Story
Although it was difficult for me to create a brand-new gift card design while paying homage to the classic Christmas theme, I decided to design my Christmas gift card in the hope of making my version remain functional and stylish throughout its shelf life while emanating the joyous reminiscences of Christmas. To make this gift card behave more than a vivid Christmas ornament, I designed it as a fully functional remote home automation interface for observing ambient weather and air quality information.
Since I wanted to design a feature-packed gift card, I developed a mobile application (Android) to control the gift card's modes and features over Bluetooth. Thus, I added an HC-06 Bluetooth module to enable Bluetooth connectivity.
To obtain weather information precisely, I utilized a BMP180 sensor (barometric pressure/temperature/altitude) and a DHT11 sensor (temperature/humidity). To detect ambient air quality accurately, I used an MQ-135 air quality sensor providing a wide detecting scope with high sensitivity, including NH3, NOx, alcohol, benzene, smoke, CO2, etc.
To build a joyous and interactive gift card, I also connected an ST7789 IPS display and an RGB LED to Arduino Nano, which performs as the eye of the snowman.
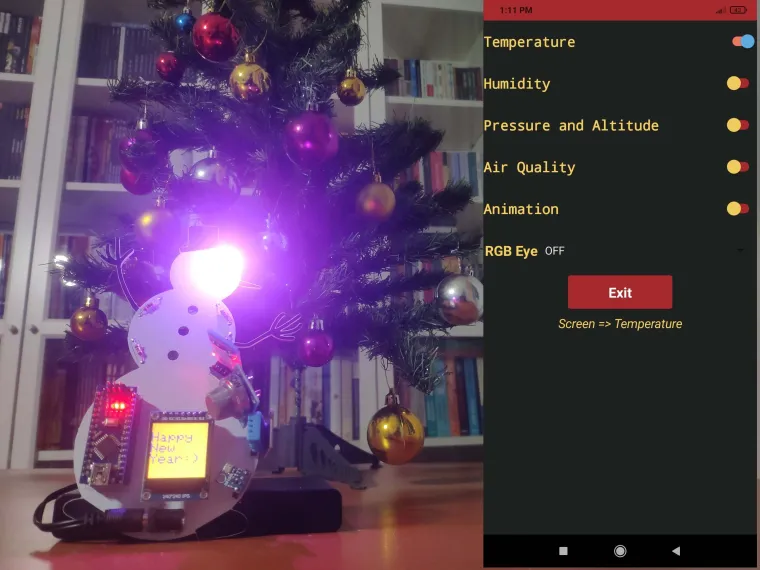
Thanks to the complementary mobile application, the gift card has six different modes (screens), providing the user with informative and festive home automation features:
- Temperature
- Humidity
- Pressure and Altitude
- Air Quality
- Animation
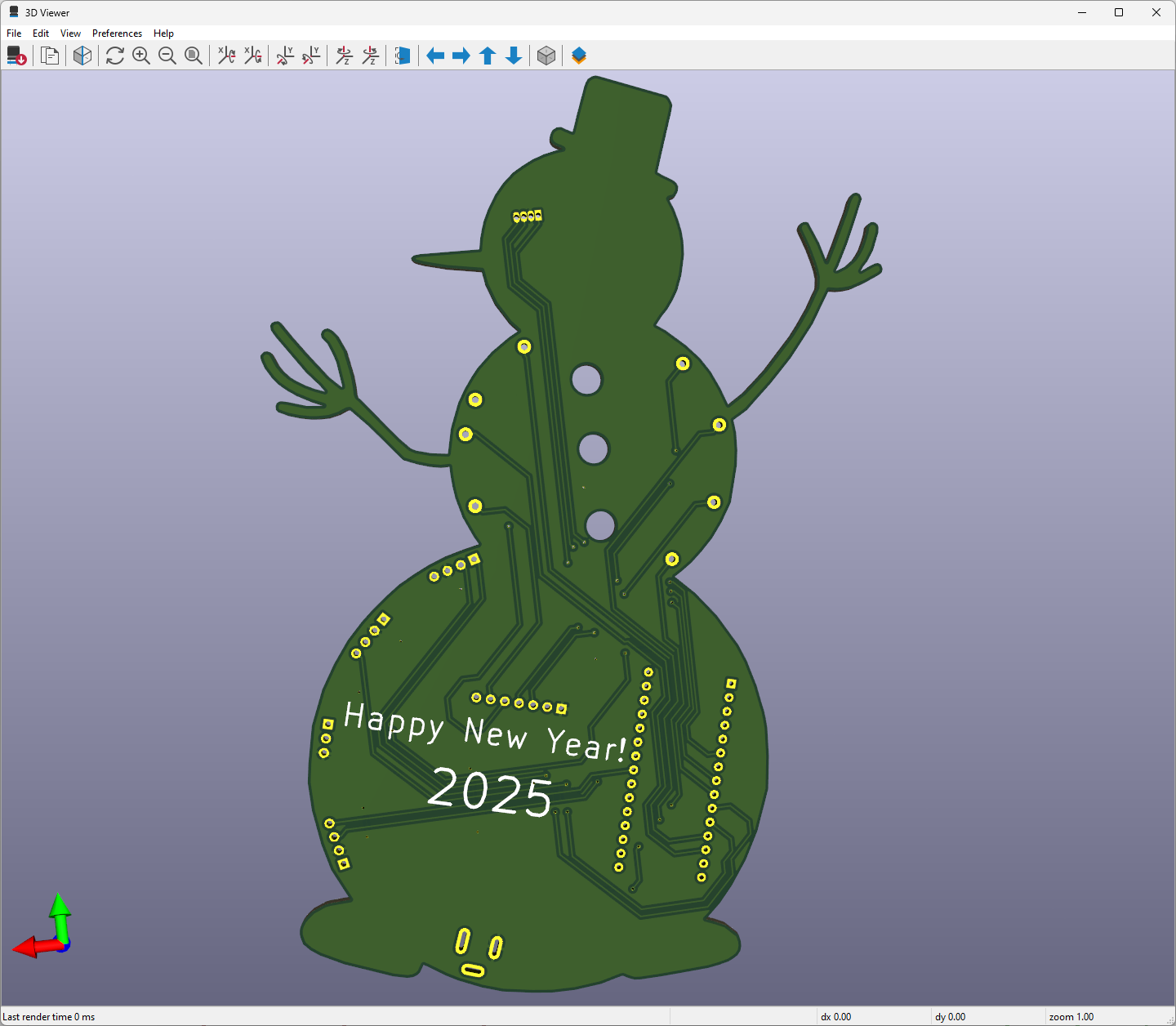
- Home Screen (Happy New Year)
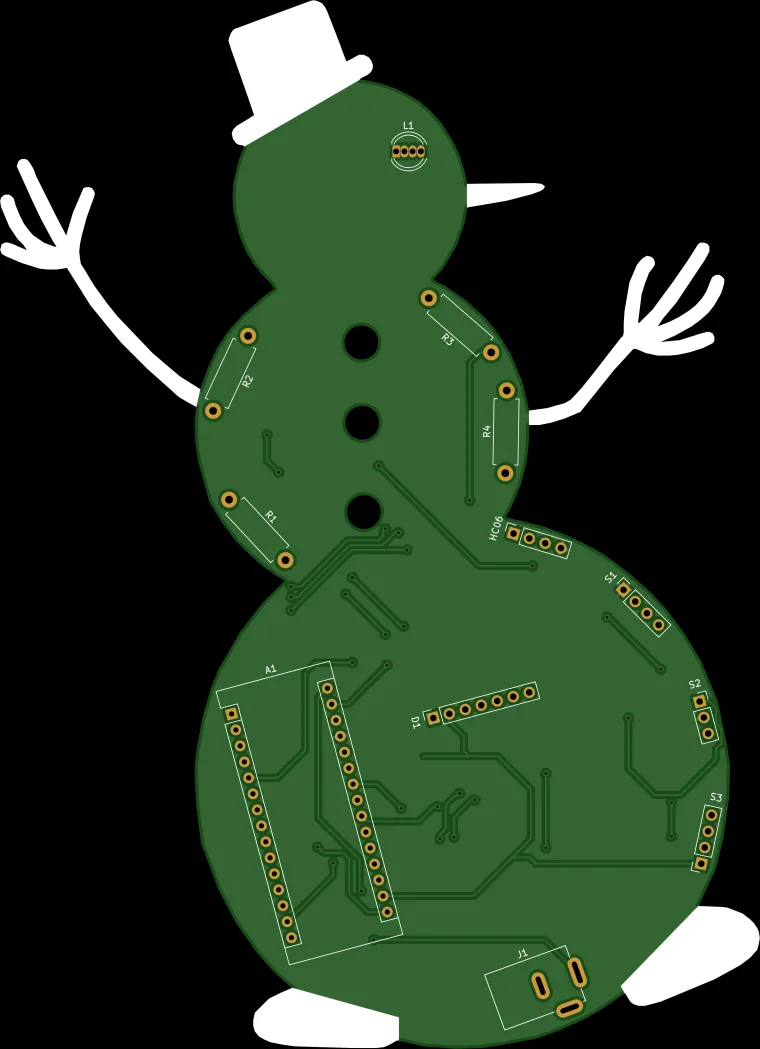
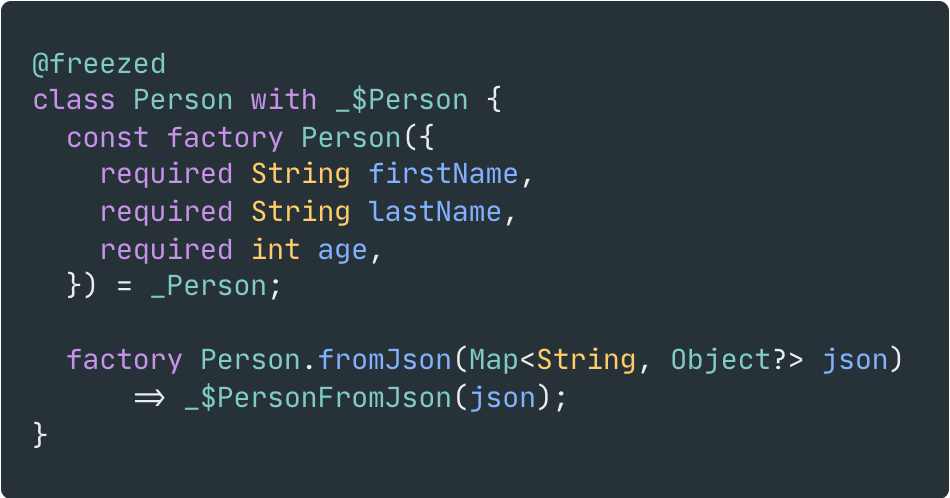
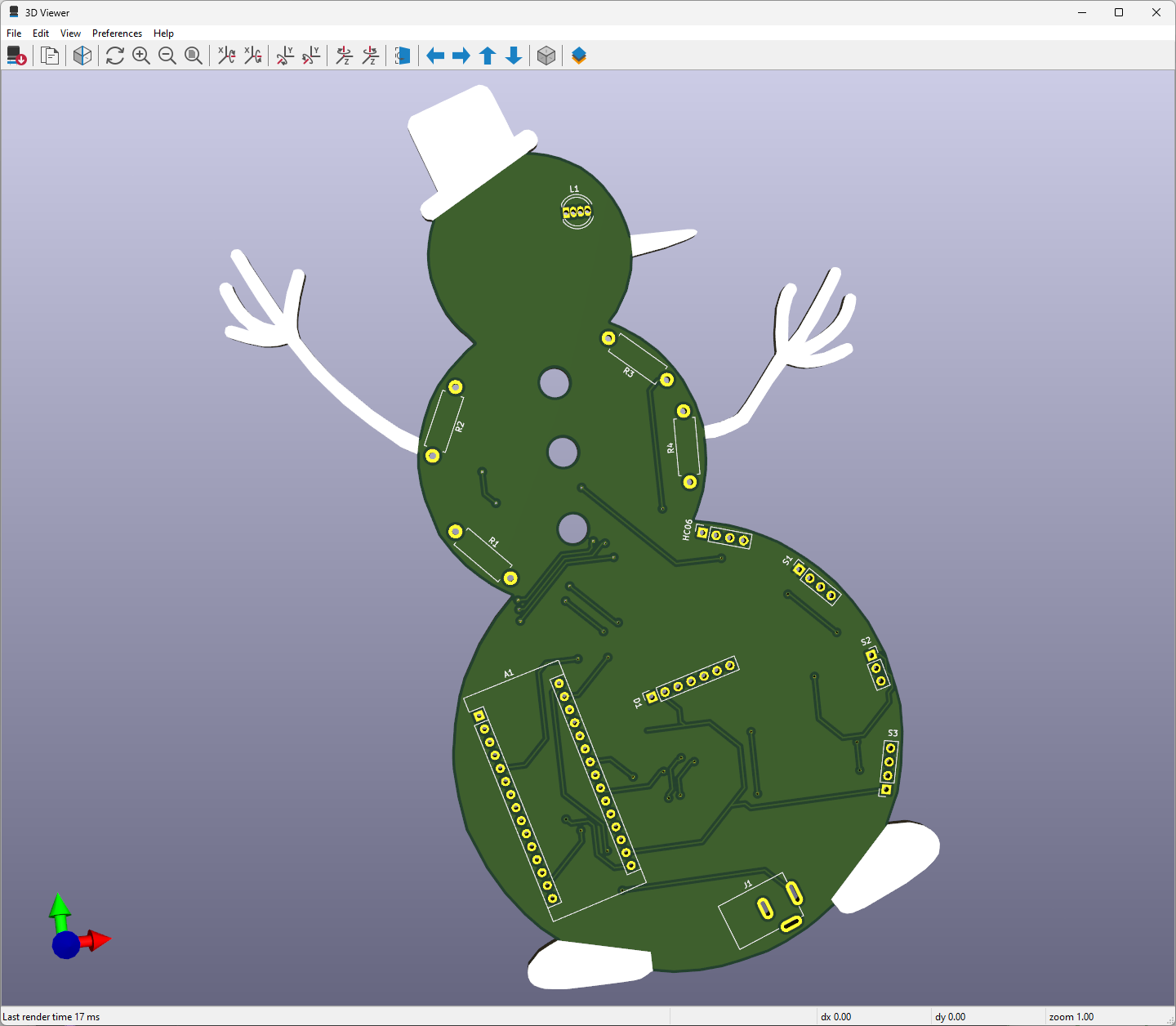
After testing and preparing electronic components, I designed a unique snowman-inspired PCB to create an intriguing yet familiar gift card layout for the New Year 🎄☃️🎅
Since I considered this project as a potential Christmas gift, I tried to keep components as ubiquitous and straightforward as possible to make the assembly process simple, even for electronic novices and beginners 🤖

