Everything you need to know about Protoboard
Everything you need to know about Protoboard
What is protoboard?
The Protoboard, also known as a breadboard, solderless breadboard, or terminal array board, is a type of building platform used to create semi-permanent prototypes of electronic circuits without soldering. Protoboards can be used over and over again because they don't need to be soldered or have their tracks destroyed, which is completely different from a stripboard (veroboard). As a result, Protoboards are widely used by electronics hobbyists, novice engineers such as students, and professionals to quickly build and test electronic circuits.
Protoboards typically come with a plastic base with a grid of holes for inserting electronic components and wires. The holes are typically arranged in rows and columns, with power rails on the sides for connecting power and ground before finalizing a design on a more permanent circuit board. Protoboards are an essential and convenient tool for anyone working with electronics.
As with standard 0.1" spaced breadboards, Protoboards work similarly. They typically have two power lines at the top and bottom, and each is usually connected all the way down the board's length. The images below show how copper connections are connected to the PCB design and how these correspond to the finished boards. The central gap allows for mounting/using IC chips. On both sides of the central gap are vertically connected rows, which allows for the installation of IC chips.
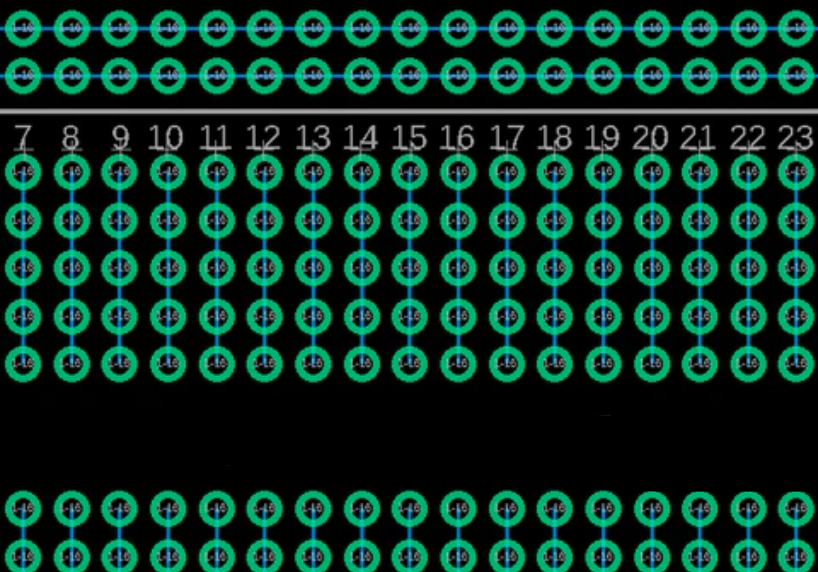
To ensure that the components are placed correctly on the board, it's important to understand the pinout of the components being used, just like when using a Protoboard, with a larger more complex circuit, one incorrect piece of wiring can cause a circuit to fail.
What is Veroboard?
In 1961, The Vero electronics department first used Veroboard for prototyping. Protoboards do not require soldering and are reusable, but Veroboard requires soldering.
Often referred to as a "strip board" or "matrix board", Veroboard is an original prototyping board with copper-clad laminate or epoxy-based substrates, both single and double-sided models are available.
