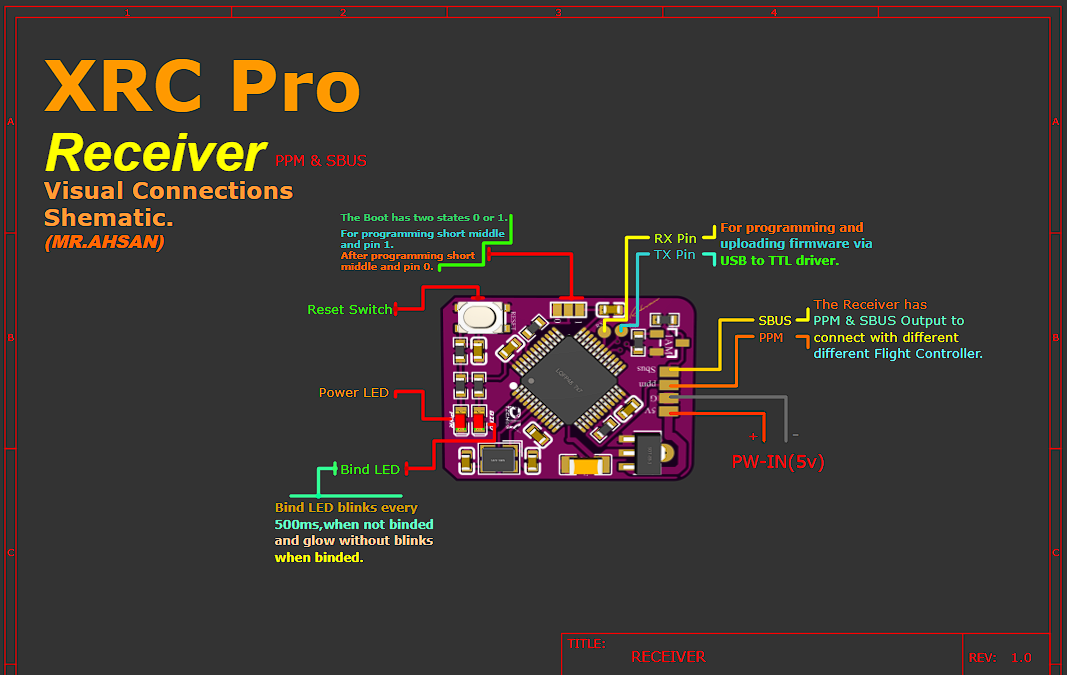
Visual and Physical Connections
I’ve designed a detailed, color-coded connection schematic for all inputs and outputs, making it easy for anyone to assemble the XRC PRO transmitter and receivers. Additionally, I’ve included high-quality these images in PDF format, which you can download below.
Transmitter
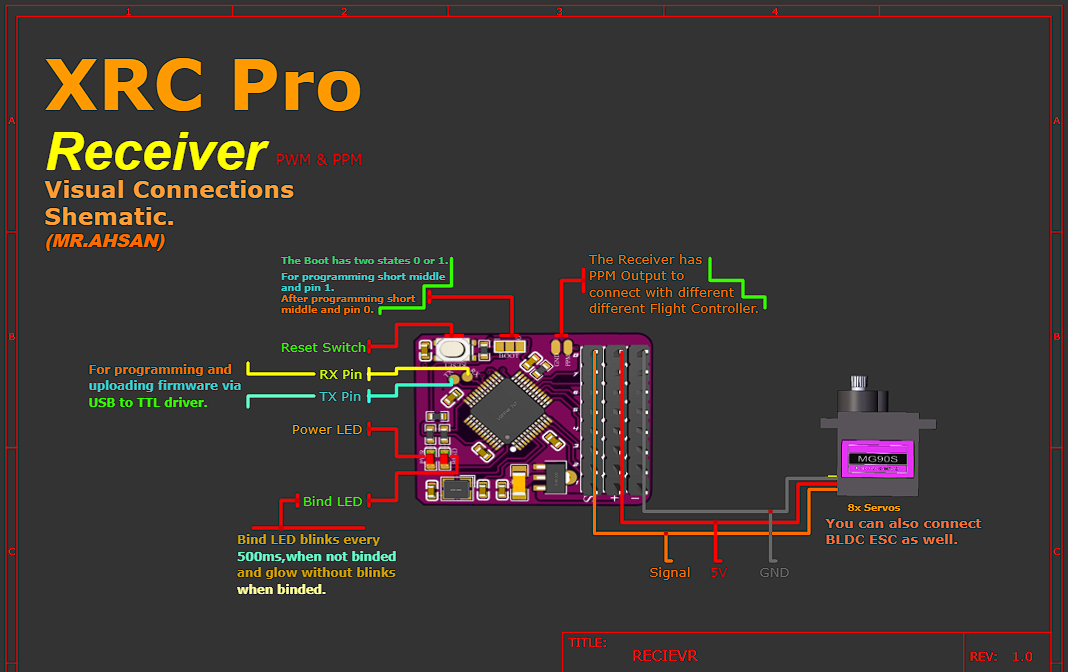
Receiver(PWM+PPM)
Receiver(PPM+SBUS)
Firmware Overview
The XRC PRO's firmware is developed in Keil uVision using the CMSIS framework for STM32. It is fully open-source, with modular code to allow easy customization and extension of the system's capabilities. The main focus of the firmware is on handling communication between the transmitter and receivers, as well as managing the various control inputs.