Step 0: PCB modifications for 2025
Since I designed this project in 2020, the snowman-inspired PCB has been conveying the New Year message for 2021. Thus, I modified the snowman-inspired PCB to display the message for 2025.
I also added the older PCB version Gerber file below if you want to inspect the original design.
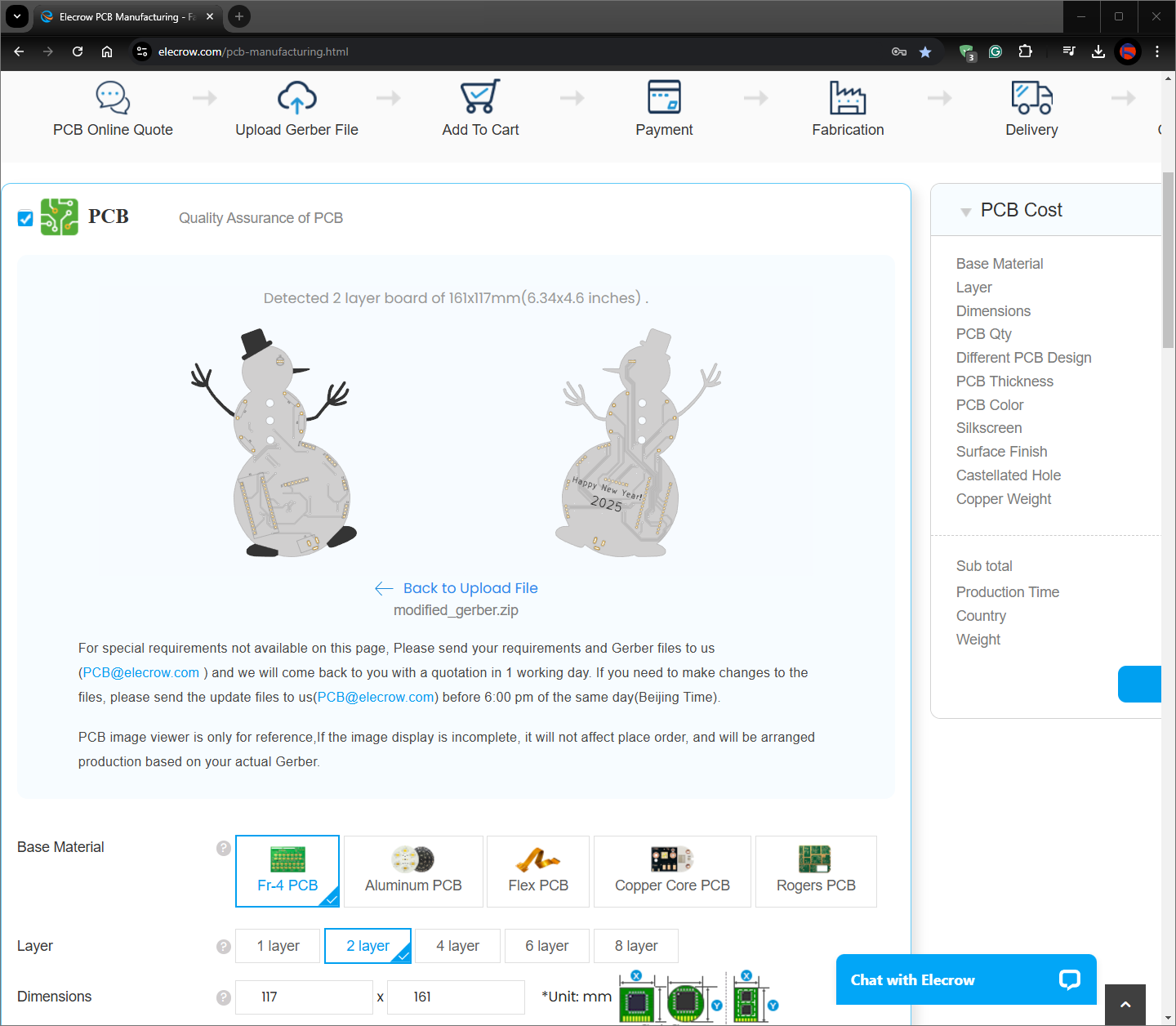
Step 1: Designing and Soldering the Snowman Gift Card PCB
Primarily, I tested all connections and modules with the Arduino Nano on the breadboard.