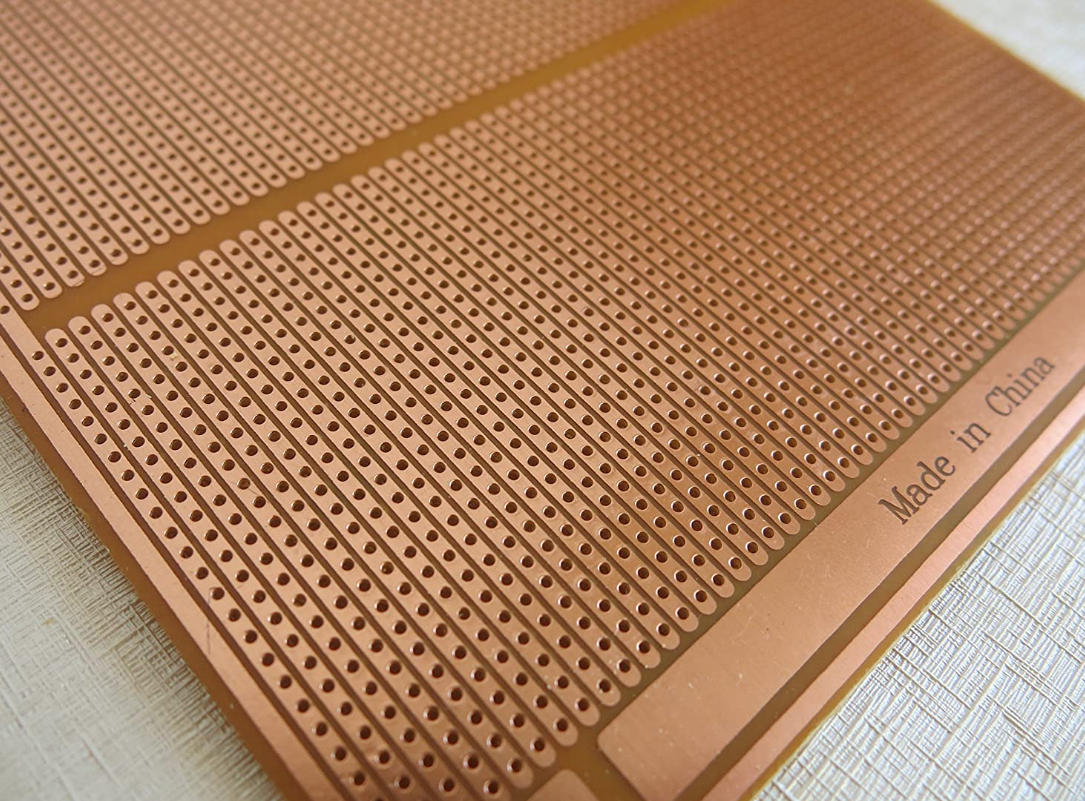

Stripboards are slightly different from Protoboards as they have all the connections going in one direction.
As the copper traces are uncovered on the board, unlike typical Protoboards, you can "cut" the traces to make separate connections within one column or row. It is necessary to solder the components on the side without the copper connections so they will be on the copper side of the board. Since there are only copper connections on one side of the board, the soldered connections need to be made there.
Advantages of Protoboards
Protoboards are a useful tool for creating temporary prototypes of projects without soldering. They are lightweight white plastic boards with tiny holes that allow easy insertion of a component's leads, making it possible to build different circuit designs. Protoboards are affordable and readily available, with no complicated components to worry about. They come in different sizes, so we can choose the size that fits our needs. The board is pre-drilled, so there is no need to drill holes. Components are easy to replace or remove, allowing for quick modifications. Protoboards are easy to modify, making them a great choice when setting up a project or connection.
Disadvantages of Protoboards
Some Protoboards are only suitable for low-current and low-frequency applications, and simple circuits require more physical space. The circuit can become cluttered with many connections because more wires are involved. Solderless boards are not well suited for high-speed designs and plugging and unplugging can disrupt other connections. The connections are less reliable and not suitable for small-scale communications.
Protoboards not suitable for those scenarios
Protoboards have drawbacks and should only be used for prototyping. They should not be used in finished products, high-voltage projects, or situations where safety is critical. Protoboard features include loose connections that can destroy circuits if a wire is accidentally pulled. Protoboards work well for through-hole components, but not for surface mount components. They should not be used for high frequency circuits or circuits that depend on low capacitance values. Avoid building circuits on a Protoboard with an operating frequency higher than 10MHz.