Here the whole files in KeiluVision:
Below are the functions broken down from the main execution code, organized into smaller functional blocks. These functions are intended to be modular and handle specific tasks like initialization, signal strength calculation, display management, and event handling:
1. setup()
This function initializes all the necessary hardware peripherals and sets up the system for operation.
void setup() {
// Initialize the delay function for timekeeping
delayInit();
// Initialize USART for serial communication
usart1Init();
// Initialize timers for PWM and other timing-related functions
timer2Init();
timer3Init();
// Initialize DMA for memory transfers
dmaInit();
// Initialize ADC for analog reading (e.g., battery level)
adcInit();
// Initialize NRF24L01 for wireless communication
if (nrf24l01Init() == NRF_OK) {
nrf24l01SetModeTX(); // Set NRF to transmit mode
} else {
// Handle NRF24L01 initialization error
beepError();
}
// OLED display initialization and show start-up screen
oledInit();
oledShowLogo();
// Perform throttle self-check and configure NRF24L01 power mode
throttleSelfCheck();
// Set up low-power mode if necessary
lowPowerModeConfig();
}2. loop()
The main loop that continuously runs during operation. It handles the display updates, signal strength checks, and key events.
void loop() {
// Handle clock alarms and time display on the OLED
handleClockAlarm();
// Update OLED display with throttle values and battery percentage
displayThrottleValues();
displayBatteryLevel();
// Update signal strength display
updateSignalStrength();
// Check for key events and menu navigation
keyEventHandle();
// Handle menu events, if any
menuEventHandle();
// Small delay to avoid constant polling
delay(50);
}3. keyEventHandle()
Handles user input through key presses. This function updates throttle settings and processes navigation within the menu.
void keyEventHandle() {
if (isKeyPressed(KEY_LEFT)) {
// Adjust throttle channel for left-hand throttle
adjustThrottleLeft();
}
if (isKeyPressed(KEY_RIGHT)) {
// Adjust throttle channel for right-hand throttle
adjustThrottleRight();
}
// Update OLED display with new throttle or menu setting
oledRefresh();
// Save user data or preferences (e.g., throttle setting)
saveUserDataToFlash();
}4. addSignalStrengthSample()
Adds a new sample to the signal strength buffer and maintains a moving average of signal strength.
void addSignalStrengthSample(int newSignalStrength) {
// Add new signal strength to the sample buffer
signalStrengthBuffer[sampleIndex] = newSignalStrength;
// Update sample index for circular buffer
sampleIndex = (sampleIndex + 1) % SIGNAL_STRENGTH_BUFFER_SIZE;
}5. getAverageSignalStrength()
Calculates the moving average of the signal strength based on the collected samples.
int getAverageSignalStrength() {
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < SIGNAL_STRENGTH_BUFFER_SIZE; i++) {
sum += signalStrengthBuffer[i];
}
return sum / SIGNAL_STRENGTH_BUFFER_SIZE;
}6. displaySignalIcon()
Displays the signal strength icon on the OLED based on the signal strength percentage.
void displaySignalIcon(int signalStrengthPercent) {
if (signalStrengthPercent >= 75) {
oledDrawIcon(iconSignal100);
} else if (signalStrengthPercent >= 50) {
oledDrawIcon(iconSignal75);
} else if (signalStrengthPercent >= 25) {
oledDrawIcon(iconSignal50);
} else if (signalStrengthPercent > 0) {
oledDrawIcon(iconSignal25);
} else {
oledDrawIcon(iconSignalOff);
}
}
7.NRF24L01 Initialization
Initializes the NRF24L01 module and sets it in transmit mode.