Then, I designed the Snowman Gift Card PCB by utilizing KiCad. You can order the snowman-inspired PCB directly from Elecrow to create a stylish and feature-rich snowman gift card to give your friends or family 🎁


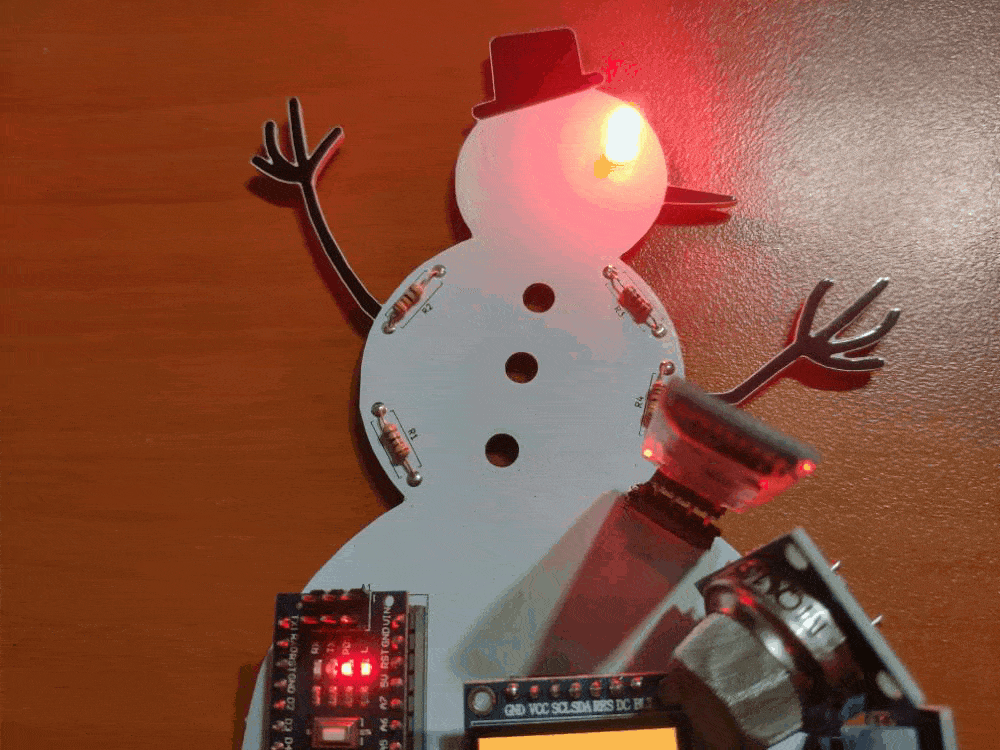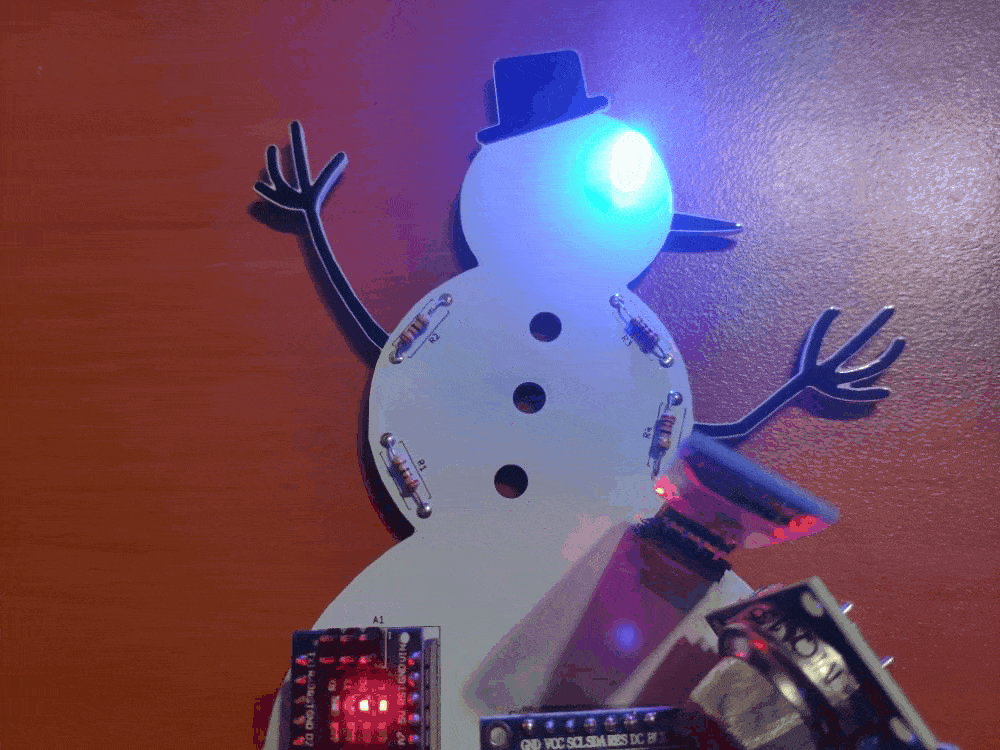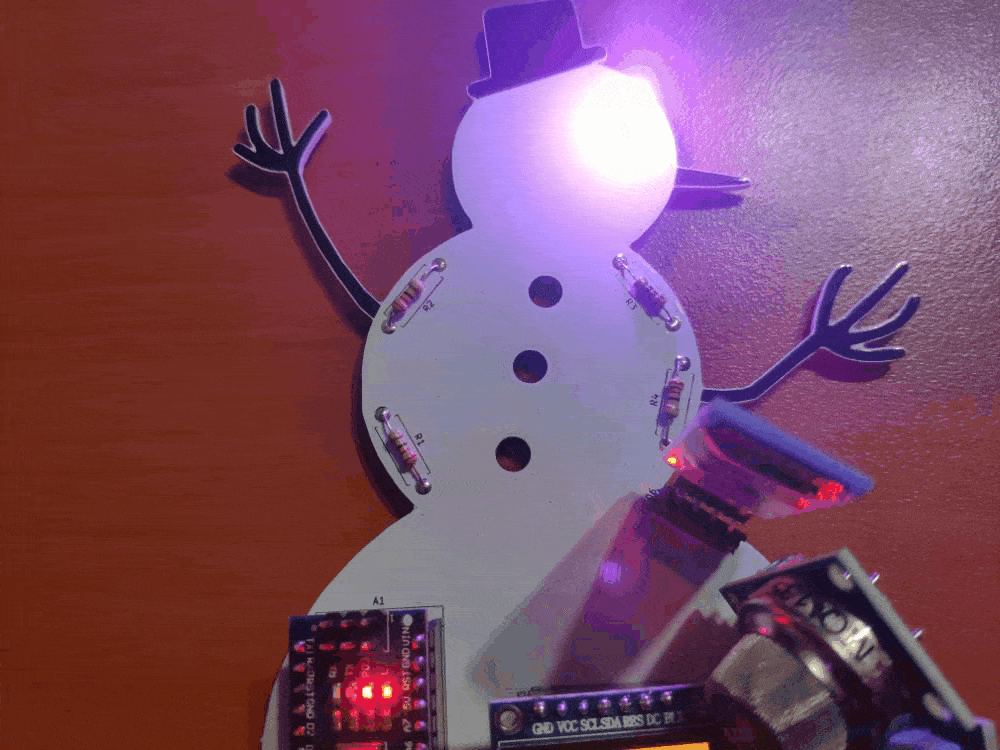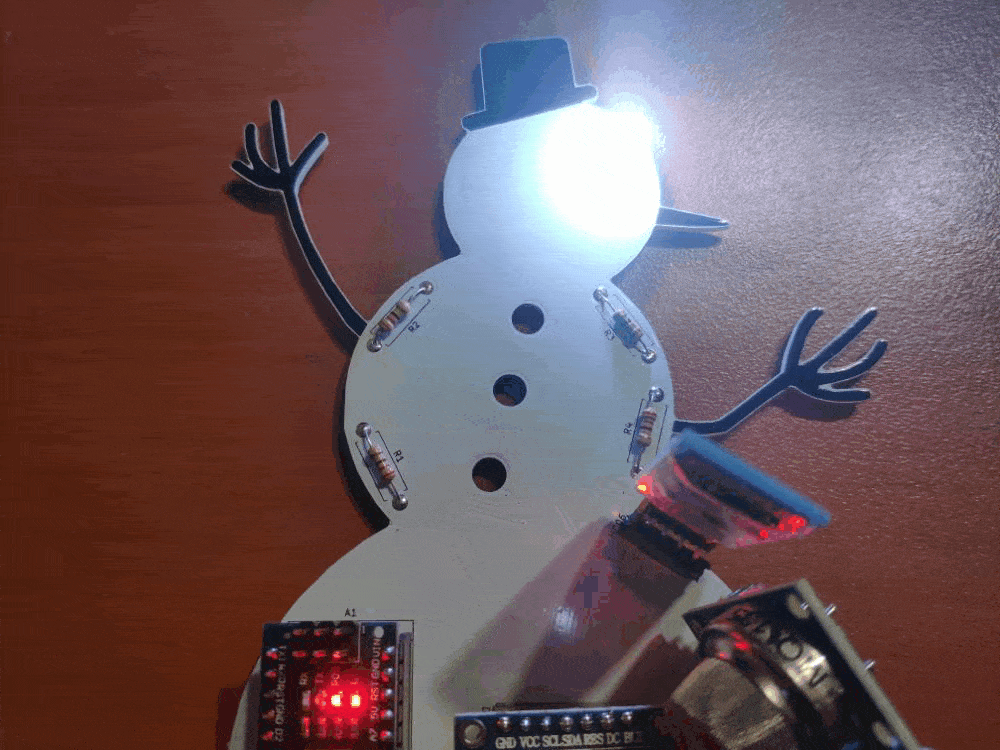
First of all, by using a soldering iron, I attached headers (female), 5mm RGB common cathode LED, 220Ω resistors, and the power jack.
Component list on the PCB:
A1 (Headers for Arduino Nano)
D1 (Headers for ST7789 240x240 IPS)
HC06 (Headers for HC-06 Bluetooth Module)
S1 (Headers for MQ-135 Air Quality Sensor)
S2 (Headers for DHT11 Temperature/Humidity Sensor)
S3 (Headers for BMP180 Barometric Pressure/Temperature/Altitude Sensor)
R1, R2, R3, R4 (220Ω Resistor)
L1 (RGB Common Cathode)
J1 (Power Jack)