Protoboard applications in modern days
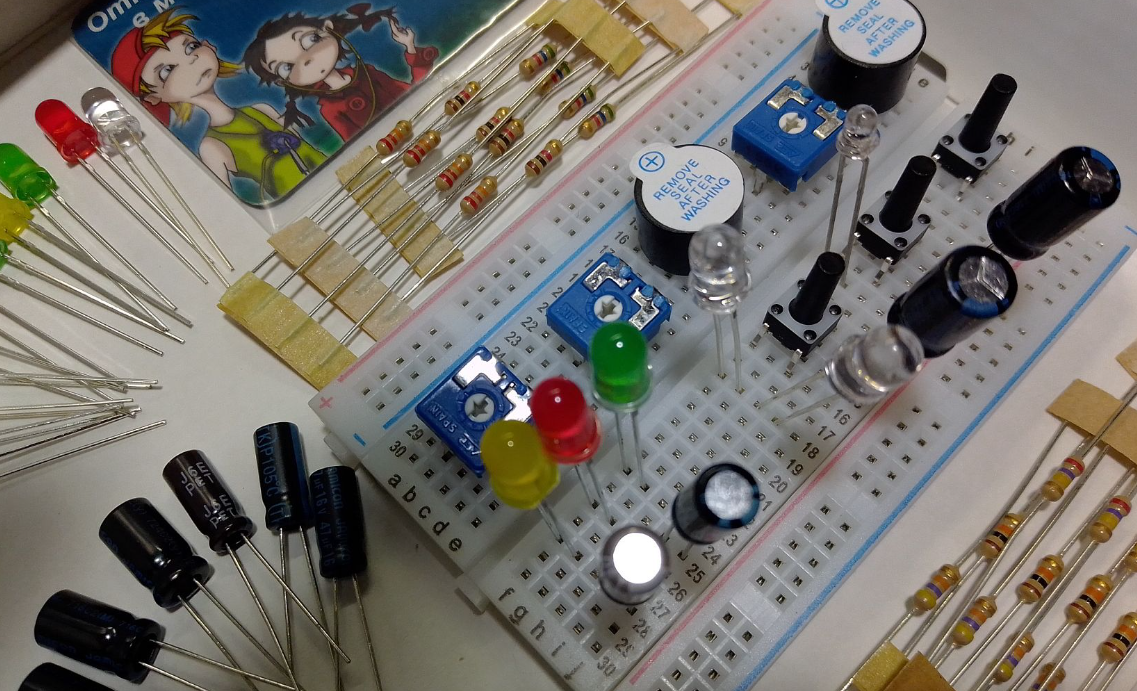
A Protoboard is a thin plastic board used to hold electronic parts such as transistors, resistors, and chips for prototyping electronic circuits. The spring-clip connections on the board are arranged in matrices, with some blocks already connected. To use the board, components are inserted into the holes, with each group of holes connected by a metal strip that forms a node. Power connections are made through the long holes in the top and bottom rows. Jumper wires are used to connect components and build the circuit. Protoboards are commonly used in introductory electronics courses, and power rails can be used to power multiple components with an Arduino or Raspberry Pi.
Integrated Circuits(IC) And Dual In-Line Packages
There is another important aspect of Protoboards to be aware of, Look at the little opening in the middle of the Protoboard, there's a reason for that, and almost every electrical gadget has integrated circuits (ICs). In addition to running motors, controlling voltage, serving as timers, and performing logic operations, they can pretty much do anything you ask of them.
While integrated circuits (ICs) come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functionalities, many of them conform to the dual in-line packaging standard (DIP), meaning that all of them have the same width. Because that breadth perfectly fits across the Protoboard's central gap, working with ICs has never been easier, since there is no need to worry about putting the wrong pins together by mistake.