void nrf24l01InitAndCheck() {
// Initialize NRF24L01
if (nrf24l01Init() == NRF_OK) {
// Set NRF24L01 to transmit mode
nrf24l01SetModeTX();
} else {
// Handle NRF24L01 error by beeping and showing error message
beepError();
oledShowErrorMessage("NRF24L01 ERROR");
}
}
8.Sending Data Packets: sendDataPacket()
This function creates a 32-byte data packet and sends it using the NRF24L01 module. The packet contains a data header and channel values (PWM data).
u8 sendDataPacket(void)
{
u8 chPacket[32]; // Array to hold the data packet
u16 t = 0;
u8 sendIsOK; // Flag to check if sending is successful
for (t = 0; t < 16; t++)
{
if (t == 0) // Add data header (0x00)
{
chPacket[2 * t] = 0x00;
chPacket[2 * t + 1] = 0x00;
}
else if (t <= chNum) // Add PWM channel data
{
chPacket[2 * t] = (u8)(PWMvalue[t - 1] >> 8) & 0xFF; // High byte of 16-bit PWM value
chPacket[2 * t + 1] = (u8)PWMvalue[t - 1] & 0xFF; // Low byte of 16-bit PWM value
}
else // Fill unused bytes with 0xFF (padding)
{
chPacket[2 * t] = 0xFF;
chPacket[2 * t + 1] = 0xFF;
}
}
sendIsOK = NRF24L01_TxPacket(chPacket); // Transmit the packet
return sendIsOK; // Return status of the transmission (success or failure)
}
9.Signal Strength Calculation: getSignalStrength()
This function measures the signal strength by sending multiple packets and calculating the percentage of successful transmissions.
int getSignalStrength(void)
{
const int totalPackets = 40; // Total number of packets to send
int successfulPackets = 0; // Counter for successful transmissions
if (setData.NRF_Mode == ON) // If the NRF mode is ON
{
NRF24L01_TX_Mode(setData.NRF_Power); // Set NRF to transmit mode
}
else
{
NRF24L01_LowPower_Mode(); // Otherwise, set it to low-power mode
}
// Loop to send multiple packets
for (int i = 0; i < totalPackets; i++)
{
if (sendDataPacket() == TX_OK) // If the packet was sent successfully
{
successfulPackets++; // Increment success counter
}
delay_us(700); // Short delay between transmissions
}
// Calculate signal strength as a percentage of successful packets
int signalStrength = (successfulPackets * 100) / totalPackets;
return signalStrength;
}
10. updateSignalStrength()
Updates the signal strength display and checks if the receiver is connected. It also adds a new sample to the signal strength buffer.
void updateSignalStrength() {
// Get current signal strength from NRF24L01
int currentSignalStrength = nrf24l01GetSignalStrength();
// Add the sample to the signal strength buffer
addSignalStrengthSample(currentSignalStrength);
// Calculate the average signal strength
int avgSignalStrength = getAverageSignalStrength();
// Display the corresponding signal strength icon
displaySignalIcon(avgSignalStrength);
// Check if receiver is connected
if (avgSignalStrength > SIGNAL_STRENGTH_THRESHOLD) {
receiverConnected();
} else {
receiverDisconnected();
}
}
11. menuEventHandle()
Handles the user interface menu and responds to user input for changing settings.
void menuEventHandle() {
// Check if a specific menu item is selected
if (isMenuItemSelected(MENU_ITEM_PWM_ADJUST)) {
adjustPWMSettings();
}
if (isMenuItemSelected(MENU_ITEM_CHANNEL_CALIBRATION)) {
calibrateChannels();
}
// Refresh OLED display with updated menu or settings
oledMenuRefresh();
}
12. Battery Voltage Display
Updates the battery level icon and percentage on the OLED based on the battery voltage.
void displayBatteryLevel() {
float batteryVoltage = readBatteryVoltage();
int batteryPercent = convertVoltageToPercentage(batteryVoltage);
// Display the battery icon and percentage on the OLED
oledDrawBatteryIcon(batteryPercent);
if (batteryVoltage < BATTERY_WARNING_THRESHOLD) {
// Beep to warn low battery
beepWarning();
}
}
13. Clock and Alarm Handling
Handles the clock and alarm functionality, beeping when an alarm is triggered.
void handleClockAlarm() {
// Check if the clock alarm is active
if (isAlarmActive()) {
// Beep if the alarm time is reached
beepAlarm();
// Display alarm icon on the OLED
oledDrawIcon(iconAlarm);
}
// Update the time on the OLED display
displayCurrentTime();
}
These functions represent the core operations of the system, which handles initialization, user input, signal strength monitoring, display updates, and more. Each function focuses on a specific aspect of the overall operation, making the code more modular and easier to manage.