Step 2: Developing the Gift Card Android application on the MIT APP Inventor 2
I chose to use the MIT APP Inventor 2 to create the Gift Card Android application due to its easy-to-use designer interface with drag and drop editor for simple functions. MIT App Inventor is a web application integrated development environment provided by Google and now maintained by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
You can download the APK file (Gift_Card.apk) of the Gift Card Android application below to install it on your phone or send it to people you want to present this gift card.
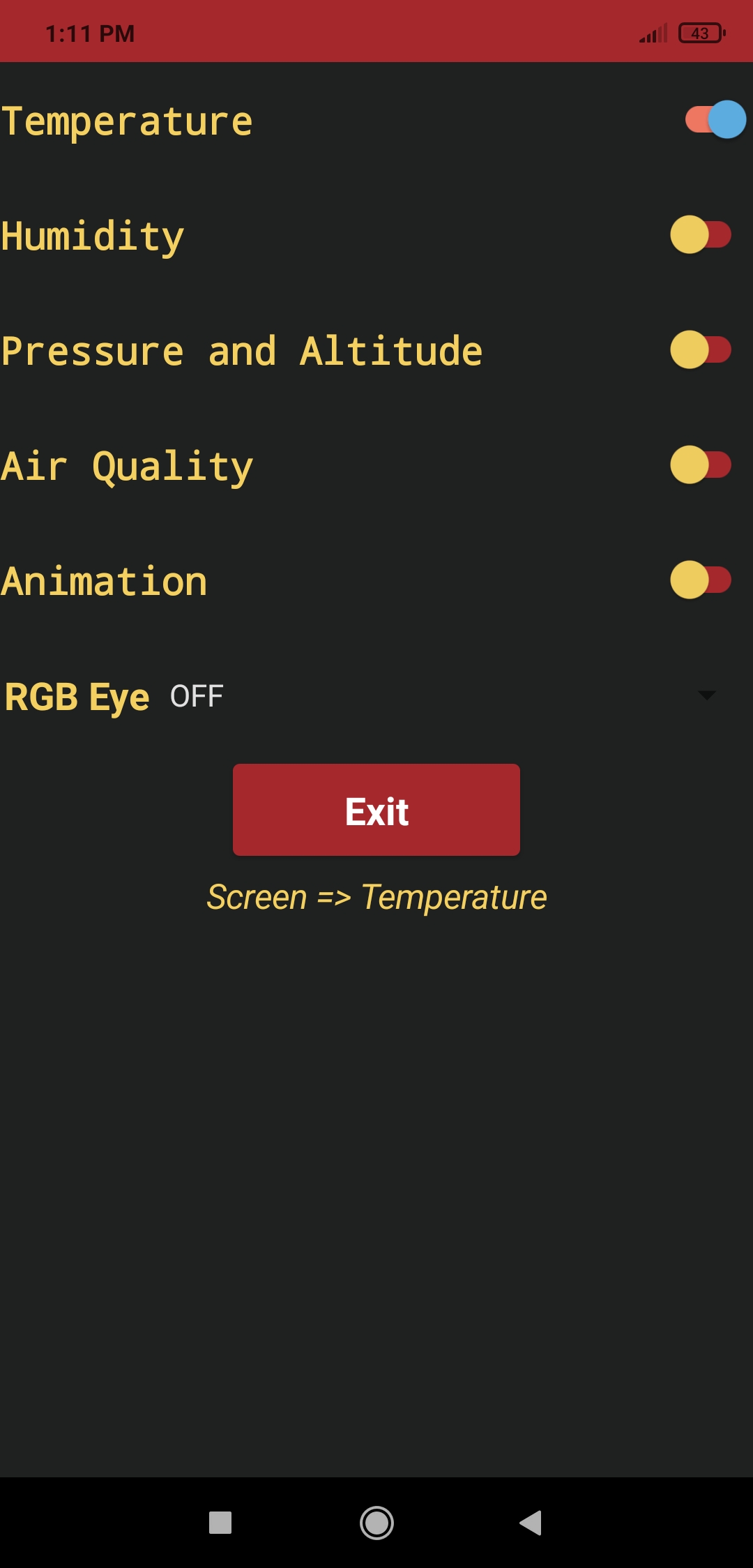
⭐ When installed, click the Connect button to view all paired Bluetooth devices.

⭐ Then, select the one named Gift Card (HC-06 Bluetooth Module) if not named differently by the user.

⭐ If the connection with the Snowman Gift Card PCB is successful after entering the given password (1234), the application prints Status: Connected. Otherwise, it prints Status: Error.

If you want to change the design of the application or view the source code to add new functions, follow the steps below:
⭐ Go to the home page of the MIT App Inventor 2 and click the Create Apps! button.
⭐ Then, import the aia file (Gift_Card.aia) of the application to the MIT App Inventor 2 to view the application settings and code.

⭐ The application has two screens, five switch buttons, one spinner, and one notification box. You can change their functions by using the Blocks editor.