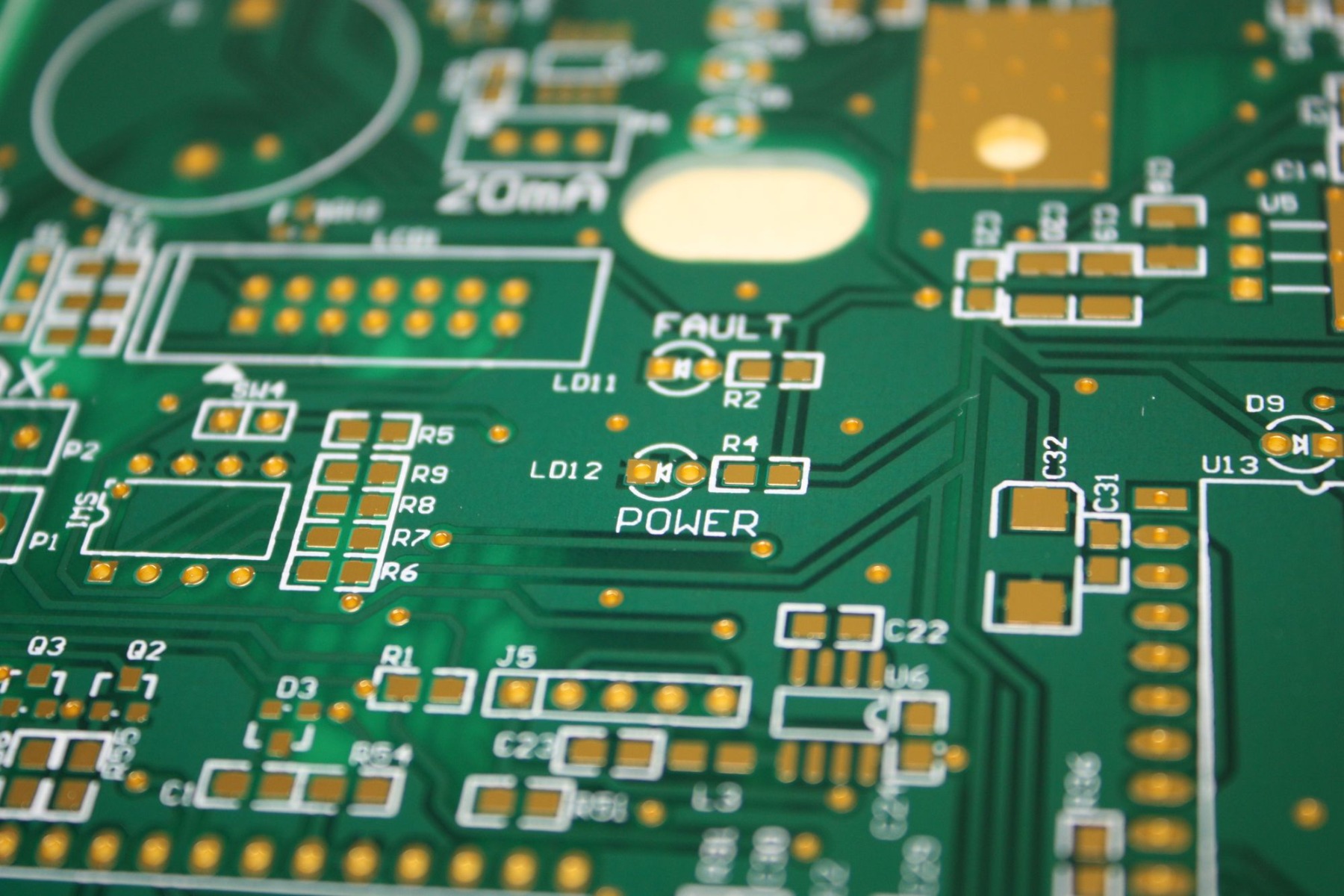
Printed Circuit Boards(PCB)
The final demonstration of your circuit is the PCB, which is a long-term solution designed specifically for your circuit. Typically, after testing on both prototypes and boards, PCBs are the next step, and you can make them at home if you want to do it all yourself.
It is important that you develop a prototype PCB as part of your project's development to serve as a small-scale test run before mass production. It is the PCB manufacturer's responsibility to perform this small test run once the electronics engineer has completed the circuit design and PCB layout.
In general, prototyping is the best way to verify the viability of a design before moving forward because there is no limit to the volume of PCBs that can be produced. Both interconnection and support are the primary functions of a PCB, which serves as both a support structure and an electrical connection method for electronic components.
Final Words
Elecrow offers a wide range of Protoboard products for your circuit design needs, Elecrow also offers high-quality PCB manufacturing to complete your electronics programs.
With state-of-the-art equipment and an experienced team, Elecrow can produce high-quality PCBs in a variety of sizes and configurations to meet your specific needs. Whether you're prototyping a new product or need a batch of PCBs for a larger project, Elecrow has you covered.
And if you're interested in selling your electronic creations, Elecrow's Partner Seller Program is a great way to get started. As a Partner Seller, you can sell your products on the Elecrow platform and gain exposure to a wide audience of electronics enthusiasts and professionals. With Elecrow's easy-to-use platform and helpful customer support team, the Partner seller Program makes it easy to turn your passion for electronics into a profitable venture.
Join Elecrow's Partner Seller Program to earn your benefits!