Firmware Uploading
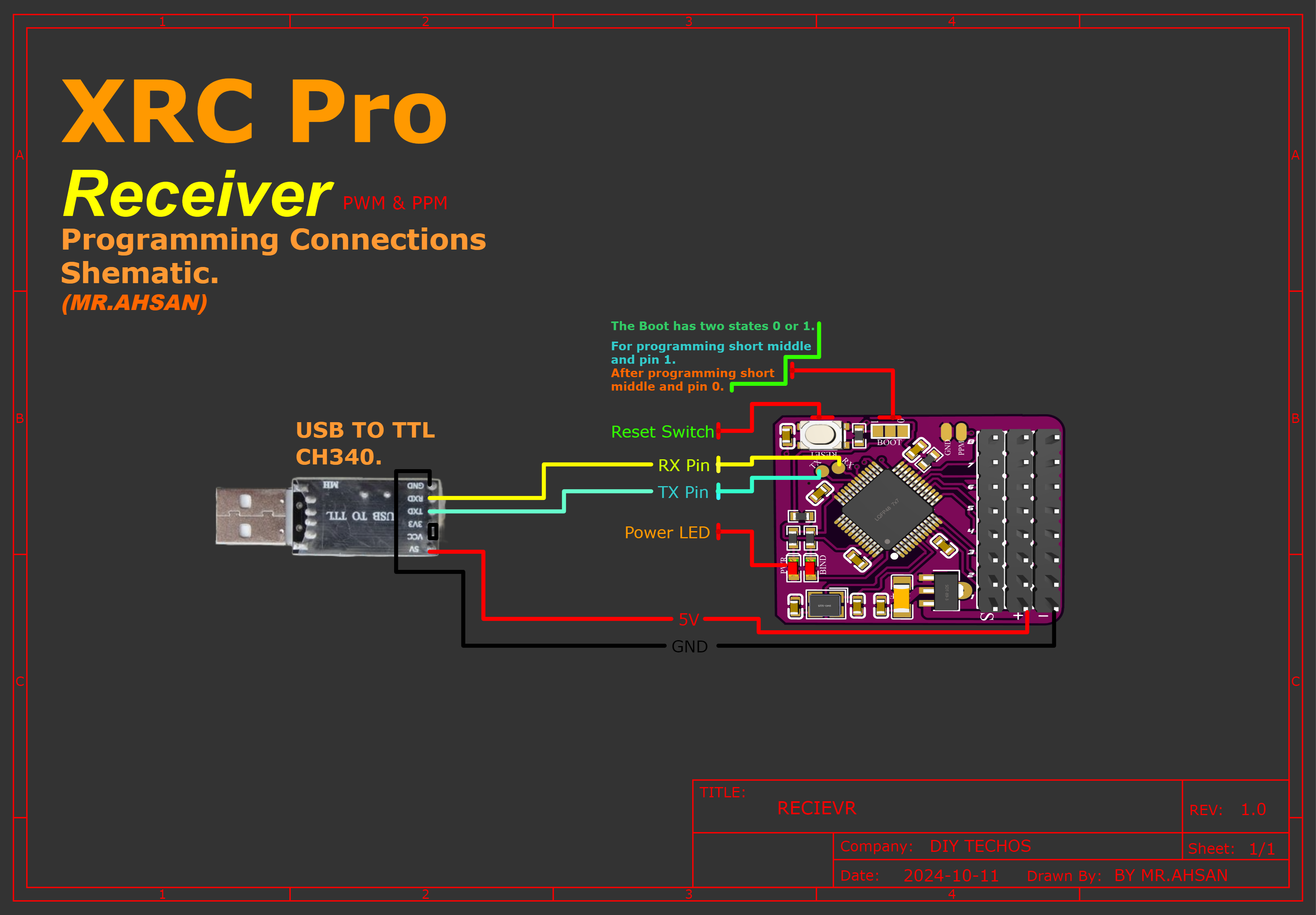
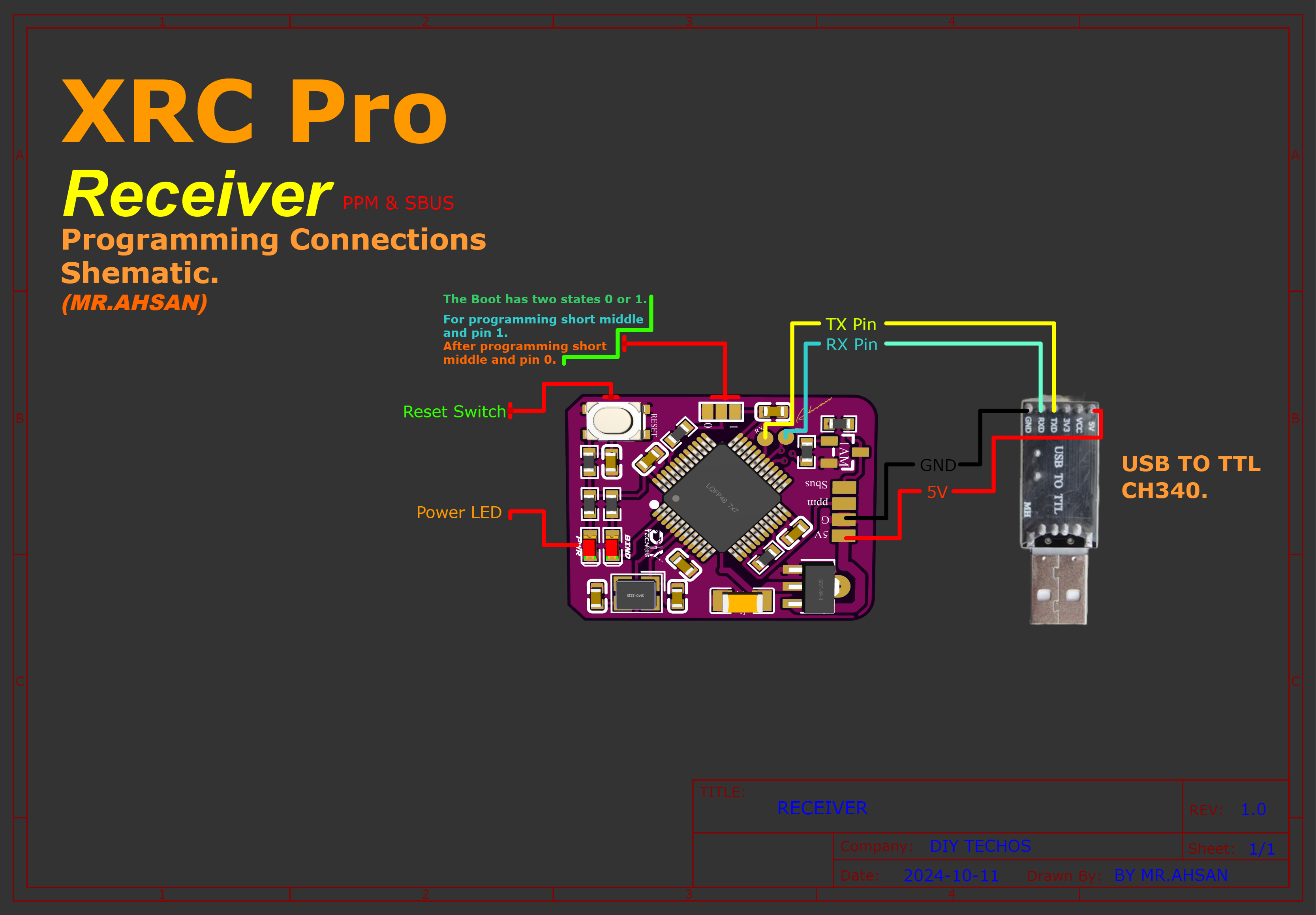
To upload the firmware to the transmitter and receivers, follow the connection diagram below. It shows how I connected the CH340 USB-to-TTL adapter to both the transmitter and receivers.
Connections
Transmitter
There are two methods of uploading code into transmitter.First,you can directly upload the code via USB TYPE-C Interface. Second,you can upload the code with the help of USB to TTL (ch340 driver).