Step 3: Programming Arduino Nano and setting up components
Download the required libraries to be able to control the modules:
BMP180 Barometric Pressure/Temperature/Altitude Sensor | Library
DHT11 Humidity and Temperature Sensor | Library
⭐ Include the required libraries.
⭐ Initiate the HC-06 Bluetooth Module. Connect the defined RX pin (7) to the TX pin on the Bluetooth module.
SoftwareSerial Gift_Card(7, 8); // RX, TX⭐ Define the BMP180 sensor settings.
Adafruit_BMP085 bmp;
double temperature, _altitude;
int pressure, pressure_sea;⭐ Define the DHT11 object.
DHT dht;
float humidity, temperature_DHT;⭐ Define the MQ-135 pin and RGB pins.
⭐ Define interface options - home, tem, hum, pres, air, ani.
⭐ Activate the Bluetooth module.
⭐ You can change the default settings of the HC-06 Bluetooth Module by uncommenting the changeBluetoothSettings() function - Name: Gift Card, Password: 1234, Baud Rate: 9600.
void changeBluetoothSettings(){
// Define the new settings.
String Name = "Gift Card";
String Password = "1234";
String Uart = "9600,0,0";
Gift_Card.print("AT+NAME"); // Change the name.
Gift_Card.println(Name);
Serial.print("Name is changed: ");
Serial.println(Name);
delay(2000);
Gift_Card.print("AT+PIN"); // Change the password.
Gift_Card.println(Password);
Serial.print("Password is changed: ");
Serial.println(Password);
delay(2000);
Gift_Card.print("AT+UART"); // Change the baud rate. If the bluetooth module is a HC-05, the default value of baud rate is 38400.
Gift_Card.println(Uart);
Serial.print("Baud rate is set: ");
Serial.println(Uart);
delay(2000);
Serial.println("Task Completed!"); // You can see in the terminal whether the task is completed correctly or not.
}
⭐ Check whether the BMP180 module is working.
⭐ Initiate the DHT11 Module.
⭐ In the Application_Commands() function, detect commands transferred by the Android Application (Gift Card).
void Application_Commands(){
// If the HC-06 Bluetooth module is receiving commands from the Android application:
if(Gift_Card.available()){
char c = Gift_Card.read();
// Execute the requested command:
switch(c){
case 'h':
// Home Screen
home = true;
tem = false;
hum = false;
pres = false;
air = false;
ani = false;
break;
case '1':
// Temperature
home = false;
tem = true;
hum = false;
pres = false;
air = false;
ani = false;
break;
case '2':
// Humidity
home = false;
tem = false;
hum = true;
pres = false;
air = false;
ani = false;
break;
...⭐ Execute the requested command - home, tem, hum, pres, air, ani.
if(home == true){
tft.fillScreen(RGBto565(248, 178, 41));
while(home == true){
Application_Commands();
// Homescreen
tft.setCursor(0, 40);
tft.setTextColor(RGBto565(22, 21, 118));
tft.setTextSize(6);
tft.println("Happy");
tft.println("New");
tft.println("Year:)");
}
}
if(tem == true){
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
while(tem == true){
Application_Commands();
// Collect data from the sensors - BMP180, DHT11, and MQ-135.
collect_Data();
// Print:
tft.setCursor(54, 0);
tft.setTextColor(RGBto565(255,69,0), BLACK);
tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.print(F("Temperature"));
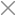
tft.fillCircle(120, 80, 40, WHITE);
tft.drawImageF(104, 64, 32, 32, temp);
tft.setCursor(40, 145);
tft.setTextSize(4);
tft.print((String)temperature + "*C");
tft.setCursor(40, 185);
tft.print((String)temperature_DHT + "*F");
}
}
if(hum == true){
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
while(hum == true){
Application_Commands();
// Collect data from the sensors - BMP180, DHT11, and MQ-135.
collect_Data();
// Print:
tft.setCursor(70, 0);
tft.setTextColor(BLUE, BLACK);
tft.setTextSize(2);
tft.print(F("Humidity"));
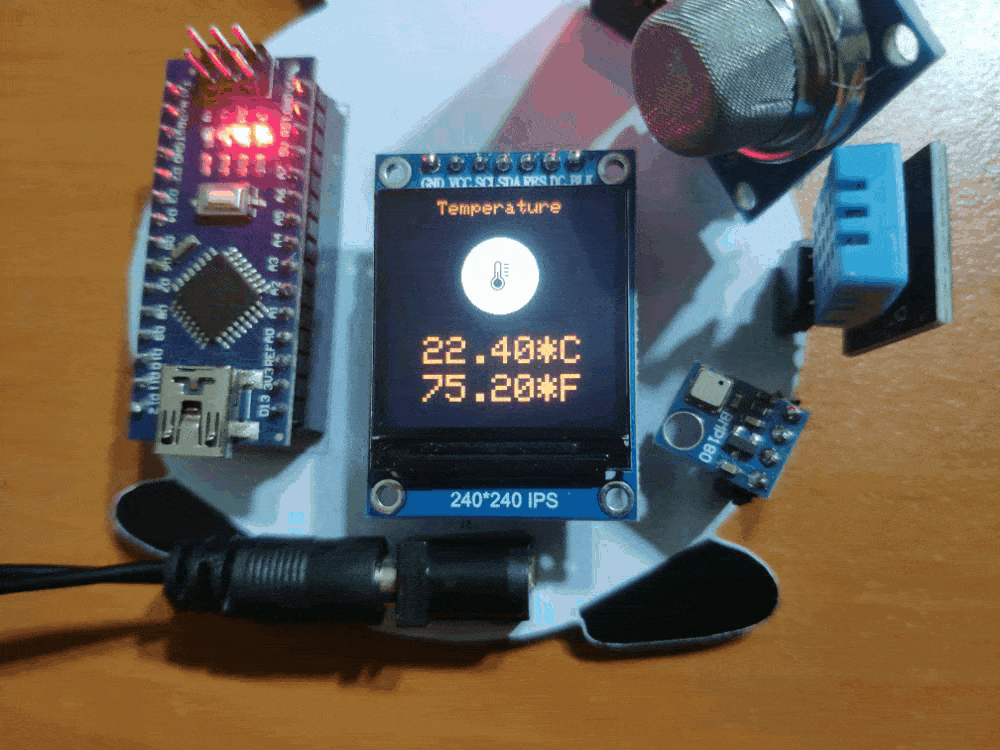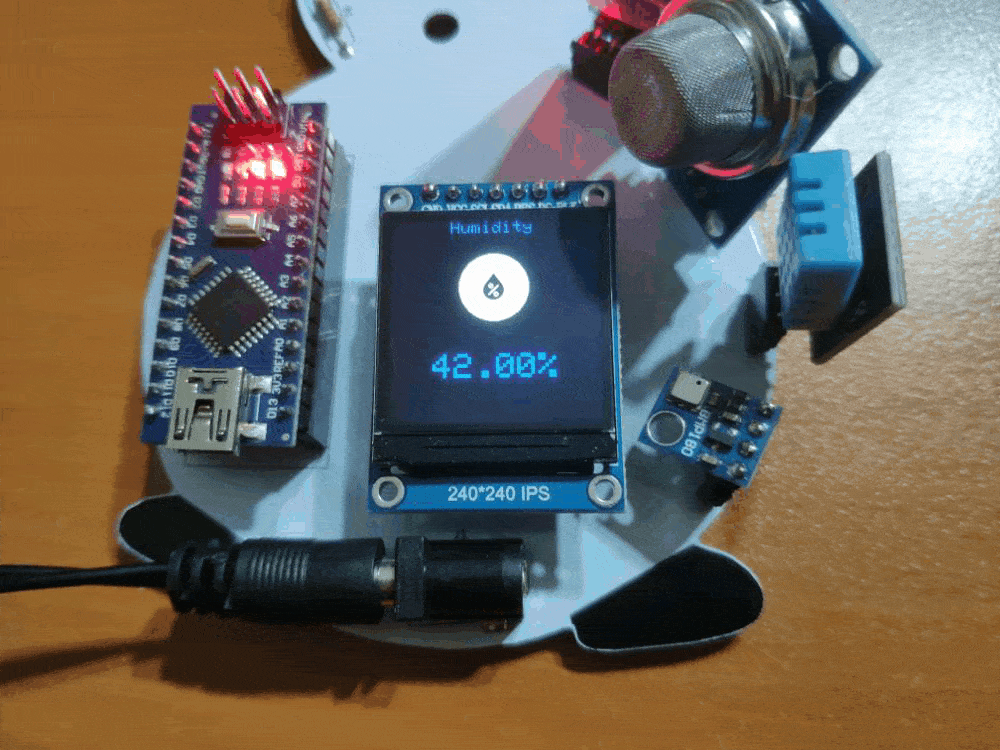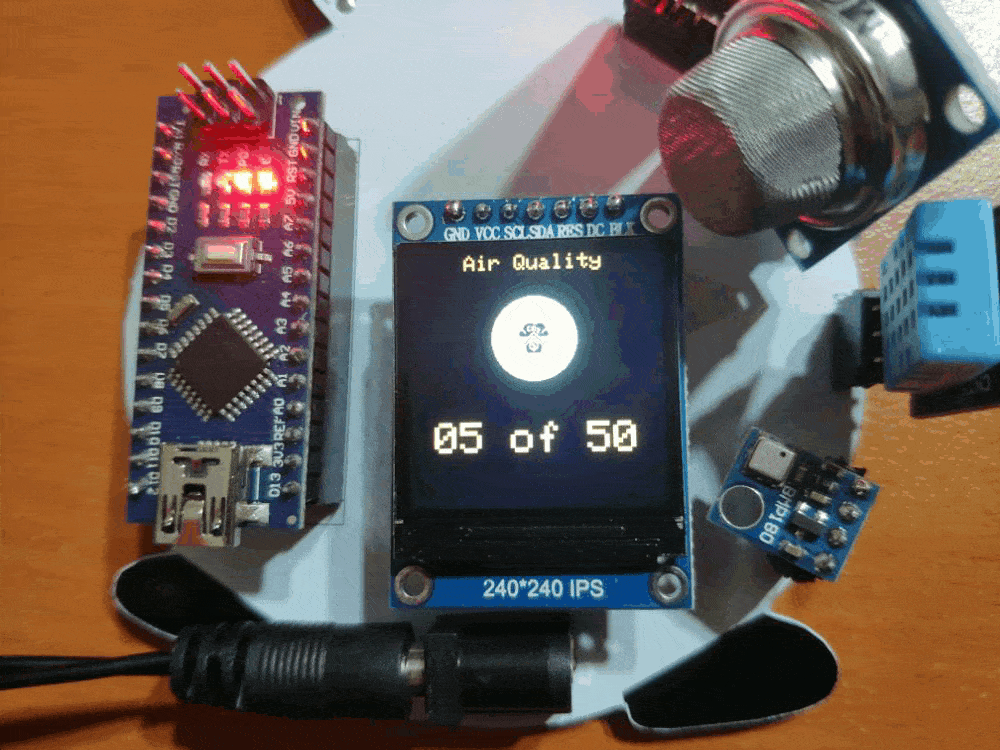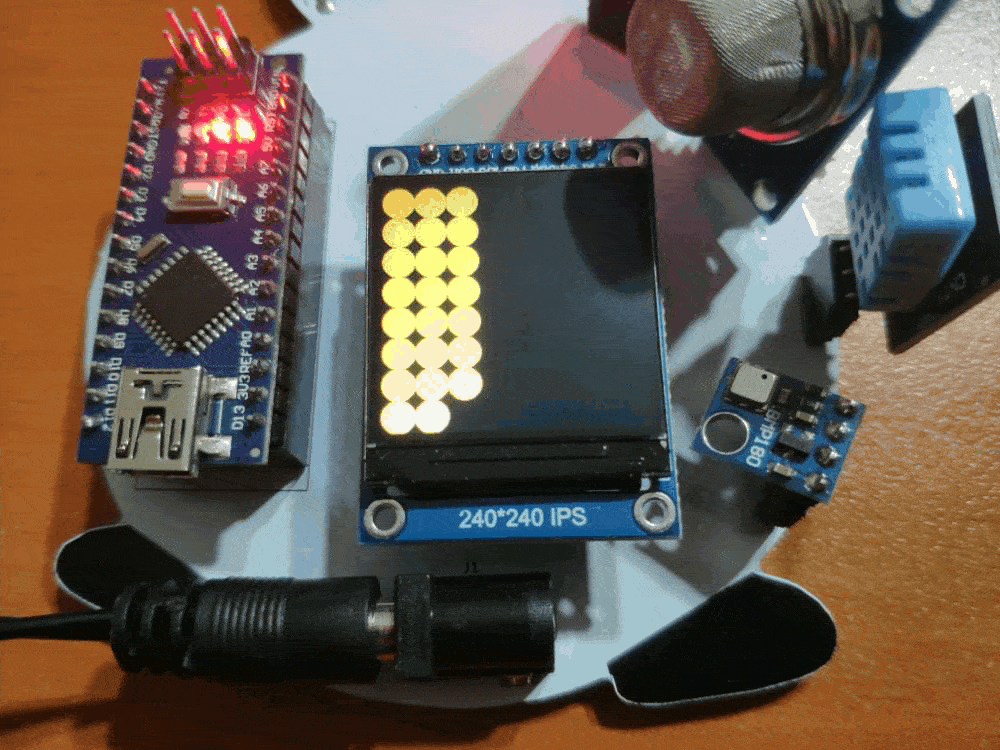
tft.fillCircle(120, 80, 40, WHITE);
tft.drawImageF(104, 64, 32, 32, humd);
tft.setCursor(50, 160);
tft.setTextSize(4);
tft.println((String)humidity + "%");
}
}
...⭐ In the collect_Data() function, get variables generated by BMP180, DHT11, and MQ-135.
⭐ Change the range of the air quality value (0 - 50) if your sensor readings differ.
void collect_Data(){
// Get variables generated by the BMP180 module.
temperature = bmp.readTemperature();
pressure = bmp.readPressure();
pressure_sea = bmp.readSealevelPressure();
// Calculate altitude assuming 'standard' barometric
// pressure of 1013.25 millibar = 101325 Pascal
_altitude = bmp.readAltitude();
// Get variables generated by the DHT11 module.
delay(dht.getMinimumSamplingPeriod());
humidity = dht.getHumidity();
temperature_DHT = dht.toFahrenheit(dht.getTemperature());
// Get variables generated by the MQ-135 sensor.
air_quality = map(analogRead(mq135), 0, 850, 0, 50);
}⭐ In the adjustColor() function, adjust the color of the RGB eye of the Snowman Gift Card PCB.
⭐ In the Animation() function, create an animation screen using filled circles.
void Animation(uint8_t radius, uint16_t color) {
int x, y, w = tft.width(), h = tft.height(), r2 = radius * 2;
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);
for(x=radius; x<w; x+=r2) {
for(y=radius; y<h; y+=r2) {
tft.fillCircle(x, y, radius, color);
delay(100);
// Halt animation if requested.
Application_Commands();
}
delay(100);
}
}