Rceiver(PWM+PPM)
Receiver(PPM+SBUS)
Software
Download and install the STMicroelectronics Flash Loader Demonstrator software: Click to download
Steps
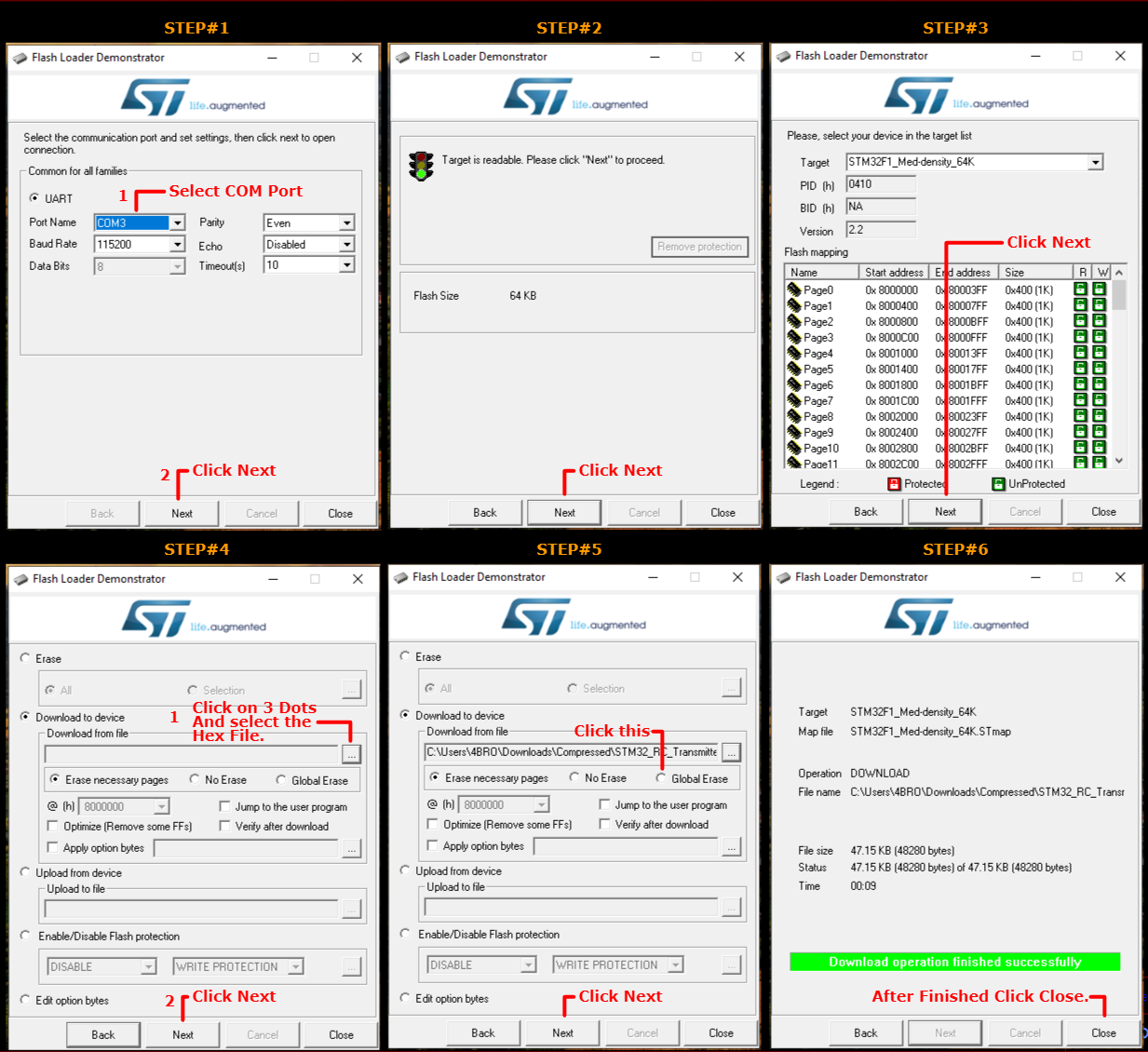
Follow:
- Plug the USB serial converter into the PC.
- Press the reset button on the STM32 board.
- Select the COM port in the software.
- Click 'Next,Next and Next.
- Select Download to device.Click on 3 dots and select the hex file.
- Select Global Erase.After that Click on Next
- Within 15 seconds, the code will be uploaded to the device.
- After finsihed.Click Close.