Step 3.1: Displaying images with the ST7789 240x240 IPS screen
Download the required libraries to be able to use the ST7789 240x240 IPS screen:
Arduino_ST7789_Fast | Library
Adafruit_GFX | Library
⭐ Define the ST7789 240x240 IPS display settings.
⭐ Initiate the ST7789 240x240 IPS display.
⭐ Open and clear the ST7789 240x240 IPS display.
#define TFT_DC 10
#define TFT_RST 9
#define SCR_WD 240
#define SCR_HT 240
...
Arduino_ST7789 tft = Arduino_ST7789(TFT_DC, TFT_RST);
...
tft.init(SCR_WD, SCR_HT);
tft.fillScreen(BLACK);⭐ Use the RGBto565() function to display RGB colors on the ST7789 as text and background color.
tft.fillScreen(RGBto565(248, 178, 41));
tft.setCursor(0, 40);
tft.setTextColor(RGBto565(22, 21, 118));
tft.setTextSize(6);
tft.println("Happy");
tft.println("New");
tft.println("Year:)");⭐ Convert the images you want to display on the ST7789 screen to.c files by using the image converter below:

⭐ You can download the converted image files I used in this project in the Code - temp.c, humd.c, pre.c, and airq.c.
⭐ Include and print the converted images.
#include "temp.c"
#include "humd.c"
#include "pre.c"
#include "airq.c"
...
tft.drawImageF(104, 64, 32, 32, temp);
tft.drawImageF(104, 64, 32, 32, humd);
tft.drawImageF(104, 64, 32, 32, pre);
tft.drawImageF(104, 64, 32, 32, airq);
Connections and Adjustments
// Connections
// Arduino Nano :
// HC-06 Bluetooth Module
// D7 --------------------------- TX
// D8 --------------------------- RX
// 5V --------------------------- 5V
// GND --------------------------- GND
// ST7789 240x240 IPS
// GND --------------------------- GND
// 3.3V -------------------------- VCC
// D13 --------------------------- SCL
// D11 --------------------------- SDA
// D9 --------------------------- RES
// D10 --------------------------- DC
// BMP180 Barometric Pressure/Temperature/Altitude Sensor
// A4 --------------------------- SDA
// A5 --------------------------- SCL
// DHT11 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
// D2 --------------------------- S
// MQ-135 Air Quality Sensor
// A3 --------------------------- S
// RGB LED
// D3 --------------------------- R
// D5 --------------------------- G
// D6 --------------------------- BAfter finishing and uploading the code to the Arduino Nano, I attached all required components to the board via headers - HC-06 Bluetooth Module, ST7789 240x240 IPS Screen, BMP180 Barometric Pressure/Temperature/Altitude Sensor, DHT11 Humidity/Temperature Sensor, and MQ-135 Air Quality Sensor.

Modes and Features
🎄⛄ In default mode, when the Snowman Gift Card starts working, it displays the home screen showing Happy New Year :)

🎄⛄ When the user clicks the Temperature switch button in the Gift Card Android application, the gift card displays the temperature variables generated by BMP180 (°C) and DHT11 (°F).



🎄⛄ When the user clicks the Humidity switch button in the Gift Card Android application, the gift card displays the humidity variable generated by the DHT11 (%).



🎄⛄ When the user clicks the Pressure and Altitude switch button in the Gift Card Android application, the gift card shows the pressure and altitude variables generated by the BMP180 (Pa / m).



🎄⛄ When the user clicks the Air Quality switch button in the Gift Card Android application, the gift card shows the air quality variable generated by the MQ-135 from 0 (OK) to 50 (DANGER).



🎄⛄ When the user clicks the Animation switch button in the Gift Card Android application, the gift card displays the animation pattern with the filled circles in the loop until the user selects other modes.



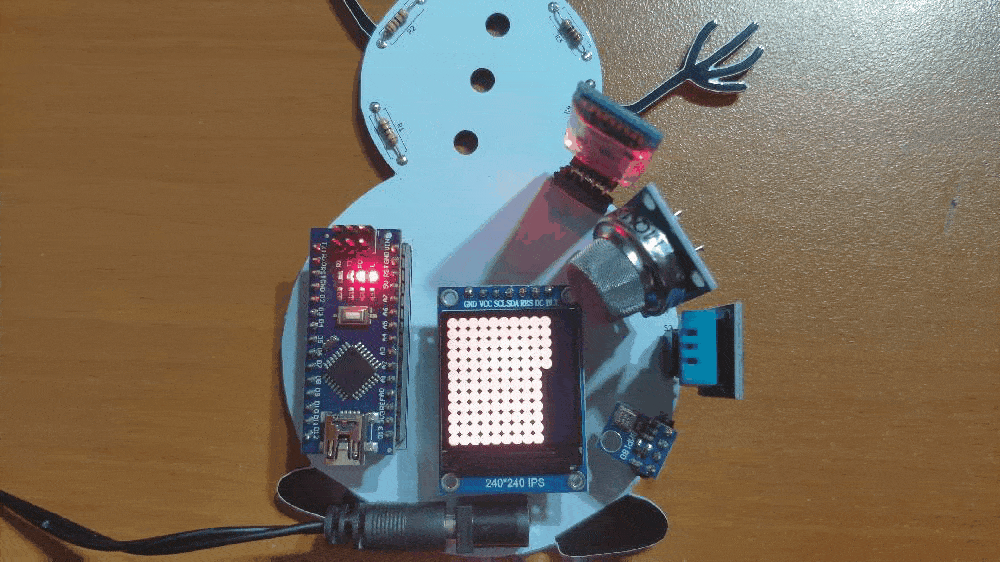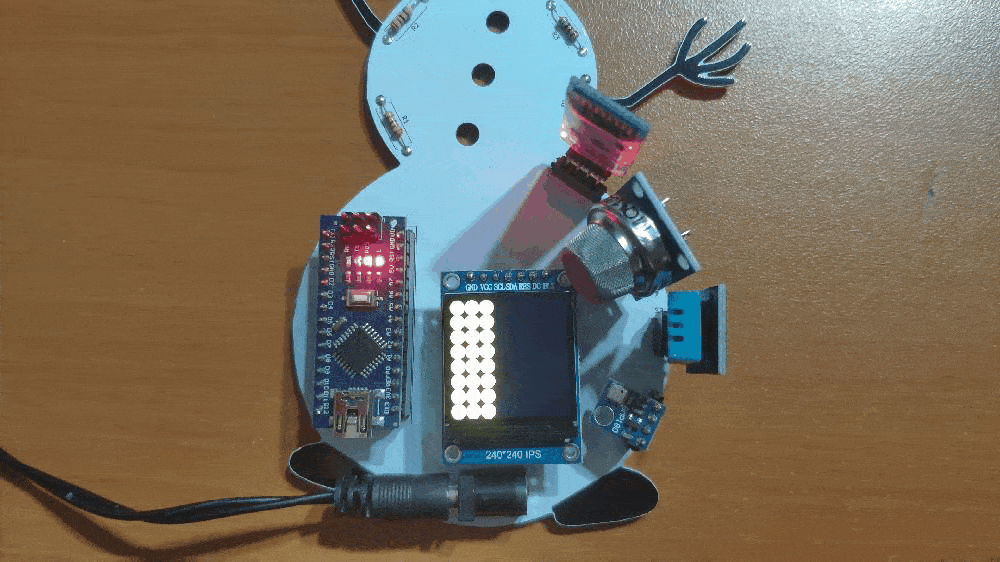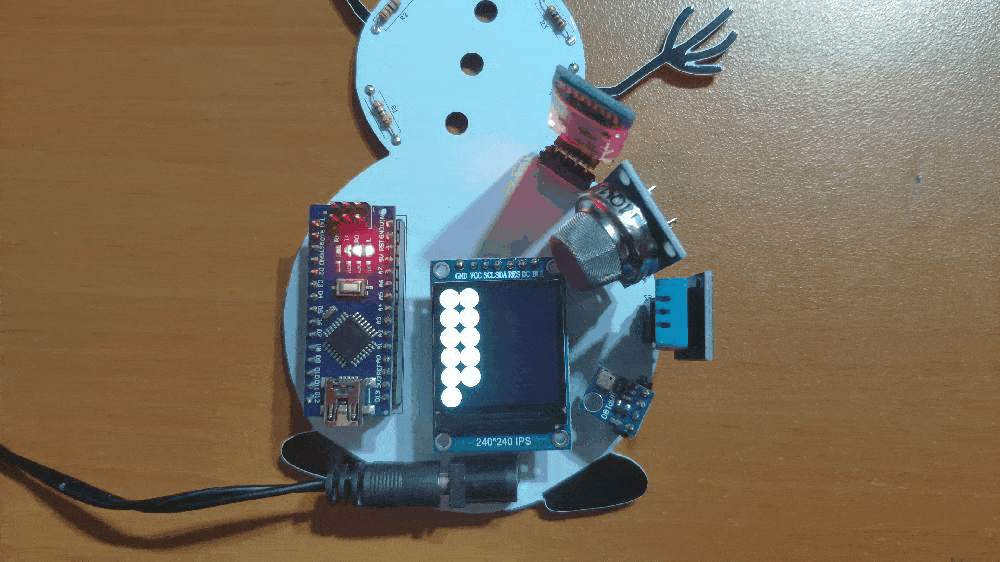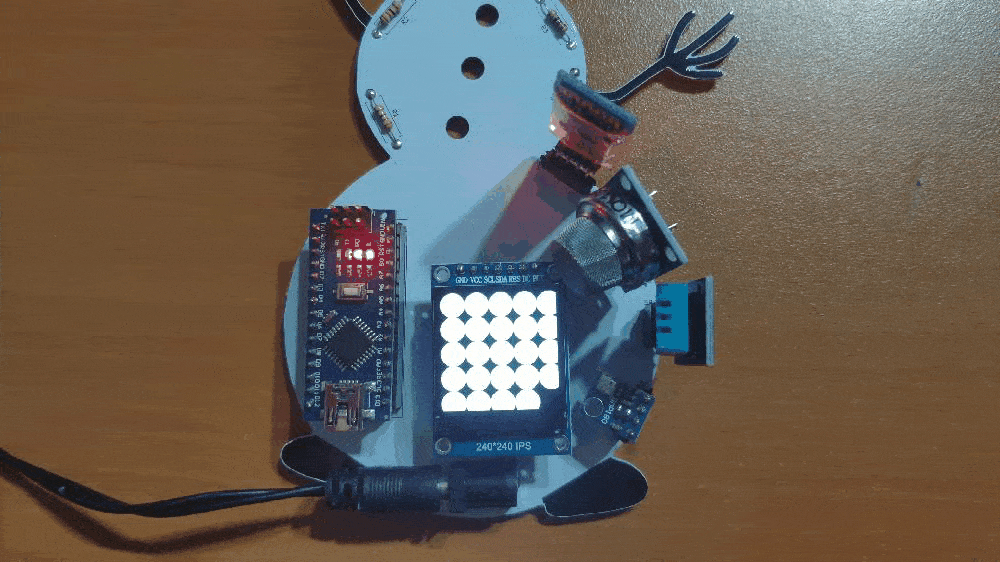
🎄⛄ The gift card adjusts the color of its RGB eye after the user selects any color option in the RGB Eye spinner in the Gift Card Android application:
- RED
- GREEN
- BLUE
- YELLOW
- PURPLE
- CYAN
- WHITE
- OFF (BLACK)





🎄⛄ If the user clicks the Exit button, the Android application shows the Disconnect notification box:
- Home Screen | Return to the home screen - Happy New Year :)
- OK | Close the application and disconnect Bluetooth!



Videos and Conclusion
After completing all the steps above, I placed the Snowman Gift Card PCB as an ornament under my Christmas tree, waiting for commands from its Android application to run the requested modes. As well as being an entertaining decoration, it functions as an impressive home automation interface :)